Дисциплина «Профессиональное общение на иностранном языке
... reprise or without it. The repriseless form is characteristic of vocal music. It can be one-thematic or two-thematic. In one-thematic form the second part develops the musical material of the first part, as it is sometimes with the second sentence of the period. 4) In the XIX century the modern type ...
... reprise or without it. The repriseless form is characteristic of vocal music. It can be one-thematic or two-thematic. In one-thematic form the second part develops the musical material of the first part, as it is sometimes with the second sentence of the period. 4) In the XIX century the modern type ...
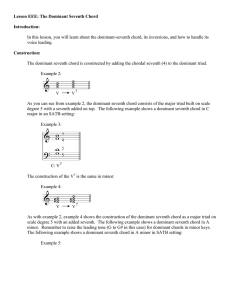
Lesson EEE: The Dominant Seventh Chord
... one of the voices.] Conclusion: In this lesson we have discussed the various formations of one of the most important harmonic progressions and cadential idioms in tonal music: V7 to I. The voice leading of these various configurations is determined primarily by the presence of tendency tones 7 and 4 ...
... one of the voices.] Conclusion: In this lesson we have discussed the various formations of one of the most important harmonic progressions and cadential idioms in tonal music: V7 to I. The voice leading of these various configurations is determined primarily by the presence of tendency tones 7 and 4 ...
Set Theory - ClarkRoss.ca
... • The Best Normal Order is usually written using letter names for pitch classes (e.g, C D Eb F#), or music notation. • The numerical label for the best normal order, where the lowest pitch = 0, is called the Prime Form. The prime form for [0 3 4 6] is [0 2 3 6]. Can you explain why? • A Set Class in ...
... • The Best Normal Order is usually written using letter names for pitch classes (e.g, C D Eb F#), or music notation. • The numerical label for the best normal order, where the lowest pitch = 0, is called the Prime Form. The prime form for [0 3 4 6] is [0 2 3 6]. Can you explain why? • A Set Class in ...
1 - USC Upstate
... process in which a musician creates new melody on top of a pre-existing chord pattern (such as a blues or "rhythm changes."). 37. Intonation - Most instruments can play pitches between the established chromatic scale degrees in Western music. Typically, musicians are trained to avoid these microtone ...
... process in which a musician creates new melody on top of a pre-existing chord pattern (such as a blues or "rhythm changes."). 37. Intonation - Most instruments can play pitches between the established chromatic scale degrees in Western music. Typically, musicians are trained to avoid these microtone ...
01_front - Massey Research Online
... topics of scales, melody, voicings, harmony and rhythm are examined in separate chapters with over two hundred notated musical examples used to demonstrate the materials in their context. This thesis also seeks to explain the relationships between these elements and presents the material in a fonn a ...
... topics of scales, melody, voicings, harmony and rhythm are examined in separate chapters with over two hundred notated musical examples used to demonstrate the materials in their context. This thesis also seeks to explain the relationships between these elements and presents the material in a fonn a ...
P5a - Piano Grade 5
... • Baroque music is performed with a clearly articulated sound, often using detached notes. There is no sustaining pedal on a harpsichord, and the tone dies away quite rapidly. • Dynamics were usually left to the performer to determine. Where they are indicated by the composer, they are often “terrac ...
... • Baroque music is performed with a clearly articulated sound, often using detached notes. There is no sustaining pedal on a harpsichord, and the tone dies away quite rapidly. • Dynamics were usually left to the performer to determine. Where they are indicated by the composer, they are often “terrac ...
My analysis and thoughts on Gershwin – An American in Paris
... fragmentation, augmentation, imitation, sequence, ostinato, layering of countermelodies above or below the melody, rhythmic displacement, etc . is dominant throughout. In terms of structure or hierarchy of the texture, Gershwin use of counterpoint makes it clear as to what role an instrument(s) is p ...
... fragmentation, augmentation, imitation, sequence, ostinato, layering of countermelodies above or below the melody, rhythmic displacement, etc . is dominant throughout. In terms of structure or hierarchy of the texture, Gershwin use of counterpoint makes it clear as to what role an instrument(s) is p ...
GCSE Music Revision - The Hazeley Academy
... Drones – long continuous note or a constantly repeated note Ostinato/loops – repeated musical ideas. The shortest ideas are called cells. Phasing – two almost identical parts which go out of sync with each other and gradually, after a number of repetitions, come back into sync again Metamorphosis ...
