Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... When a neuron is not transmitting a signal, it is said to be “at rest.” However, this does not mean that the neuron is inactive. Neurons work to maintain a charge difference across their membranes, which keeps them ready to transmit impulses when they become stimulated. While a neuron is at rest, ...
... When a neuron is not transmitting a signal, it is said to be “at rest.” However, this does not mean that the neuron is inactive. Neurons work to maintain a charge difference across their membranes, which keeps them ready to transmit impulses when they become stimulated. While a neuron is at rest, ...
Descending Tracts
... It receives projection fibers from the globus pallidus of the basal ganglia, and gives origin to two descending extrapyramidal tracts: •The lateral tectospinal tract: Originates from the superior colliculus (the center of visual reflexes), crosses to the opposite side and terminates in the cervical ...
... It receives projection fibers from the globus pallidus of the basal ganglia, and gives origin to two descending extrapyramidal tracts: •The lateral tectospinal tract: Originates from the superior colliculus (the center of visual reflexes), crosses to the opposite side and terminates in the cervical ...
Segregated cholinergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area
... Since cholinergic neurons of the PPN and LDT are components of functionally distinct forebrain circuits, we tested the hypothesis that they may innervate functionally distinct subsets of VTA neurons. We injected a tracer into the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) shell to retrogradely label the so-called, me ...
... Since cholinergic neurons of the PPN and LDT are components of functionally distinct forebrain circuits, we tested the hypothesis that they may innervate functionally distinct subsets of VTA neurons. We injected a tracer into the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) shell to retrogradely label the so-called, me ...
Synaptic pathways and inhibitory gates in the spinal cord dorsal horn
... low-threshold afferent input.19 These PKC␥ + positive (PKC␥ + ) neurons are a key element for activated circuits after disinhibition by intrathecal application of glycine receptor antagonist, unmasking normally blocked local excitatory circuits onto nociceptive output neurons.2,3 However, this circu ...
... low-threshold afferent input.19 These PKC␥ + positive (PKC␥ + ) neurons are a key element for activated circuits after disinhibition by intrathecal application of glycine receptor antagonist, unmasking normally blocked local excitatory circuits onto nociceptive output neurons.2,3 However, this circu ...
Sequential Development of Electrical and Chemical Synaptic
... (e.g., connections become stronger and more reliable) or qualitative (e.g., synapses form, are lost, or switch from electrical to chemical or from excitatory to inhibitory). To explore how these synaptic events contribute to behavioral circuits, we have studied the formation of a circuit that produc ...
... (e.g., connections become stronger and more reliable) or qualitative (e.g., synapses form, are lost, or switch from electrical to chemical or from excitatory to inhibitory). To explore how these synaptic events contribute to behavioral circuits, we have studied the formation of a circuit that produc ...
Cholinergic modulation of synaptic properties of cortical layer VI
... enhance the gain for the stream of peripheral information on its way to the cortex. Our results support also the notion that neuromodulatory systems may play a significant role in spike timing based information coding (Ponulak and Kasiński 2011). The question arises whether pre- or postsynaptic mech ...
... enhance the gain for the stream of peripheral information on its way to the cortex. Our results support also the notion that neuromodulatory systems may play a significant role in spike timing based information coding (Ponulak and Kasiński 2011). The question arises whether pre- or postsynaptic mech ...
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters are the nervous system`s “off switches
... Aspartic Acid, also known as aspartate, is an excitatory neurotransmitter in the brainstem and spinal cord. Aspartic acid is the excitatory counterpart to glycine, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Low levels have been linked to feelings of fatigue and low mood, whereas high levels have been linked t ...
... Aspartic Acid, also known as aspartate, is an excitatory neurotransmitter in the brainstem and spinal cord. Aspartic acid is the excitatory counterpart to glycine, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Low levels have been linked to feelings of fatigue and low mood, whereas high levels have been linked t ...
Diversity and wiring variability of visual local neurons in the
... was then carried over into this model. The GMR-GAL4 expressing pattern was manually segmented in Amira 4.1.2 and compiled into the common 3D framework of our representative M6 volume model, as described above. Global and local registrations were performed as described previously (Chiang et al., 2011 ...
... was then carried over into this model. The GMR-GAL4 expressing pattern was manually segmented in Amira 4.1.2 and compiled into the common 3D framework of our representative M6 volume model, as described above. Global and local registrations were performed as described previously (Chiang et al., 2011 ...
