Chromaticism II: Tonicization/Modulation
... Mixture is a type of chromaticism involving the introduction of elements from another mode. In contrast, Tonicization and Modulation involve the introduction of elements from another key. More specifically, tonicization and modulation are concerned with a change of key. Tonicization versus Modulatio ...
... Mixture is a type of chromaticism involving the introduction of elements from another mode. In contrast, Tonicization and Modulation involve the introduction of elements from another key. More specifically, tonicization and modulation are concerned with a change of key. Tonicization versus Modulatio ...
image by Hans-Christoph Steiner based on Grey, JM 1979, JASA
... The time envelope in terms of rise, duration, and decay. The changes both of spectral envelope (formant-glide) and fundamental frequency (micro-intonation). 5. The prefix, an onset of a sound quite dissimilar to the ...
... The time envelope in terms of rise, duration, and decay. The changes both of spectral envelope (formant-glide) and fundamental frequency (micro-intonation). 5. The prefix, an onset of a sound quite dissimilar to the ...
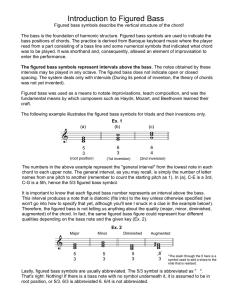
Intro to Figured Bass
... The bass is the foundation of harmonic structure. Figured bass symbols are used to indicate the bass positions of chords. The practice is derived from Baroque keyboard music where the player read from a part consisting of a bass line and some numerical symbols that indicated what chord was to be pla ...
... The bass is the foundation of harmonic structure. Figured bass symbols are used to indicate the bass positions of chords. The practice is derived from Baroque keyboard music where the player read from a part consisting of a bass line and some numerical symbols that indicated what chord was to be pla ...
CFA I
... 9. Time Signature: specifies how many beats are in each measure and what note value constitutes one beat. 10.Whole Note: A note that receives 4 beats of sound in 4/4 time 11.Bass Clef: mainly used by the men and is also called the F clef 12.Bass: The lowest male singing voice 13.Clef: A musical symb ...
... 9. Time Signature: specifies how many beats are in each measure and what note value constitutes one beat. 10.Whole Note: A note that receives 4 beats of sound in 4/4 time 11.Bass Clef: mainly used by the men and is also called the F clef 12.Bass: The lowest male singing voice 13.Clef: A musical symb ...
CADENCES AND PHRASES
... CADENCES AND PHRASES A cadence is where the music reaches some kind of goal – often accompanied by a rhythmic pause. There are four basic types of cadences and each is defined by its specific use of harmony. The music between cadences is called a phrase. Cadences separate phrases and act very much l ...
... CADENCES AND PHRASES A cadence is where the music reaches some kind of goal – often accompanied by a rhythmic pause. There are four basic types of cadences and each is defined by its specific use of harmony. The music between cadences is called a phrase. Cadences separate phrases and act very much l ...
a geometric model for the analysis of pop music
... growing interest can partly be explained as a consequence of the flexibility of some of the formal tools and concepts that have been developed recently in music analysis and particularly within the transformational tradition—a branch that extends the settheoretical paradigm as well as includes other ...
... growing interest can partly be explained as a consequence of the flexibility of some of the formal tools and concepts that have been developed recently in music analysis and particularly within the transformational tradition—a branch that extends the settheoretical paradigm as well as includes other ...
Romantic and impressionist harmony
... mass) a nice example with the remarkable progressions of F major, F# minor, C# major, D major, Eb minor, Bb major, B major, C minor and F major. The leading tone then becomes more important and enables the chromatic world of Liszt and Wagner with their complex chords and fast key interactions (which ...
... mass) a nice example with the remarkable progressions of F major, F# minor, C# major, D major, Eb minor, Bb major, B major, C minor and F major. The leading tone then becomes more important and enables the chromatic world of Liszt and Wagner with their complex chords and fast key interactions (which ...
A Crash Course in Renaissance Counterpoint
... This is a little complex, however. Sometimes there are so-called ‘consonant’ fourths, as in the common cadential harmonic figure 3443 over the dominant. Here the dissonant fourth on the third beat is ‘prepared’ on the second beat (but over the same bass note!). ...
... This is a little complex, however. Sometimes there are so-called ‘consonant’ fourths, as in the common cadential harmonic figure 3443 over the dominant. Here the dissonant fourth on the third beat is ‘prepared’ on the second beat (but over the same bass note!). ...
MUS 1110 Elementary Harmony
... MUS 1110 Elementary Harmony, Counterpoint, and Ethnic Music Writing Description: This course is designed for students who have a background in music as one of the subjects offered for the Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education (UACE) or the equivalent or a good diploma certificate in which music w ...
... MUS 1110 Elementary Harmony, Counterpoint, and Ethnic Music Writing Description: This course is designed for students who have a background in music as one of the subjects offered for the Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education (UACE) or the equivalent or a good diploma certificate in which music w ...
AP Music Theory
... 9. Hear, identify and notate all intervals major, minor, diminished and augmented within ...
... 9. Hear, identify and notate all intervals major, minor, diminished and augmented within ...
The Staff Notes
... Music notes are named after the first _______________ letters of the alphabet, A B C D E F G. By their ______________________ on the staff, they can represent the entire ___________________ of musical sound. _______________ signs help us _____________________ the staff so notes can be easily _______ ...
... Music notes are named after the first _______________ letters of the alphabet, A B C D E F G. By their ______________________ on the staff, they can represent the entire ___________________ of musical sound. _______________ signs help us _____________________ the staff so notes can be easily _______ ...