... Drones – long continuous note or a constantly repeated note Ostinato/loops – repeated musical ideas. The shortest ideas are called cells. Phasing – two almost identical parts which go out of sync with each other and gradually, after a number of repetitions, come back into sync again Metamorphosis ...
Unit 2: The Staff, Notes, and Pitches
... pitch If the notes appear LOWER on the staff, they sound LOWER in pitch ...
... pitch If the notes appear LOWER on the staff, they sound LOWER in pitch ...
SEVENTH CHORDS Every triad can be extended by adding another
... Seventh chords can be inverted. A seventh chord is inverted if the bottom-most note, the bass, is not the root of the chord. Since there are four notes (instead of 3 in a triad), there is a root position and first, second and third inversion of a seventh chord. ...
... Seventh chords can be inverted. A seventh chord is inverted if the bottom-most note, the bass, is not the root of the chord. Since there are four notes (instead of 3 in a triad), there is a root position and first, second and third inversion of a seventh chord. ...
2015 Chorus Midterm Review Sheet
... quarter note – a note one-quarter the value of a whole note rest – a symbol used for duration of silence rhythm – the pattern of musical sound. root – the name given to the bottom tone of a triad scale – an ascending or descending series of tones arranged in definite order within an octave sharp – a ...
... quarter note – a note one-quarter the value of a whole note rest – a symbol used for duration of silence rhythm – the pattern of musical sound. root – the name given to the bottom tone of a triad scale – an ascending or descending series of tones arranged in definite order within an octave sharp – a ...
class9#
... Ab and G# are not part of C, so they will point to some other scale and behave according to there function in that context. Another possibility: In a CHROMATHIC PASSAGE, the chromatic not assigned any harmonic function. In that case, an upward is indicated by an uplifting alteration -- #, and a down ...
... Ab and G# are not part of C, so they will point to some other scale and behave according to there function in that context. Another possibility: In a CHROMATHIC PASSAGE, the chromatic not assigned any harmonic function. In that case, an upward is indicated by an uplifting alteration -- #, and a down ...
MTO 18.2: Sly, Review of Damschroder
... analysis using Damschroder’s approach, given beneath that, preserves the “parent” chord designation (II) through the chromatic evolution of the supertonic harmony, and in so doing illuminates a process that is obscured—or at least deemphasized—by the more usual nomenclature. Consider further that in ...
... analysis using Damschroder’s approach, given beneath that, preserves the “parent” chord designation (II) through the chromatic evolution of the supertonic harmony, and in so doing illuminates a process that is obscured—or at least deemphasized—by the more usual nomenclature. Consider further that in ...
Pitch, tonality, and the missing fundamentals of music cognition
... Is this dynamic (higher-arousal) negativity? afraid, angry, tense, frustrated… ...
... Is this dynamic (higher-arousal) negativity? afraid, angry, tense, frustrated… ...
GCSE set works condensed info
... the sitar augments the harmony with the improvised melody. But generally, no sense of harmony because emphasis is placed on the melody (therefore a ...
... the sitar augments the harmony with the improvised melody. But generally, no sense of harmony because emphasis is placed on the melody (therefore a ...
Area of Study 03
... • These are all different kinds of melodic note patterns. • Conjunct – notes in the melody move mainly by step (they are mostly next to each other in pitch) • Disjunct – moves mainly by leaps (big intervals between the notes) • Triadic – the melody begins by using notes that belong to the triad (of ...
... • These are all different kinds of melodic note patterns. • Conjunct – notes in the melody move mainly by step (they are mostly next to each other in pitch) • Disjunct – moves mainly by leaps (big intervals between the notes) • Triadic – the melody begins by using notes that belong to the triad (of ...
Grade 9 Music Exam Review
... of the components of the horizontal aspect The quality of a sound that distinguished it from another. Texture of an instrument of voice is determined by its shape, material, what starts the sound, and what causes the sound to resonate. ...
... of the components of the horizontal aspect The quality of a sound that distinguished it from another. Texture of an instrument of voice is determined by its shape, material, what starts the sound, and what causes the sound to resonate. ...
(Answers and Exam Piece).
