Dopamine
... and its postsynaptic actions are often stymied by the myriad of actions that this neurotransmitter can produce. Thus, DA has been found to exert actions on the neurons it innervates both directly and via G-protein–coupled receptors. Moreover, this transmitter can modulate afferent input within these ...
... and its postsynaptic actions are often stymied by the myriad of actions that this neurotransmitter can produce. Thus, DA has been found to exert actions on the neurons it innervates both directly and via G-protein–coupled receptors. Moreover, this transmitter can modulate afferent input within these ...
PT 311 NEUROSCIENCE
... The cortex is made up of neuronal cell bodies, their dendrites, and the terminal arborizations of axons coming from the thalamus and other sources, mainly from other neurons in the cerebral cortex. Indeed, many neurons in the cortex send axons that travel some considerable distance in the central ne ...
... The cortex is made up of neuronal cell bodies, their dendrites, and the terminal arborizations of axons coming from the thalamus and other sources, mainly from other neurons in the cerebral cortex. Indeed, many neurons in the cortex send axons that travel some considerable distance in the central ne ...
Activity of Ventral Medial Thalamic Neurons during
... France) and then digitized with a sampling rate of 20 kHz (intracellular signals), 10 kHz (extracellular signals), or 300 Hz (EEG) for off-line analysis. To perform spectral analysis of EEG potentials, fast Fourier transforms were applied using Spike 2 (CED Software; Cambridge Electronic Design, Cam ...
... France) and then digitized with a sampling rate of 20 kHz (intracellular signals), 10 kHz (extracellular signals), or 300 Hz (EEG) for off-line analysis. To perform spectral analysis of EEG potentials, fast Fourier transforms were applied using Spike 2 (CED Software; Cambridge Electronic Design, Cam ...
Mouse Nerve Growth Factor Prevents Degeneration of Axotomized
... targets of these neurons express NGF mRNA and protein (Korsching et al., 1985; Shelton and Reichardt, 1986; AyerLeLievre et al., 1988).At target fields, NGF is taken up by highaffinity NGF receptors (NGF-R) on nerve terminals (Greene and Shooter, 1980; Taniuchi et al., 1986; Stach and Perez-Polo, 19 ...
... targets of these neurons express NGF mRNA and protein (Korsching et al., 1985; Shelton and Reichardt, 1986; AyerLeLievre et al., 1988).At target fields, NGF is taken up by highaffinity NGF receptors (NGF-R) on nerve terminals (Greene and Shooter, 1980; Taniuchi et al., 1986; Stach and Perez-Polo, 19 ...
The thesis
... Morphology of spinal motoneurons The cell bodies of spinal motoneurons lie in lamina IX in the Rexed of ventral horn (Rexed, 1954; Rexed, 1952; Jankowska and Lundberg, 1981; Schomburg, 1990). Motoneurons form four separate columns in the human cord: the ventromedial, the ventrolateral, the dorsolate ...
... Morphology of spinal motoneurons The cell bodies of spinal motoneurons lie in lamina IX in the Rexed of ventral horn (Rexed, 1954; Rexed, 1952; Jankowska and Lundberg, 1981; Schomburg, 1990). Motoneurons form four separate columns in the human cord: the ventromedial, the ventrolateral, the dorsolate ...
Effects of the Abused Inhalant Toluene on the
... subpopulations of DA neurons in the VTA that have different signaling properties and projection targets [20]. In the standard acute slice preparation, it is not possible to determine the efferent projection of the DA neuron being recorded from or to verify that the recorded neuron is in fact dopamin ...
... subpopulations of DA neurons in the VTA that have different signaling properties and projection targets [20]. In the standard acute slice preparation, it is not possible to determine the efferent projection of the DA neuron being recorded from or to verify that the recorded neuron is in fact dopamin ...
Interval time coding by neurons in the presupplementary and
... two monkeys and found that the ratio of the s.d. over the mean was initiation of the key-release movement (Table 1). In a majority of these neurons (n ¼ 112, 90%), the magnitude of activity during the approximately constant, generally showing a scalar property. We examined the activity of 200 preSMA ...
... two monkeys and found that the ratio of the s.d. over the mean was initiation of the key-release movement (Table 1). In a majority of these neurons (n ¼ 112, 90%), the magnitude of activity during the approximately constant, generally showing a scalar property. We examined the activity of 200 preSMA ...
