Document
... ________________________ 1. Avoid A2 and A4…circle and identify undesirable intervals ...
... ________________________ 1. Avoid A2 and A4…circle and identify undesirable intervals ...
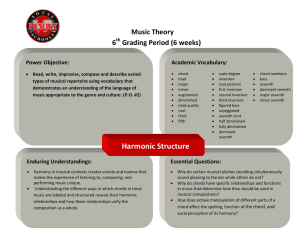
View printable PDF of 2.2 Roman numerals
... When analyzing with roman numerals, always go through these steps: 1. STACK-OF-THIRDS: Reorder the notes in a single octave so that they form a stack of only thirds. You may have to try several notes on the bottom before you find the "stack-of-thirds" formation. 2. Determine the root. The bottom not ...
... When analyzing with roman numerals, always go through these steps: 1. STACK-OF-THIRDS: Reorder the notes in a single octave so that they form a stack of only thirds. You may have to try several notes on the bottom before you find the "stack-of-thirds" formation. 2. Determine the root. The bottom not ...
View printable PDF of 6.7 Contemporary Chords and Harmonic
... Tone cluster with 2 notes raised an octave ...
... Tone cluster with 2 notes raised an octave ...
File
... basically of numbers representing intervals above the bass to be formed by the members of the chord, but the notes could actually be played in any octave above the bass. The system dwelt only with intervals, not with roots of chords, because the theory of chord roots had not been derived when figu ...
... basically of numbers representing intervals above the bass to be formed by the members of the chord, but the notes could actually be played in any octave above the bass. The system dwelt only with intervals, not with roots of chords, because the theory of chord roots had not been derived when figu ...
Defintions - WordPress.com
... A capella- choral music without instrumental accompaniment Accents- emphasis on a note (either louder, longer, higher) compared to notes around it Arpeggio (Broken Chord) - sounding of the individual tones of a chord in sequence rather than simultaneously Bar/Measure- a group set off by bar lines, c ...
... A capella- choral music without instrumental accompaniment Accents- emphasis on a note (either louder, longer, higher) compared to notes around it Arpeggio (Broken Chord) - sounding of the individual tones of a chord in sequence rather than simultaneously Bar/Measure- a group set off by bar lines, c ...
definitions - St. Joseph`s High School Crossmaglen
... Techno- style of dance music with electronic sounds and high-energy, rhythmic beat. Riff- a repeated pattern within a song Reverb/delay- an echo or repetitions of sound. Glissando- a rapid sliding up or down the scale on a musical instrument. Disco- dance music, melodic with a regular bass beat, int ...
... Techno- style of dance music with electronic sounds and high-energy, rhythmic beat. Riff- a repeated pattern within a song Reverb/delay- an echo or repetitions of sound. Glissando- a rapid sliding up or down the scale on a musical instrument. Disco- dance music, melodic with a regular bass beat, int ...
Twentieth Century New scales New chords (almost any combination
... Concerto for Orchestra‐ “Concerto” in the sense that every section of the orchestra is featured as “soloists” at some point, and much of the music is technically demanding as a concerto would be. ...
... Concerto for Orchestra‐ “Concerto” in the sense that every section of the orchestra is featured as “soloists” at some point, and much of the music is technically demanding as a concerto would be. ...
File
... Including: Seventh chords – a triad with an added seventh Inversions – changing the order of notes in the chord by changing what note is in the bass Cluster chords – a chord with at least three notes adjacent in the scale A sequence of tones that are all perfect fifths above each other. C maj – no s ...
... Including: Seventh chords – a triad with an added seventh Inversions – changing the order of notes in the chord by changing what note is in the bass Cluster chords – a chord with at least three notes adjacent in the scale A sequence of tones that are all perfect fifths above each other. C maj – no s ...
Learning Outcome
... The concepts of whole, half and quarter note rests. The concept of sharp and flat notes. Identify and play the notes F# and C# within the first 4 frets. How to play a simple melody with eighth notes at a steady tempo (example: Frere Jacques, Minuet in G) How to play a chord progression with the chor ...
... The concepts of whole, half and quarter note rests. The concept of sharp and flat notes. Identify and play the notes F# and C# within the first 4 frets. How to play a simple melody with eighth notes at a steady tempo (example: Frere Jacques, Minuet in G) How to play a chord progression with the chor ...
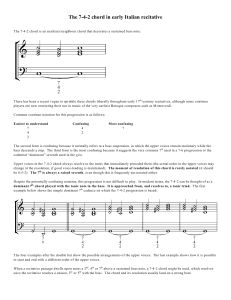
The 7-4-2 chord in early Italian recitative
... change at the resolution, if good voice-leading is maintained). The moment of resolution of this chord is rarely notated (it should be 8-5-3). The 7th is always a raised seventh, even though this is frequently not notated either. Despite the potentially confusing notation, this progression is not di ...
... change at the resolution, if good voice-leading is maintained). The moment of resolution of this chord is rarely notated (it should be 8-5-3). The 7th is always a raised seventh, even though this is frequently not notated either. Despite the potentially confusing notation, this progression is not di ...
Diatonic Triads Powerpoint
... What is the roman numeral used to represent the tonic chord in a major scale? What is the roman numeral used to represent the dominant chord in a minor scale? What is the name of the chord built on the fourth scale degree called? What is the bottom note of a triad called? ...
... What is the roman numeral used to represent the tonic chord in a major scale? What is the roman numeral used to represent the dominant chord in a minor scale? What is the name of the chord built on the fourth scale degree called? What is the bottom note of a triad called? ...
