Areas_of_study
... the key of the 5th chord. E.g. music in C major would modulate to G major. G is the 5th chord of C major. ...
... the key of the 5th chord. E.g. music in C major would modulate to G major. G is the 5th chord of C major. ...
A Farewell to the Avant-garde— Krzesany by Wojciech Kilar
... the chord d-f r -g r -a (the already-familiar D major with Lydian fourth) in the trumpets and trombones, repeated ostinato in a fff dynamic, then expanded into the form of a dense chord comprised of the notes of the ‘highland’ scale in d (e q in the clarinet is a printing error)—transitions abruptly ...
... the chord d-f r -g r -a (the already-familiar D major with Lydian fourth) in the trumpets and trombones, repeated ostinato in a fff dynamic, then expanded into the form of a dense chord comprised of the notes of the ‘highland’ scale in d (e q in the clarinet is a printing error)—transitions abruptly ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 5 Pinciples of Voice Leading
... o Avoid overly spacious sonorities, keeping adjacent upper parts within an octave No more than an octave between soprano and alto No more than an octave between alto and tenor It is acceptable to have more than an octave between tenor and bass Observe the range of each voicing (refer to Exam ...
... o Avoid overly spacious sonorities, keeping adjacent upper parts within an octave No more than an octave between soprano and alto No more than an octave between alto and tenor It is acceptable to have more than an octave between tenor and bass Observe the range of each voicing (refer to Exam ...
Triads
... the melodic configuration above the bass. The second example is one of multiple dissonance, all of which resolve at the same time. The details of this will also be discussed in a later chapter. Note that all of the figures are referring to intervals above the bass line and can be realized in any oct ...
... the melodic configuration above the bass. The second example is one of multiple dissonance, all of which resolve at the same time. The details of this will also be discussed in a later chapter. Note that all of the figures are referring to intervals above the bass line and can be realized in any oct ...
A Psychophysical Explanation for Why Major Chords are “Bright
... a psychophysical model of harmony perception. There are only two ways to move away from such tension: an increase or decrease in the pitch of any the tones. Without exception, a semitone increase in pitch leads to a minor chord and a semitone decrease leads to a major chord (Fig. 4 & Appendix). This ...
... a psychophysical model of harmony perception. There are only two ways to move away from such tension: an increase or decrease in the pitch of any the tones. Without exception, a semitone increase in pitch leads to a minor chord and a semitone decrease leads to a major chord (Fig. 4 & Appendix). This ...
Article: Phrasing...Speaking in Musical Sentences.Blue Grass News
... study the music before performing it. After our analysis is complete, we are much better prepared to create a convincing execution of the phrases. However, there is a fundamental difference between a craftsman and a musician. The musician produces sounds, which can be helpful in the analysis phase, ...
... study the music before performing it. After our analysis is complete, we are much better prepared to create a convincing execution of the phrases. However, there is a fundamental difference between a craftsman and a musician. The musician produces sounds, which can be helpful in the analysis phase, ...
Lesson SSS - Diatonic Sequences
... right where it began: with a I chord. With that in mind, we can consider the entire passage from the second half of m. 5 to the downbeat of m. 9 to expand tonic harmony. When successive repetitions occur at different but predictable pitch levels, as in Example 1, the patterning is called a sequence. ...
... right where it began: with a I chord. With that in mind, we can consider the entire passage from the second half of m. 5 to the downbeat of m. 9 to expand tonic harmony. When successive repetitions occur at different but predictable pitch levels, as in Example 1, the patterning is called a sequence. ...
Diatonic Autoharps Explained
... available on a chromatic ‘harp. The big disadvantage is that with this ‘harp you are limited to play only in the designated key. Not only that, if the song you want to play has accidentals, you must fake it, or pass it up for play on that ‘harp. The big advantage is that since there are no accidenta ...
... available on a chromatic ‘harp. The big disadvantage is that with this ‘harp you are limited to play only in the designated key. Not only that, if the song you want to play has accidentals, you must fake it, or pass it up for play on that ‘harp. The big advantage is that since there are no accidenta ...