Lecture #1 - University of Utah
... Function: Selective inhibition (specific to particular terminal) Mech. : Reduces Ca+2 influx less transmitter released by: A) Decrease Voltage sens of Ca+2 channels B) Increased Cl- g ; decreases Depol. Of terminal (short circuit shunt) *GABA: can produce both types of Presynaptic inhibition & Pos ...
... Function: Selective inhibition (specific to particular terminal) Mech. : Reduces Ca+2 influx less transmitter released by: A) Decrease Voltage sens of Ca+2 channels B) Increased Cl- g ; decreases Depol. Of terminal (short circuit shunt) *GABA: can produce both types of Presynaptic inhibition & Pos ...
Spatial organization of thalamocortical and corticothalamic
... of local interactions among neurons within an individual barrel, suggesting that information processing within a vibrissal column reflects operations of experimentally identifiable networks of cortical neurons. In this regard it may be significant that cytochrome oxidase (CO) staining in the barrel ...
... of local interactions among neurons within an individual barrel, suggesting that information processing within a vibrissal column reflects operations of experimentally identifiable networks of cortical neurons. In this regard it may be significant that cytochrome oxidase (CO) staining in the barrel ...
Nancy A. O`Rourke Nicholas C. Weiler Kristina D
... that there has been a great expansion in the number of proteins present at the mammalian postsynaptic density (PSD) relative to those of Drosophila and other invertebrates, highlighting the potential for tremendous complexity 2. Box 1 illustrates the vast number of synaptic proteins distributed acro ...
... that there has been a great expansion in the number of proteins present at the mammalian postsynaptic density (PSD) relative to those of Drosophila and other invertebrates, highlighting the potential for tremendous complexity 2. Box 1 illustrates the vast number of synaptic proteins distributed acro ...
Cuneiform Neurons Activated during
... higher magnification in Figure 1C. This cholinergic population corresponds to the lateral part of the PPT (Jones and Beaudet, 1987; Rye et al., 1987; Vincent and Reiner, 1987). The nuclei of these cholinergic cells, which are not part of the Cun nucleus, did not contain detectable amounts of the Fos ...
... higher magnification in Figure 1C. This cholinergic population corresponds to the lateral part of the PPT (Jones and Beaudet, 1987; Rye et al., 1987; Vincent and Reiner, 1987). The nuclei of these cholinergic cells, which are not part of the Cun nucleus, did not contain detectable amounts of the Fos ...
Taste
... • Sensory nerve endings synapse with their lower poles. • Their life span is 1-2 week (10 days) 3. Basal cells: • They are stem cells for production of new receptor cells. ...
... • Sensory nerve endings synapse with their lower poles. • Their life span is 1-2 week (10 days) 3. Basal cells: • They are stem cells for production of new receptor cells. ...
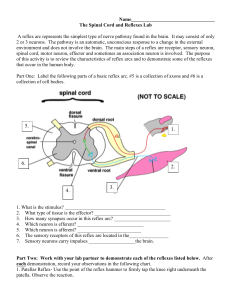
Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord
... A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex are receptor, sensory neuron, spi ...
... A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex are receptor, sensory neuron, spi ...
Kandel ch. 42 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Mossy fibers originate from nuclei in the spinal cord and brain stem and carry sensory information from the periphery as well as information from the cerebral cortex. They terminate as excitatory synapses on the dendrites of granule cells in the granular layer (Figure 42-4). The axons of the granule ...
... Mossy fibers originate from nuclei in the spinal cord and brain stem and carry sensory information from the periphery as well as information from the cerebral cortex. They terminate as excitatory synapses on the dendrites of granule cells in the granular layer (Figure 42-4). The axons of the granule ...
Cranial Nerves
... Ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular divisions •Sensory: Touch, pain, temp, proprioception for face, oral and nasal cavities. •Motor: Muscles for mastication. ...
... Ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular divisions •Sensory: Touch, pain, temp, proprioception for face, oral and nasal cavities. •Motor: Muscles for mastication. ...
stereological estimates of dopaminergic, gabaergic and
... the cell body of positive neurons. This blue–purple precipitate was clearly absent from the nucleus, with little or no product found in dendritic processes. Immunolabeling using the DAB-peroxidase system resulted in the formation of a brown precipitate within the cell body, axonal and dendritic proc ...
... the cell body of positive neurons. This blue–purple precipitate was clearly absent from the nucleus, with little or no product found in dendritic processes. Immunolabeling using the DAB-peroxidase system resulted in the formation of a brown precipitate within the cell body, axonal and dendritic proc ...
