Full version (PDF file)
... On the basis of their axon targeting, cortical interneurons can be divided into dendrite-targeting (with many subgroups), soma-targeting and axon-targeting interneurons. The CR+ neurons are mostly dendrite targeting, similarly as CB+ neurons, but unlike PV+ neurons which typically innervate soma or ...
... On the basis of their axon targeting, cortical interneurons can be divided into dendrite-targeting (with many subgroups), soma-targeting and axon-targeting interneurons. The CR+ neurons are mostly dendrite targeting, similarly as CB+ neurons, but unlike PV+ neurons which typically innervate soma or ...
Contact guidance of CNS neurites on grooved quartz: influence of
... perpendicular regions and presumptive dendrites emerged from parallel regions of hippocampal somas on grooves. Presumptive dendrites maintained parallel growth as they extended (Fig. 3B). This implies that the physical contour of the environment influences the fine structural, and therefore function ...
... perpendicular regions and presumptive dendrites emerged from parallel regions of hippocampal somas on grooves. Presumptive dendrites maintained parallel growth as they extended (Fig. 3B). This implies that the physical contour of the environment influences the fine structural, and therefore function ...
kbook or W NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
... Can we use what we know to control someone else’s brain? How likely is it that once we know exactly how the brain functions that we will be able to control another person’s brain? It sounds like science fiction, but we can actually do it right now, even with the limited knowledge we have. Transcrani ...
... Can we use what we know to control someone else’s brain? How likely is it that once we know exactly how the brain functions that we will be able to control another person’s brain? It sounds like science fiction, but we can actually do it right now, even with the limited knowledge we have. Transcrani ...
powerpoint lecture
... • How stretch reflex works – Stretch activates muscle spindle – Sensory neurons synapse directly with motor neurons in spinal cord – motor neurons cause stretched muscle to contract – Reciprocal inhibition also occurs – fibers synapse with interneurons that inhibit motor neurons of antagonisti ...
... • How stretch reflex works – Stretch activates muscle spindle – Sensory neurons synapse directly with motor neurons in spinal cord – motor neurons cause stretched muscle to contract – Reciprocal inhibition also occurs – fibers synapse with interneurons that inhibit motor neurons of antagonisti ...
Activity-Dependent Regulation of Potassium Currents in an
... Golowasch, E. Marder, and L.F. Abbott, unpublished data). The type of neuronal plasticity we report in this paper may act as a driving force for this variability by linking the conductances of a neuron to its recent history of activity. Under physiological conditions, neurons of the STG are rhythmic ...
... Golowasch, E. Marder, and L.F. Abbott, unpublished data). The type of neuronal plasticity we report in this paper may act as a driving force for this variability by linking the conductances of a neuron to its recent history of activity. Under physiological conditions, neurons of the STG are rhythmic ...
STOCHASTIC GENERATION OF BIOLOGICALLY - G
... acquired from new three-dimensional microscopes, such as the Serial Block Face Scanning Electron Microscope (SBF-SEM) [9] and the Knife-Edge Scanning Microscope (KESM) [10], the reconstructed empirical datasets can be continuously mined to find new basic circuits. C. Outline of the thesis Fig. 1 rep ...
... acquired from new three-dimensional microscopes, such as the Serial Block Face Scanning Electron Microscope (SBF-SEM) [9] and the Knife-Edge Scanning Microscope (KESM) [10], the reconstructed empirical datasets can be continuously mined to find new basic circuits. C. Outline of the thesis Fig. 1 rep ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... The origin of the preganglionic fibers in the spinal cord defines the two division of the autonomic nervous system. Thus, the cell bodies of sympathetic preganglionic neurones are located in the inter-mediolateral column of the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord. Shortly after the dorsal ...
... The origin of the preganglionic fibers in the spinal cord defines the two division of the autonomic nervous system. Thus, the cell bodies of sympathetic preganglionic neurones are located in the inter-mediolateral column of the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord. Shortly after the dorsal ...
Action Potentials in Earthworms
... voltage-sensitive potassium channels and re-primes the sodium channels so that they are ready to open once more. This is called the refractory period. Propagation of the action potential from the site of initiation to other locations along the nerve cell is caused by the positive charges in the cell ...
... voltage-sensitive potassium channels and re-primes the sodium channels so that they are ready to open once more. This is called the refractory period. Propagation of the action potential from the site of initiation to other locations along the nerve cell is caused by the positive charges in the cell ...
Temporal Sequence Detection with Spiking Neurons: Towards
... demonstrated to effectively train the neuron towards a selective response determined by the spatio-temporal pattern of the onsets of input spike trains. The model is used in the implementation of a part of a robotic system for natural language instructions. We test the model with a robot whose goal ...