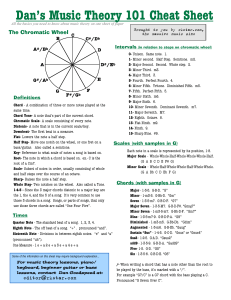
Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet
... Root- The note in which a chord is based on. ex.- C is the root of a Cm7. Scale- Subset of notes in order, usually consisting of whole and half steps over the course of an octave. Sharp- Raises the note a half step. Whole Step- Two notches on the wheel. Also called a Tone. 1-4-5 - Since the 3 major ...
... Root- The note in which a chord is based on. ex.- C is the root of a Cm7. Scale- Subset of notes in order, usually consisting of whole and half steps over the course of an octave. Sharp- Raises the note a half step. Whole Step- Two notches on the wheel. Also called a Tone. 1-4-5 - Since the 3 major ...
Voice leading from IV-V
... Parallel fifths and octaves The bass-tenor interval in the IV chord is a fifth, and the bass-alto interval is an octave. This pattern is repeated in the V chord. These progressions are known as parallel fifths and parallel octaves, and should be avoided when writing homophonic and homorhythmic music ...
... Parallel fifths and octaves The bass-tenor interval in the IV chord is a fifth, and the bass-alto interval is an octave. This pattern is repeated in the V chord. These progressions are known as parallel fifths and parallel octaves, and should be avoided when writing homophonic and homorhythmic music ...
Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet []
... Root- The note in which a chord is based on. ex.- C is the root of a Cm7. Scale- Subset of notes in order, usually consisting of whole and half steps over the course of an octave. Sharp- Raises the note a half step. Whole Step- Two notches on the wheel. Also called a Tone. 1-4-5 - Since the 3 major ...
... Root- The note in which a chord is based on. ex.- C is the root of a Cm7. Scale- Subset of notes in order, usually consisting of whole and half steps over the course of an octave. Sharp- Raises the note a half step. Whole Step- Two notches on the wheel. Also called a Tone. 1-4-5 - Since the 3 major ...
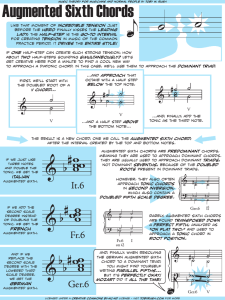
AUGMENTED SIXTH CHORDS Definition
... A6 chords are most often built on the note a half step above the dominant (b6) of the scale in both major and minor keys (as the above examples in the key of C). A6 chords may also be built on the note a half step above the tonic (b2) or the fourth scale degree (see below for examples). Sound: It6 s ...
... A6 chords are most often built on the note a half step above the dominant (b6) of the scale in both major and minor keys (as the above examples in the key of C). A6 chords may also be built on the note a half step above the tonic (b2) or the fourth scale degree (see below for examples). Sound: It6 s ...
Harmony from the Inside
... Key = overall sense of ‘home’ Barbershop Sevenths: Only barbershoppers call them this! (Others call them: dominant sevenths or major-minor sevenths.) Like a major triad, but with an extra note on top. Called ‘7th chord’ because of number of steps between root and the top note. There are different ty ...
... Key = overall sense of ‘home’ Barbershop Sevenths: Only barbershoppers call them this! (Others call them: dominant sevenths or major-minor sevenths.) Like a major triad, but with an extra note on top. Called ‘7th chord’ because of number of steps between root and the top note. There are different ty ...
Augmented Sixth Chords
... meaning they are used to approach dominant chords. they are usually used to approach dominant triads, not dominant sevenths, because of the doubled roots present in dominant triads. however, they also often approach tonic chords in second inversion, which also contain a doubled fifth scale degree. ...
... meaning they are used to approach dominant chords. they are usually used to approach dominant triads, not dominant sevenths, because of the doubled roots present in dominant triads. however, they also often approach tonic chords in second inversion, which also contain a doubled fifth scale degree. ...
Baroque-Era Algorithmic Composition Kevin Deisz 1st Step – Keys
... Cmaj dominant chord is Gmaj, Gmaj dominant chord is Dmaj (with an F#) ...
... Cmaj dominant chord is Gmaj, Gmaj dominant chord is Dmaj (with an F#) ...
Inversions
... useful rule applying to all intervals (that is those of one octave or less). The number of any interval and the number of its inversion always add up to nine. Thus a fifth (number 5) and its inverse or complement, a fourth (number is 4) add up to 9. Do not forget that chord quality is still a factor ...
... useful rule applying to all intervals (that is those of one octave or less). The number of any interval and the number of its inversion always add up to nine. Thus a fifth (number 5) and its inverse or complement, a fourth (number is 4) add up to 9. Do not forget that chord quality is still a factor ...
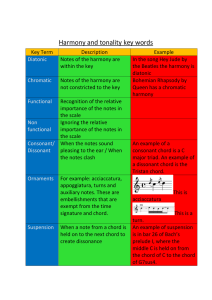
Chapter 3
... Diatonic sounds more stable, because it draws most of its material from the notes of the scale it uses. Chromatic sounds a little wilder, because it often departs from the key of the piece and uses tones that are not considered part of the scale. ...
... Diatonic sounds more stable, because it draws most of its material from the notes of the scale it uses. Chromatic sounds a little wilder, because it often departs from the key of the piece and uses tones that are not considered part of the scale. ...
Four-Part Harmony
... Stems for the soprano and tenor always point up. Stems for the alto and bass always point down. This helps to make it clear which notes to follow when two parts share a staff. Each voice or part contributes to a note in the chord, with one note in the chord doubled (since most chords only need three ...
... Stems for the soprano and tenor always point up. Stems for the alto and bass always point down. This helps to make it clear which notes to follow when two parts share a staff. Each voice or part contributes to a note in the chord, with one note in the chord doubled (since most chords only need three ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.









![Dan`s Music Theory 101 Cheat Sheet []](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007752700_2-d39806ec781c16b3e6c991a5c61a970a-300x300.png)