... of the components of the horizontal aspect The quality of a sound that distinguished it from another. Texture of an instrument of voice is determined by its shape, material, what starts the sound, and what causes the sound to resonate. ...
... of the components of the horizontal aspect The quality of a sound that distinguished it from another. Texture of an instrument of voice is determined by its shape, material, what starts the sound, and what causes the sound to resonate. ...
Lewin, David “A Formal Theory of Generalized Tonal Functions”
... moves as well. A “Relative”-operation then takes you a minor third down from a major chord and a minor third up from a minor chord. The leap of a major third is called a “Leittone-exchange”. From a major chord a “L”-operation takes you a major third up, from a minor chord the “L”-operation takes you ...
... moves as well. A “Relative”-operation then takes you a minor third down from a major chord and a minor third up from a minor chord. The leap of a major third is called a “Leittone-exchange”. From a major chord a “L”-operation takes you a major third up, from a minor chord the “L”-operation takes you ...
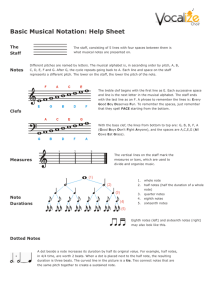
Basic Musical Notation: Help Sheet
... what kind of note gets the beat. In this example, 4/4 time, there are 4 beats per measure, and the quarter note (bottom 4) gets the beat. In 3/4 time, the quarter note would still get the beat, but there would only be 3 beats in a measure. In 6/8 time, the eighth note gets the beat, and there are 6 ...
... what kind of note gets the beat. In this example, 4/4 time, there are 4 beats per measure, and the quarter note (bottom 4) gets the beat. In 3/4 time, the quarter note would still get the beat, but there would only be 3 beats in a measure. In 6/8 time, the eighth note gets the beat, and there are 6 ...
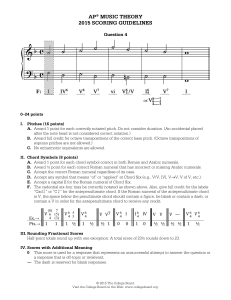
ap® music theory 2015 scoring guidelines
... A. Award 1 point for each correctly notated pitch. Do not consider duration. (An accidental placed after the note head is not considered correct notation.) B. Award full credit for octave transpositions of the correct bass pitch. (Octave transpositions of soprano pitches are not allowed.) C. No enha ...
... A. Award 1 point for each correctly notated pitch. Do not consider duration. (An accidental placed after the note head is not considered correct notation.) B. Award full credit for octave transpositions of the correct bass pitch. (Octave transpositions of soprano pitches are not allowed.) C. No enha ...
the fundamental principles of harmony
... Over the course of my long teaching career, I have noticed that the usual study of Harmony « at the desk » (that is, away from the piano) has proven ineffectual for most students. Students often lack the sufficient mastery of solfège required to read the traditional harmony exercise displayed in fou ...
... Over the course of my long teaching career, I have noticed that the usual study of Harmony « at the desk » (that is, away from the piano) has proven ineffectual for most students. Students often lack the sufficient mastery of solfège required to read the traditional harmony exercise displayed in fou ...
Tippett - Concerto for Double String Orchestra movement I (Harmony)
... harmony. The most important functions of the chords are subdominant, dominant, and tonic (S, D, T). They are usually represented by scale degrees II/IV, V, and I, but other degrees can be substituted for them as well. ...
... harmony. The most important functions of the chords are subdominant, dominant, and tonic (S, D, T). They are usually represented by scale degrees II/IV, V, and I, but other degrees can be substituted for them as well. ...
6/26/06 Introduction We all have a mental/aural image of “music
... vibrating string of the monochord sounds at full wavelength, a tone is produced. This sound is the fundamental. When the wavelength is progressively divided into 2, 3, etc., new tones are produced. Each new tone has a specific mathematical relationship (proportion) to the fundamental. The proportion ...
... vibrating string of the monochord sounds at full wavelength, a tone is produced. This sound is the fundamental. When the wavelength is progressively divided into 2, 3, etc., new tones are produced. Each new tone has a specific mathematical relationship (proportion) to the fundamental. The proportion ...
6th Grade Choir NAME__________________________ Quarter 1
... 3. Barline = those vertical lines that go through the staff to separate them into measures. ...
... 3. Barline = those vertical lines that go through the staff to separate them into measures. ...