Music Theory Vocabulary - Trinity Bend Performing Arts
... Also "common practice period or era": Historical period spanning approximately 1650-1900 (described loosely as J.S. Bach to Brahms) during which music functioned according to the concept of tonal harmony; the pre-eminence of key signatures and tonic-dominant harmony. The perceived stability of a com ...
... Also "common practice period or era": Historical period spanning approximately 1650-1900 (described loosely as J.S. Bach to Brahms) during which music functioned according to the concept of tonal harmony; the pre-eminence of key signatures and tonic-dominant harmony. The perceived stability of a com ...
Music Theory Unplugged Functional Harmony
... In (Example 3.3) the Dm7 chord uses an upper case roman numeral but also shows that it is a minor seventh chord with the inclusion of the (m7) next to the roman numeral II. Similarly the FMa7 chord uses an upper case roman numeral and also includes the (Ma7) next to the roman numeral IV. Let us just ...
... In (Example 3.3) the Dm7 chord uses an upper case roman numeral but also shows that it is a minor seventh chord with the inclusion of the (m7) next to the roman numeral II. Similarly the FMa7 chord uses an upper case roman numeral and also includes the (Ma7) next to the roman numeral IV. Let us just ...
Year-9-Music
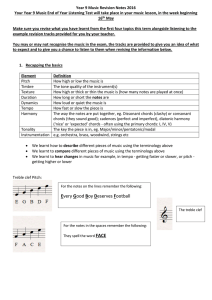
... We learnt that about the key parts of music in film: o A ‘film score’ is the original music that is heard in a movie. o A score is part of the ‘soundtrack’, o The rest of the soundtrack is made from non-original music found in the film – like songs by the pop stars you know. o The film score makes u ...
... We learnt that about the key parts of music in film: o A ‘film score’ is the original music that is heard in a movie. o A score is part of the ‘soundtrack’, o The rest of the soundtrack is made from non-original music found in the film – like songs by the pop stars you know. o The film score makes u ...
Word - asboa
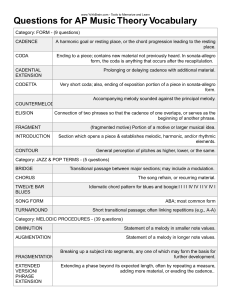
... A chord with a raised fifth interval A musical period around 1600-1750 A symbol used to denote pitches below middle C Resting point at the end of a phrase, section, or complete composition Simultaneous combination of three or more different pitches Movement from one chord to another A series of half ...
... A chord with a raised fifth interval A musical period around 1600-1750 A symbol used to denote pitches below middle C Resting point at the end of a phrase, section, or complete composition Simultaneous combination of three or more different pitches Movement from one chord to another A series of half ...
Jefferson College Course Syllabus MSC101 Fundamentals of Music
... Identify and draw on the staff the following: whole note, half note, quarter note, eighth note, sixteenth note, whole rest, half rest, quarter rest, eighth rest, sixteenth rest, treble clef, bass clef, common time and numerical time ...
... Identify and draw on the staff the following: whole note, half note, quarter note, eighth note, sixteenth note, whole rest, half rest, quarter rest, eighth rest, sixteenth rest, treble clef, bass clef, common time and numerical time ...
Modulation I: Diatonic common chords
... Can take place between keys that are close, foreign or relative. Uses a diatonic chord (or chords) that is (are) common to the two keys and pivots from one key to the next on that chord (surprisingly enough, the common chord is also called a pivot chord). Has a smooth effect as one key transitions t ...
... Can take place between keys that are close, foreign or relative. Uses a diatonic chord (or chords) that is (are) common to the two keys and pivots from one key to the next on that chord (surprisingly enough, the common chord is also called a pivot chord). Has a smooth effect as one key transitions t ...
Music Theory & Ear Training for Busy Adults
... E.g., The C major scale and the A natural minor scale are relative major and minor, respectively. (By the way, the C major and A natural minor scales are special cases in that they use only white keys.) 7. Modes are scales which use the same menu of notes as major and minor scales, but have other ro ...
... E.g., The C major scale and the A natural minor scale are relative major and minor, respectively. (By the way, the C major and A natural minor scales are special cases in that they use only white keys.) 7. Modes are scales which use the same menu of notes as major and minor scales, but have other ro ...
AP Music Theory
... 13. Notate a melody from dictation of 6 to 12 measures in simple or compound meter, with mostly diatonic pitches in major with 3 or 4 repetitions. 14. Notate a melody from dictation of 6 to 12 measures in simple or compound meter utilizing chromatic alterations for harmonic or melodic minor with 3 ...