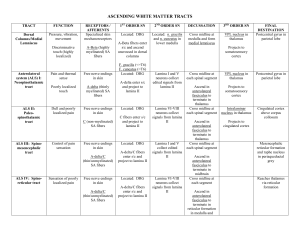
SOMATOSENSORY PATHWAYS
... bodily sensations of touch, pain, temperature, vibration, and proprioception (limb or joint position sense). The posterior column-medial lemniscal pathway conveys proprioception, vibration sense, and fine, discriminative touch. The anterolateral (or ventrolateral) pathways, include the spinothalamic ...
... bodily sensations of touch, pain, temperature, vibration, and proprioception (limb or joint position sense). The posterior column-medial lemniscal pathway conveys proprioception, vibration sense, and fine, discriminative touch. The anterolateral (or ventrolateral) pathways, include the spinothalamic ...
Decoding Motor Commands in Cortico-Basal Ganglia Circuits for the
... The BehaviourGUI toolbox allows data to be synchronised so several data sets (such as a video recording and computed velocity) easily can be analysed simultaneously. This is of great help when trying to find when the rat is moving. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A perievent time his ...
... The BehaviourGUI toolbox allows data to be synchronised so several data sets (such as a video recording and computed velocity) easily can be analysed simultaneously. This is of great help when trying to find when the rat is moving. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A perievent time his ...
Remembering or Forgetting: The Lifetime of Memories
... grain of sand (they are actually much smaller!) we could fill around 8,500 soda cans with neurons from one single human brain. The job of neurons is to send signals between cells. Each of our neurons has about 10,000 opportunities to form connections with neighboring neurons. And not all neurons are ...
... grain of sand (they are actually much smaller!) we could fill around 8,500 soda cans with neurons from one single human brain. The job of neurons is to send signals between cells. Each of our neurons has about 10,000 opportunities to form connections with neighboring neurons. And not all neurons are ...
MECHANISMS OF VERTEBRATE SYNAPTOGENESIS
... encoding synaptic proteins are turned on, resulting in the formation, accumulation, and directional trafficking of vesicles carrying pre- and postsynaptic protein complexes. During this time, the specification of correct neuronal connections is determined, as axons and dendrites make contact and estab ...
... encoding synaptic proteins are turned on, resulting in the formation, accumulation, and directional trafficking of vesicles carrying pre- and postsynaptic protein complexes. During this time, the specification of correct neuronal connections is determined, as axons and dendrites make contact and estab ...
nervous system
... (A)The end-bulb of the presynaptic (transmitting) axon has vesicles containing neurotransmitter, which is released into the synaptic cleft to the membrane of the postsynaptic (receiving) cell. (B) Close-up of a synapse showing receptors for neurotransmitter in the postsynaptic cell membrane. Copyrig ...
... (A)The end-bulb of the presynaptic (transmitting) axon has vesicles containing neurotransmitter, which is released into the synaptic cleft to the membrane of the postsynaptic (receiving) cell. (B) Close-up of a synapse showing receptors for neurotransmitter in the postsynaptic cell membrane. Copyrig ...
Common Peroneal Nerve Syndrome
... Tingling – similar to pins and needles, this occurs in the same region as the numbness and, ...
... Tingling – similar to pins and needles, this occurs in the same region as the numbness and, ...
18-1 PITUITARY GLAND AND HYPOTHALAMUS 1. The pituitary
... 2. The pituitary gland was once considered the "master" gland because hormones released from the pituitary control other endocrine glands and many body functions. It is now known that the regulation of release of hormones from the pituitary is controlled by the hypothalamus. Thus the endocrine syste ...
... 2. The pituitary gland was once considered the "master" gland because hormones released from the pituitary control other endocrine glands and many body functions. It is now known that the regulation of release of hormones from the pituitary is controlled by the hypothalamus. Thus the endocrine syste ...
Bridging Areas of Injury in the Spinal Cord
... Peripheral nerve was placed into a complete transection gap of 5 or 10 mm (Richardson and others 1980). After 3 to 4 months, tracing demonstrated that fibers grow into and across the implant from both stumps. A mean of 5850 myelinated axons are found in the graft if the nearby dorsal roots are avuls ...