Variance and invariance of neuronal long
... of neuronal populations are actively regulated and of potentially high functional and behavioural relevance. Also in this structure, longitudinal studies have first provided seemingly contradictory evidence. Early chronic electrophysiological recordings from a small number of neurons in the hippocam ...
... of neuronal populations are actively regulated and of potentially high functional and behavioural relevance. Also in this structure, longitudinal studies have first provided seemingly contradictory evidence. Early chronic electrophysiological recordings from a small number of neurons in the hippocam ...
PDF
... As a starting point for our analysis, we wanted to characterize neural crest migration in the absence of Nrp1/Sema3A signaling, with or without Nrp2 function. Because Nrp1/Nrp2 double mutants die from vascular defects at E8.5, prior to trunk neural crest migration and DRG formation (Takashima et al. ...
... As a starting point for our analysis, we wanted to characterize neural crest migration in the absence of Nrp1/Sema3A signaling, with or without Nrp2 function. Because Nrp1/Nrp2 double mutants die from vascular defects at E8.5, prior to trunk neural crest migration and DRG formation (Takashima et al. ...
a.Nerve Regeneration
... • Mature neurons do not divide • If damage to a neuron occurs to the axon and the cell body remains intact, cut or compressed axons can regenerate: – Post-trauma axon regrowth is never exactly the same as what existed before the injury – Much of the functional recovery after nerve injury involves re ...
... • Mature neurons do not divide • If damage to a neuron occurs to the axon and the cell body remains intact, cut or compressed axons can regenerate: – Post-trauma axon regrowth is never exactly the same as what existed before the injury – Much of the functional recovery after nerve injury involves re ...
Title Goes here
... A great proportion of “glutazinergic” neurons are found in the cerebral cortex and the amygdala ...
... A great proportion of “glutazinergic” neurons are found in the cerebral cortex and the amygdala ...
Chapter 18: Control and Coordination
... Although the spinal cord is surrounded by the bones in your spine called vertebrae, spinal cord injuries do occur. They can be just as dangerous as a brain injury. Injury to the spine can bring about damage to nerve pathways and result in paralysis (puh RAH luh suhs), which is the loss of muscle mov ...
... Although the spinal cord is surrounded by the bones in your spine called vertebrae, spinal cord injuries do occur. They can be just as dangerous as a brain injury. Injury to the spine can bring about damage to nerve pathways and result in paralysis (puh RAH luh suhs), which is the loss of muscle mov ...
Organization of the Honey Bee Mushroom Body
... Studies of the mushroom bodies of Drosophila melanogaster have suggested that their gamma lobes specifically support short-term memory, whereas their vertical lobes are essential for long-term memory. Developmental studies have demonstrated that the Drosophila gamma lobe, like its equivalent in the ...
... Studies of the mushroom bodies of Drosophila melanogaster have suggested that their gamma lobes specifically support short-term memory, whereas their vertical lobes are essential for long-term memory. Developmental studies have demonstrated that the Drosophila gamma lobe, like its equivalent in the ...
descending projections from the trigeminal ganglion and
... its own peripheral innervation area. Briefly, the ophtalmic nerve innervates the forehead, upper eyelid, cornea, conjunctiva, dorsum of the nose, and the mucosa of frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses, and the anterior portion of the nose; the maxillary nerve supplies the upper lip, lateral portion ...
... its own peripheral innervation area. Briefly, the ophtalmic nerve innervates the forehead, upper eyelid, cornea, conjunctiva, dorsum of the nose, and the mucosa of frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses, and the anterior portion of the nose; the maxillary nerve supplies the upper lip, lateral portion ...
EFFECTS OF INTERLEUKM 1p ON JSOLATED RAT
... The location of SFO at the blood-brain interface allows it to receive information fiom the periphery and then communicate this to neural structures located deeper within the brain. A number of different techniques, including anatomical tracing and electrophysiology, have identified projections of SF ...
... The location of SFO at the blood-brain interface allows it to receive information fiom the periphery and then communicate this to neural structures located deeper within the brain. A number of different techniques, including anatomical tracing and electrophysiology, have identified projections of SF ...
Disruption of Target Interactions Prevents the Development of
... developmental mechanismsthat give rise to the differential expression of neuropeptides by individual neurons are incompletely understood. One of the first stepstoward understanding how diverse peptidergic phenotypes are generated is elucidating the pattern of peptide expressionduring normal developm ...
... developmental mechanismsthat give rise to the differential expression of neuropeptides by individual neurons are incompletely understood. One of the first stepstoward understanding how diverse peptidergic phenotypes are generated is elucidating the pattern of peptide expressionduring normal developm ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.