... demonstrated to effectively train the neuron towards a selective response determined by the spatio-temporal pattern of the onsets of input spike trains. The model is used in the implementation of a part of a robotic system for natural language instructions. We test the model with a robot whose goal ...
JEB Classics - Journal of Experimental Biology
... tendency of extrafusal contraction to silence the spindle was offset by the intrafusal contraction. Katz discussed the significance of this clearly, with the proposal that when an extended muscle is contracted actively in life, the inevitable simultaneous intrafusal contraction would ensure that aff ...
... tendency of extrafusal contraction to silence the spindle was offset by the intrafusal contraction. Katz discussed the significance of this clearly, with the proposal that when an extended muscle is contracted actively in life, the inevitable simultaneous intrafusal contraction would ensure that aff ...
SHORT COMMUNICATION Localization of a vocal pattern generator
... (CED). For the identification of vocalization-correlated and auditory units, conventional peri-event time histograms and peri-stimulus time histograms, respectively, were constructed after having submitted the original recording to a spike-sorting procedure (template-based spikeclustering). To avoid ...
... (CED). For the identification of vocalization-correlated and auditory units, conventional peri-event time histograms and peri-stimulus time histograms, respectively, were constructed after having submitted the original recording to a spike-sorting procedure (template-based spikeclustering). To avoid ...
Specificity and Plasticity of Thalamocortical Connections in Sema6A
... appear homogeneous in cytoarchitecture, and connections between them form in a smoothly topographic fashion, with dorsolateral thalamus projecting to caudal cortex and ventromedial thalamus to rostral cortex [6–8]. The cytoarchitectonic resolution of these fields into discrete cortical areas and thal ...
... appear homogeneous in cytoarchitecture, and connections between them form in a smoothly topographic fashion, with dorsolateral thalamus projecting to caudal cortex and ventromedial thalamus to rostral cortex [6–8]. The cytoarchitectonic resolution of these fields into discrete cortical areas and thal ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 17 Martini Lecture Outline
... Organization and Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Division Preganglionic fibers leave the brain via: CN III (to the intrinsic eye muscles, pupil, and lens) CN VII (to the tear glands and salivary glands) CN IX (to the parotid salivary glands) CN X (to the visceral organs of the thoracic cavity and abd ...
... Organization and Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Division Preganglionic fibers leave the brain via: CN III (to the intrinsic eye muscles, pupil, and lens) CN VII (to the tear glands and salivary glands) CN IX (to the parotid salivary glands) CN X (to the visceral organs of the thoracic cavity and abd ...
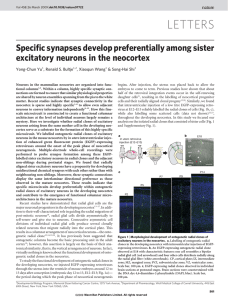
Specific synapses develop preferentially among sister excitatory
... non-siblings during postnatal stages. We found that radially aligned sister excitatory neurons have a propensity for developing unidirectional chemical synapses with each other rather than with neighbouring non-siblings. Moreover, these synaptic connections display the same interlaminar directional ...
... non-siblings during postnatal stages. We found that radially aligned sister excitatory neurons have a propensity for developing unidirectional chemical synapses with each other rather than with neighbouring non-siblings. Moreover, these synaptic connections display the same interlaminar directional ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Lecture Outline Adapted from Martini
... Organization and Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Division Preganglionic fibers leave the brain via: CN III (to the intrinsic eye muscles, pupil, and lens) CN VII (to the tear glands and salivary glands) CN IX (to the parotid salivary glands) CN X (to the visceral organs of the thoracic cavity and abd ...
... Organization and Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Division Preganglionic fibers leave the brain via: CN III (to the intrinsic eye muscles, pupil, and lens) CN VII (to the tear glands and salivary glands) CN IX (to the parotid salivary glands) CN X (to the visceral organs of the thoracic cavity and abd ...
Regulation of neuronal survival and death by extracellular signals
... and C, are shown. Group B neurons obtain neurotrophic factors from four sources: (i) from target cells or neurons [group A neurons secrete this neurotrophic factor (red dots) which binds to receptors on the axon terminals of neurons B, and is internalized and retrogradely transported (direction of r ...
... and C, are shown. Group B neurons obtain neurotrophic factors from four sources: (i) from target cells or neurons [group A neurons secrete this neurotrophic factor (red dots) which binds to receptors on the axon terminals of neurons B, and is internalized and retrogradely transported (direction of r ...
(B) rosiglitazone
... neurons from wild-type (WT) (a, b), Ucp2-/- (c), and POMC-mut-Kir6.2 (d) mice. Recordings were made for 5–10 min in aCSF solution containing 5mM glucose. Once stable firing rates were observed, the recording chamber was perfused with aCSF solution containing 3mM glucose for 5–10 min, and then genipi ...