... Peripheral nerve was placed into a complete transection gap of 5 or 10 mm (Richardson and others 1980). After 3 to 4 months, tracing demonstrated that fibers grow into and across the implant from both stumps. A mean of 5850 myelinated axons are found in the graft if the nearby dorsal roots are avuls ...
Dynamics of Spontaneous Activity in Neocortical Slices
... neocortical brain slices can sustain spontaneous activity. In the past, slices have been used to study the responses of neurons to electrical or pharmacological stimulations. At the same time, EPSPs and IPSPs are routinely recorded intracellularly from neurons in slices even under conditions in whic ...
... neocortical brain slices can sustain spontaneous activity. In the past, slices have been used to study the responses of neurons to electrical or pharmacological stimulations. At the same time, EPSPs and IPSPs are routinely recorded intracellularly from neurons in slices even under conditions in whic ...
Neural integration
... At spinal segment it targets, an axon in anterior corticospinal tract crosses over to opposite side of spinal cord in anterior white commissure before synapsing on lower motor neurons in anterior gray horns ...
... At spinal segment it targets, an axon in anterior corticospinal tract crosses over to opposite side of spinal cord in anterior white commissure before synapsing on lower motor neurons in anterior gray horns ...
The Neurophysiological Basis of Learning and Memory in Advanced
... The amount of current flowing in the extracellular space due to neuron activity, such as an action potential, is usually tiny. Because the extracellular impedance is very low (approximately three or four orders of magnitude lower than the neurons’ input resistance), only summed field potentials gene ...
... The amount of current flowing in the extracellular space due to neuron activity, such as an action potential, is usually tiny. Because the extracellular impedance is very low (approximately three or four orders of magnitude lower than the neurons’ input resistance), only summed field potentials gene ...
of 17 Keywords A-waves Sometimes called Axon
... A CMAP recorded from any motor nerve activated by antidromic stimulation that travels centrally into the spinal cord through the interneurons and anterior horn cells and then orthodromically from the spinal cord to the muscle. The F-wave amplitude is much smaller and of longer latency than the direc ...
... A CMAP recorded from any motor nerve activated by antidromic stimulation that travels centrally into the spinal cord through the interneurons and anterior horn cells and then orthodromically from the spinal cord to the muscle. The F-wave amplitude is much smaller and of longer latency than the direc ...
A comparison of the distribution and morphology of ChAT
... ABSTRACT: Present knowledge concerning the organization of cholinergic structures of the spinal cord has been derived primarily from studies on small laboratory animals, while there is a complete lack of information concerning its structure in the pig. In the present study we employed choline acetyl ...
... ABSTRACT: Present knowledge concerning the organization of cholinergic structures of the spinal cord has been derived primarily from studies on small laboratory animals, while there is a complete lack of information concerning its structure in the pig. In the present study we employed choline acetyl ...
48x36 Poster Template
... My topic is neuronal primary cilia and the role they play in neuro-degeneration. Even though cilia were discovered over 100 years ago, many scientists to this day do not know the function of primary cilia. My research question is: What role do neuronal primary cilia have in the neuro-degeneration in ...
... My topic is neuronal primary cilia and the role they play in neuro-degeneration. Even though cilia were discovered over 100 years ago, many scientists to this day do not know the function of primary cilia. My research question is: What role do neuronal primary cilia have in the neuro-degeneration in ...
cortical input to the basal forebrain
... terminals were immunonegative for GABA, and in the cases investigated, were found to contain glutamate immunoreactivity. In material stained for the anterograde tracer and choline acetyltransferase, a total of 63 Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin varicosities closely associated with cholinergic pro ...
... terminals were immunonegative for GABA, and in the cases investigated, were found to contain glutamate immunoreactivity. In material stained for the anterograde tracer and choline acetyltransferase, a total of 63 Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin varicosities closely associated with cholinergic pro ...
Cerebellum Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the
... Cerebellum Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the students will be able to know: • Gross anatomy of the cerebellum • Various terms like folia, vermis, tracts and nuclei of cerebellum • Major efferent and afferent pathways and their function • Human diseases associated with cerebellar dy ...
... Cerebellum Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the students will be able to know: • Gross anatomy of the cerebellum • Various terms like folia, vermis, tracts and nuclei of cerebellum • Major efferent and afferent pathways and their function • Human diseases associated with cerebellar dy ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.