Benward Chapter 9
... Each member of the triad is named in relation to the tone on which the chord is constructed, which is the root of the triad. The note a third above the root is called the third of the triad. The fifth above the root is the fifth of the triad. Triads are named by the root and the quality of sound: th ...
... Each member of the triad is named in relation to the tone on which the chord is constructed, which is the root of the triad. The note a third above the root is called the third of the triad. The fifth above the root is the fifth of the triad. Triads are named by the root and the quality of sound: th ...
41. George Gershwin Summertime from Porgy and Bess
... In verse 1 (7-24) the melody is supported by block chords, with contrasting melodic movement in the accompaniment being lines used to fill in underneath long notes in the vocal part, in bars 14-15, 19-20 and 22-23. There is a limited form of imitation between orchestral parts in bars 14-15 and in 22 ...
... In verse 1 (7-24) the melody is supported by block chords, with contrasting melodic movement in the accompaniment being lines used to fill in underneath long notes in the vocal part, in bars 14-15, 19-20 and 22-23. There is a limited form of imitation between orchestral parts in bars 14-15 and in 22 ...
The Functional Tonal Musical System and its Mathematical
... configuration of the tonal schematic of the sound.2 “The term (author’s note harmonic relationships) implies not only the fact that a chord is followed by another but also that the succession is controlled and orderly”.3 Starting from the musical sense of each function, the tonal harmony will decide ...
... configuration of the tonal schematic of the sound.2 “The term (author’s note harmonic relationships) implies not only the fact that a chord is followed by another but also that the succession is controlled and orderly”.3 Starting from the musical sense of each function, the tonal harmony will decide ...
GCSE set works condensed info
... 3rd mvt. (fast) From Electric Counterpoint, by Steve Reich Fluctuates on a small scale because motif keeps getting repeated. ...
... 3rd mvt. (fast) From Electric Counterpoint, by Steve Reich Fluctuates on a small scale because motif keeps getting repeated. ...
sign lesson term definition
... natural minor scale with the 6th and 7th raised on the way up and lowered on the way down ...
... natural minor scale with the 6th and 7th raised on the way up and lowered on the way down ...
document - Far Western District
... genres, even setting it apart from its a cappella cousins. Tonight we’ll review and experience some of those elements. The Basics • While some experts still debate some finite elements, there are a handful of undeniable characteristics that are agreed both inside and outside the Barbershop Harmony S ...
... genres, even setting it apart from its a cappella cousins. Tonight we’ll review and experience some of those elements. The Basics • While some experts still debate some finite elements, there are a handful of undeniable characteristics that are agreed both inside and outside the Barbershop Harmony S ...
Higher Revision Booklet - Glow Blogs
... “…the rhythmic feature” = anacrusis/scotch snap/3 against 2/ cross rhythms (etc.) “…the ornament” = acciaccatura/mordent/trill “a ….. scale” = major/harmonic or melodic minor/chromatic/pentatonic/ whole tone ...
... “…the rhythmic feature” = anacrusis/scotch snap/3 against 2/ cross rhythms (etc.) “…the ornament” = acciaccatura/mordent/trill “a ….. scale” = major/harmonic or melodic minor/chromatic/pentatonic/ whole tone ...
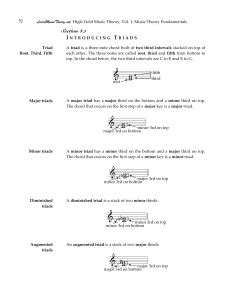
Introducing Triads - LearnMusicTheory.net
... LearnMusicTheory.net High-Yield Music Theory, Vol. 1: Music Theory Fundamentals ...
... LearnMusicTheory.net High-Yield Music Theory, Vol. 1: Music Theory Fundamentals ...
KS4 Booklet 2012 - St Michael`s Catholic Academy
... the key of the 5th chord. E.g. music in C major would modulate to G major. G is the 5th chord of C major. ...
... the key of the 5th chord. E.g. music in C major would modulate to G major. G is the 5th chord of C major. ...