... 13. Notate a melody from dictation of 6 to 12 measures in simple or compound meter, with mostly diatonic pitches in major with 3 or 4 repetitions. 14. Notate a melody from dictation of 6 to 12 measures in simple or compound meter utilizing chromatic alterations for harmonic or melodic minor with 3 ...
the fundamental principles of harmony
... elucidation of the first-inversion chord and its many secrets. This book is a rare document indeed. It is first a major source of the core teachings of Nadia Boulanger on Harmony. It is also a codification and clarification of her many intuitions on the subject. Finally, it is the fruit of Narcis Bo ...
... elucidation of the first-inversion chord and its many secrets. This book is a rare document indeed. It is first a major source of the core teachings of Nadia Boulanger on Harmony. It is also a codification and clarification of her many intuitions on the subject. Finally, it is the fruit of Narcis Bo ...
GRADE FOUR Expectations in Class Active Participation with
... Begin altered sounds using “#”, “b” and natural accidentals; Begin introduction of Melodic and Harmonic minor scales; Introduce orchestra instruments; Introduce treble & bass clef; Letter names of notes Harmony Intervals of chords within the major scale using syllables and note names; Identify caden ...
... Begin altered sounds using “#”, “b” and natural accidentals; Begin introduction of Melodic and Harmonic minor scales; Introduce orchestra instruments; Introduce treble & bass clef; Letter names of notes Harmony Intervals of chords within the major scale using syllables and note names; Identify caden ...
A Few Notes on the Piano Works of Luca Lombardi
... determination, by hearing, of distinct autonomous entities by means of contrasts, silences or section indicators, perception of continuity and prolongations” (Jean-Jacques Nattiez, in reference to Boulez’s Répons). Also significant are these remarks by Foucault: “Listening to music becomes more diff ...
... determination, by hearing, of distinct autonomous entities by means of contrasts, silences or section indicators, perception of continuity and prolongations” (Jean-Jacques Nattiez, in reference to Boulez’s Répons). Also significant are these remarks by Foucault: “Listening to music becomes more diff ...
P5a - Piano Grade 5
... 9. Explain any musical signs or terms that occur in the piece. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 9. Explain any musical signs or terms that occur in the piece. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Jazz Improvisation for Classical Musicians
... be equipped with certain skills and an appropriate knowledge base. I guess the “auditionee” referred to above felt he lacked the proficiency (and confidence) to be able to state that he could “improvise”, but there is no reason why he, and anyone else for that matter, can’t improvise well. Of course ...
... be equipped with certain skills and an appropriate knowledge base. I guess the “auditionee” referred to above felt he lacked the proficiency (and confidence) to be able to state that he could “improvise”, but there is no reason why he, and anyone else for that matter, can’t improvise well. Of course ...
The Sound of It: Chords and “Sonority”
... clear up the problems created when we borrow terms from Western music and then apply them to bagpipe music. The following terms and their definitions enable us to explain to other musicians why the drones are not a limitation, but an asset: the prime factor in making one tune different from the next, ...
... clear up the problems created when we borrow terms from Western music and then apply them to bagpipe music. The following terms and their definitions enable us to explain to other musicians why the drones are not a limitation, but an asset: the prime factor in making one tune different from the next, ...
Maths and music - Project Jugaad
... half steps between two pitches (the distance between any key on the keyboard on the immediate neighbour is a half step.) Knowing the number of letter names and how many half-steps there are between one note and another are what allow you to determine the interval, and what 'quality,' it has, i.e. ma ...
... half steps between two pitches (the distance between any key on the keyboard on the immediate neighbour is a half step.) Knowing the number of letter names and how many half-steps there are between one note and another are what allow you to determine the interval, and what 'quality,' it has, i.e. ma ...
MTO 1.1: Rothgeb, The Tristan Chord
... context. For example, the interval 0–4 (in “atonal” notation) is automatically interpreted by the ear as a major third. An appropriate context can oblige the ear to hear it as a diminished fourth (in which case it sounds radically different), but the conditions under which this will occur are very s ...
... context. For example, the interval 0–4 (in “atonal” notation) is automatically interpreted by the ear as a major third. An appropriate context can oblige the ear to hear it as a diminished fourth (in which case it sounds radically different), but the conditions under which this will occur are very s ...
Rossini`s - The Spirit of Great Oak
... Synopsis of “Petite Messe Solennelle” Rossini’s mass was very solemn, the last of his Péchés de vieillesse (sins of old age). He dedicated it to the Countess Louise Pillet-Will and given its first performance at her private chapel in March 1864. Originally scored for two pianos, harmonium and 12 so ...