... neurons from wild-type (WT) (a, b), Ucp2-/- (c), and POMC-mut-Kir6.2 (d) mice. Recordings were made for 5–10 min in aCSF solution containing 5mM glucose. Once stable firing rates were observed, the recording chamber was perfused with aCSF solution containing 3mM glucose for 5–10 min, and then genipi ...
microcircuits in the striatum striatal cell types and their
... neurons emit 2-4 large primary dendrites that give rise to higher order dendrites that span an area up to millimeter in diameter. Although clearly an aspiny neuron, the distal dendrites may be sparsely invested with spine-like appendages. Unlike the spiny projection neurons, the cholinergic interneu ...
... neurons emit 2-4 large primary dendrites that give rise to higher order dendrites that span an area up to millimeter in diameter. Although clearly an aspiny neuron, the distal dendrites may be sparsely invested with spine-like appendages. Unlike the spiny projection neurons, the cholinergic interneu ...
Chapter 3
... ake a look at the painting in Figure 3.1. It is pleasing, colorful, and nicely done. It features realistic color, perspective, and shadowing. It seems, perhaps, not extraordinary—except by virtue of its maker. He cannot see at all. Born blind to an impoverished family in Turkey, Esref Armagan starte ...
... ake a look at the painting in Figure 3.1. It is pleasing, colorful, and nicely done. It features realistic color, perspective, and shadowing. It seems, perhaps, not extraordinary—except by virtue of its maker. He cannot see at all. Born blind to an impoverished family in Turkey, Esref Armagan starte ...
The importance of mixed selectivity in complex
... Allows us to start asking the question: Do the responses in individual conditions encode information about tasktype through nonlinear interaction between the cue and the task-type? ...
... Allows us to start asking the question: Do the responses in individual conditions encode information about tasktype through nonlinear interaction between the cue and the task-type? ...
A soft-wired hypothalamus
... recording in slice preparations together with stereology to quantify the synaptic density onto these cells. The results showed that leptin-deficient ob/ob mice differed from wild-type mice in the numbers of excitatory and inhibitory synapses and postsynaptic currents onto NPY and POMC neurons. When ...
... recording in slice preparations together with stereology to quantify the synaptic density onto these cells. The results showed that leptin-deficient ob/ob mice differed from wild-type mice in the numbers of excitatory and inhibitory synapses and postsynaptic currents onto NPY and POMC neurons. When ...
Structural Repair and Functional Recovery Following Cerebral
... does not follow the shortest path to the presumptive bud site, as would be expected if guidance by a soluble factor gradient were the primary mechanism. Recent observations performed with the help of Dr. Keith We are currently investigating the ability Snyder indicate that the initial guidance of so ...
... does not follow the shortest path to the presumptive bud site, as would be expected if guidance by a soluble factor gradient were the primary mechanism. Recent observations performed with the help of Dr. Keith We are currently investigating the ability Snyder indicate that the initial guidance of so ...
Hippocampus – Why is it studied so frequently?
... merge. In layer III pyramidal cells are predominant. Pyramidal cells in layer V vary from grouped large, darkly stained neurons to rather loose arranged smaller pyramidal cells altogether with polymorphic cells. Cells in layer VI are heterogenous in size and shape. Columnar organization at caudal le ...
... merge. In layer III pyramidal cells are predominant. Pyramidal cells in layer V vary from grouped large, darkly stained neurons to rather loose arranged smaller pyramidal cells altogether with polymorphic cells. Cells in layer VI are heterogenous in size and shape. Columnar organization at caudal le ...
Trigeminal pathways handout
... synapse in spinal nucleus of V. The tract is continuous with the dorsolateral fasciculus (Lissauer’s tract) in the spinal cord, again emphasizing the similarities with the ALS system. 2. The Spinal (descending) nucleus extends caudally as far as C2-C3 and is continuous with the dorsal horn. This mea ...
... synapse in spinal nucleus of V. The tract is continuous with the dorsolateral fasciculus (Lissauer’s tract) in the spinal cord, again emphasizing the similarities with the ALS system. 2. The Spinal (descending) nucleus extends caudally as far as C2-C3 and is continuous with the dorsal horn. This mea ...
Self Assessment Chapter 14 - CM
... sympathetic preganglionic axons and postganglionic neurons; postganglionic axons then transmit action potentials to target cell • At synapse with their target cells, postganglionic axons release one of three neurotransmitters: ACh, epinephrine (adrenalin), or norepinephrine (noradrenalin; most frequ ...
... sympathetic preganglionic axons and postganglionic neurons; postganglionic axons then transmit action potentials to target cell • At synapse with their target cells, postganglionic axons release one of three neurotransmitters: ACh, epinephrine (adrenalin), or norepinephrine (noradrenalin; most frequ ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.