Figured Bass and Tonality Recognition
... tonal and harmonic analysis, we first point out the problems raised by harmonic reduction. We then describe our algorithm, and show its use in some examples. In the subsequent section, we show the application of a simple process of tonality detection on top of harmonic reduction. The analysis tools ...
... tonal and harmonic analysis, we first point out the problems raised by harmonic reduction. We then describe our algorithm, and show its use in some examples. In the subsequent section, we show the application of a simple process of tonality detection on top of harmonic reduction. The analysis tools ...
File - Harris Ac Music
... Minor chord differs from a major chord in that it consists of the intervals of a minor third and a major third. It is denoted in popular music by adding a lower case m after the letter designating the chord root. ...
... Minor chord differs from a major chord in that it consists of the intervals of a minor third and a major third. It is denoted in popular music by adding a lower case m after the letter designating the chord root. ...
2016 Chief Assessor`s Report
... correctly. Students could consider producing two copies of their arrangement at the completion of the arranging process: one that plays back in the desired manner, and can be used to create the recording; and one that reads correctly, with chord symbols for guitar and correct drum mapping, which is ...
... correctly. Students could consider producing two copies of their arrangement at the completion of the arranging process: one that plays back in the desired manner, and can be used to create the recording; and one that reads correctly, with chord symbols for guitar and correct drum mapping, which is ...
AP Music Theory Student Sample (2016) – Question 3
... after the notehead is not considered correct notation.) B. Award full credit for octave transpositions of the correct bass pitch. (Octave transpositions of soprano pitches are not allowed.) C. No enharmonic equivalents are allowed. II. Chord Symbols (8 points) A. Award 1 point for each chord symbol ...
... after the notehead is not considered correct notation.) B. Award full credit for octave transpositions of the correct bass pitch. (Octave transpositions of soprano pitches are not allowed.) C. No enharmonic equivalents are allowed. II. Chord Symbols (8 points) A. Award 1 point for each chord symbol ...
WAYS TO REMEMBER MUSIC THEORY
... The same method can also be used to find other minor 7th chords, using the easy chords of Dm7, Em7 and Am7. To convert them into half-diminished chords, just flatten their 5ths. To find other dominant 7th chords, you can use a different approach. Start with the major 7th chords and then flatten the ...
... The same method can also be used to find other minor 7th chords, using the easy chords of Dm7, Em7 and Am7. To convert them into half-diminished chords, just flatten their 5ths. To find other dominant 7th chords, you can use a different approach. Start with the major 7th chords and then flatten the ...
Proficiencies—Piano Student Name: First Last Course Number
... performance in the Freshman year. Complete 2 public performances (one per semester) in the Sophomore year. Complete 2 public performances in the first semester of the Junior year. Perform one memorized solo from standard intermediate piano repertoire. Play all major and harmonic minor key scales, ar ...
... performance in the Freshman year. Complete 2 public performances (one per semester) in the Sophomore year. Complete 2 public performances in the first semester of the Junior year. Perform one memorized solo from standard intermediate piano repertoire. Play all major and harmonic minor key scales, ar ...
Lesson_SSS_-_Diatoni..
... Db and Cb). The descending-fifth sequence that follows, beginning with iv in m. 26, completes the cycle from the initial i chord to the tonic in m. 32. Harmonically, the iv chord in m. 33 continues the descending-fifth series, but by then, the melodic pattern in the upper voice is broken. Sequences ...
... Db and Cb). The descending-fifth sequence that follows, beginning with iv in m. 26, completes the cycle from the initial i chord to the tonic in m. 32. Harmonically, the iv chord in m. 33 continues the descending-fifth series, but by then, the melodic pattern in the upper voice is broken. Sequences ...
ap® music theory syllabus
... Define and recognize basic musical terms and theory concepts Understand, notate, and aurally identify major, minor, pentatonic, chromatic, whole tone scales, and church modes Understand, notate, and identify major and minor key signatures Analyze, notate, and aurally identify major, minor, diminishe ...
... Define and recognize basic musical terms and theory concepts Understand, notate, and aurally identify major, minor, pentatonic, chromatic, whole tone scales, and church modes Understand, notate, and identify major and minor key signatures Analyze, notate, and aurally identify major, minor, diminishe ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.