... Synopsis of “Petite Messe Solennelle” Rossini’s mass was very solemn, the last of his Péchés de vieillesse (sins of old age). He dedicated it to the Countess Louise Pillet-Will and given its first performance at her private chapel in March 1864. Originally scored for two pianos, harmonium and 12 so ...
iReal Pro - Johnathon Bower
... Simply put chords are based off of scale degrees so it only takes knowing the degree of which a mode is based to play correctly. ...
... Simply put chords are based off of scale degrees so it only takes knowing the degree of which a mode is based to play correctly. ...
Concepts Word Bank - Stage 5
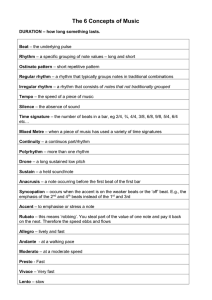
... 12 Bar Blues Form – 12 bars made up of chords I, IV and V. Binary form – 2 parts AB Verse/Chorus Form – the typical form of a piece of popular music also featuring an intro, bridge or middle 8 and outro Ternary form – 3 parts ABA Free form – no structure Strophic form – where each verse has the same ...
... 12 Bar Blues Form – 12 bars made up of chords I, IV and V. Binary form – 2 parts AB Verse/Chorus Form – the typical form of a piece of popular music also featuring an intro, bridge or middle 8 and outro Ternary form – 3 parts ABA Free form – no structure Strophic form – where each verse has the same ...
Music Theory Terms
... 2. Scales: The two most common types of scales are the major and minor scales, both of which are referred to as diatonic, meaning that they have seven notes between octaves and follow a repeating pattern of whole steps and half steps. While there is only one major scale, there are three common varia ...
... 2. Scales: The two most common types of scales are the major and minor scales, both of which are referred to as diatonic, meaning that they have seven notes between octaves and follow a repeating pattern of whole steps and half steps. While there is only one major scale, there are three common varia ...
MSP_lecture8 - New York University
... 1. play the first row (we’ll call the “base” scale) 2. play the "harmony 1" scale simultaneously with the base scale 3. play the "harmony 2" scale simultaneously with the base scale *This is known as parallel motion ...
... 1. play the first row (we’ll call the “base” scale) 2. play the "harmony 1" scale simultaneously with the base scale 3. play the "harmony 2" scale simultaneously with the base scale *This is known as parallel motion ...
Lesson_QQQ_-_Advance..
... indicates a major triad, lowercase a minor triad, and lowercase with a supplementary degree sign (“o”). Seventh chords are also analyzed with Roman numerals. Their case, upper or lower, corresponds with the quality of the triad on which they are built. Figured bass numerals can be added to indicate ...
... indicates a major triad, lowercase a minor triad, and lowercase with a supplementary degree sign (“o”). Seventh chords are also analyzed with Roman numerals. Their case, upper or lower, corresponds with the quality of the triad on which they are built. Figured bass numerals can be added to indicate ...
word setting over a chromatic chord sequence
... As a group, discuss students’ emotional response as well as key features of piece –e.g. pace, dynamics and instrumentation. Students should be encouraged to listen out for the chromatic chord sequence at the opening which creates tension. Play Verdi’s chromatic chord sequence Using melodic instrumen ...
... As a group, discuss students’ emotional response as well as key features of piece –e.g. pace, dynamics and instrumentation. Students should be encouraged to listen out for the chromatic chord sequence at the opening which creates tension. Play Verdi’s chromatic chord sequence Using melodic instrumen ...
COURSE TITLE - Metropolitan Community College
... Practice drawing the treble and bass clefs. B. Locate and name pitches in terms of the treble and bass clefs. C. Determine high and low pitches on the Grand Staff. 2. Differentiate between whole, half, quarter, eighth and sixteenth notes. A. Define the relative length of each note in respect to the ...
... Practice drawing the treble and bass clefs. B. Locate and name pitches in terms of the treble and bass clefs. C. Determine high and low pitches on the Grand Staff. 2. Differentiate between whole, half, quarter, eighth and sixteenth notes. A. Define the relative length of each note in respect to the ...
38. Schubert Der Doppelgänger Background information and performance circumstances 1
... The harmony is functional, but with some unusual aspects for the 1820s: 1. Prominent ‘incomplete’ chords, notably: • The very first chord, which lacks a third. It sounds bare and desolate, but at this point is ambiguous too – major or minor? • The second chord: B minor Vb without C sharp. • The thir ...
... The harmony is functional, but with some unusual aspects for the 1820s: 1. Prominent ‘incomplete’ chords, notably: • The very first chord, which lacks a third. It sounds bare and desolate, but at this point is ambiguous too – major or minor? • The second chord: B minor Vb without C sharp. • The thir ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.