Answer Key
... Genre of the composition – organum; This composition is based on a preexisting chant/plainchant/plainsong/Gregorian chant Describe the melody and rhythm of the highest voice: the melody “undulates and cascades in a virtuosic way”, it is free, rhapsodic, melismatic; the rhythm is unmeasured and can a ...
... Genre of the composition – organum; This composition is based on a preexisting chant/plainchant/plainsong/Gregorian chant Describe the melody and rhythm of the highest voice: the melody “undulates and cascades in a virtuosic way”, it is free, rhapsodic, melismatic; the rhythm is unmeasured and can a ...
The Augmented Sixth Chord
... The German chord is an interesting case because its quality is that of a major-minor 7th chord (although it doesn't resolve like one in its conventional use). Composers exploited the possibility of using a Gr+6 as a pivot chord in a modulation. For instance, the Gr+6 could become a V7 just by resolv ...
... The German chord is an interesting case because its quality is that of a major-minor 7th chord (although it doesn't resolve like one in its conventional use). Composers exploited the possibility of using a Gr+6 as a pivot chord in a modulation. For instance, the Gr+6 could become a V7 just by resolv ...
AP Music Theory - Stratford Public Schools
... Write cadences in 3 and 4 part harmony. Analyze music in terms of phrases and periods aurally and in written form. Create diagrams of musical form based on phrases, periods, and cadences. Recognize a motive and how it is developed in a composition. ...
... Write cadences in 3 and 4 part harmony. Analyze music in terms of phrases and periods aurally and in written form. Create diagrams of musical form based on phrases, periods, and cadences. Recognize a motive and how it is developed in a composition. ...
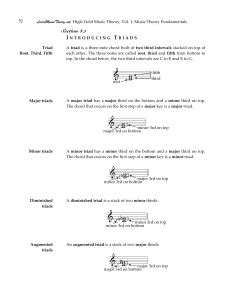
Introducing Triads - LearnMusicTheory.net
... LearnMusicTheory.net High-Yield Music Theory, Vol. 1: Music Theory Fundamentals ...
... LearnMusicTheory.net High-Yield Music Theory, Vol. 1: Music Theory Fundamentals ...
Generating Guitar Scores from a MIDI Source
... Figure 3: Snapshot of the user interface l If the raised note is over the twelfth cell on the highest string, lower the note to its original position. 4.4. User intervention: A reasonably good guitar score can be generated automatically using the above process. However, some user intervention may f ...
... Figure 3: Snapshot of the user interface l If the raised note is over the twelfth cell on the highest string, lower the note to its original position. 4.4. User intervention: A reasonably good guitar score can be generated automatically using the above process. However, some user intervention may f ...
Elements of Music
... c. When a composition contains several different parts and when the first part repeats alternately with other parts, the form may be identified as rondo. d. When a composition presents a given melody (theme), followed by repetitions of it with alterations, either in the melody itself or in its accom ...
... c. When a composition contains several different parts and when the first part repeats alternately with other parts, the form may be identified as rondo. d. When a composition presents a given melody (theme), followed by repetitions of it with alterations, either in the melody itself or in its accom ...
The Renaissance 4/4 Other Features of the Style
... Renaissance avoided doubling the following notes: • leading notes • dominant 7ths • dissonances • chromatically-altered notes. This is because: 1. by their dissonance these notes were already ‘prominent’ and so did not need ‘doubling’ - which unbalances the harmony. 2. ‘notes of motion’ need to be r ...
... Renaissance avoided doubling the following notes: • leading notes • dominant 7ths • dissonances • chromatically-altered notes. This is because: 1. by their dissonance these notes were already ‘prominent’ and so did not need ‘doubling’ - which unbalances the harmony. 2. ‘notes of motion’ need to be r ...
Music Notation Guide - Delta Academies Trust Arts
... Tempo (Italian for time) is the speed/pace of a given piece. The tempo of a piece will typically be written at the start of a piece of music, and is usually indicated in beats per minute (BPM). This means that a particular note value (for example, a quarter note or crotchet) is specified as the beat ...
... Tempo (Italian for time) is the speed/pace of a given piece. The tempo of a piece will typically be written at the start of a piece of music, and is usually indicated in beats per minute (BPM). This means that a particular note value (for example, a quarter note or crotchet) is specified as the beat ...
"Tonal Organization in Schoenberg`s Six Little Piano Pieces, Op. 19"
... Piano Pieces, Op. 19. In 1911, when they were written, Schoenberg had been composing in his new atonal style for some time, having already completed the monodrama Erwartung (1909), and being just over a year away from the completion of Pierrot Lunaire (1912). Thus, lying as they do between these two ...
... Piano Pieces, Op. 19. In 1911, when they were written, Schoenberg had been composing in his new atonal style for some time, having already completed the monodrama Erwartung (1909), and being just over a year away from the completion of Pierrot Lunaire (1912). Thus, lying as they do between these two ...
Basic Music Theory
... The music commonly played in our part of the world has twelve different notes: A, B, C, D, E, F, and G with a sharp (#) or flat (b) note between all the notes except B and C and E and F. The notes between the letters can be called either sharp or flat. A sharp (#) note is one fret higher than the le ...
... The music commonly played in our part of the world has twelve different notes: A, B, C, D, E, F, and G with a sharp (#) or flat (b) note between all the notes except B and C and E and F. The notes between the letters can be called either sharp or flat. A sharp (#) note is one fret higher than the le ...
Behind The Guitar Chords 1. Tempered Notes Plucking a string will
... The mentioned addition of the sus = s main value as 4 can be obtained by replacing s with s/4. Placing our imaginary capo or cape anywhere, will create a possible key choice on the guitar. The rule for basic chords is to use only three kinds from the seven basic notes above. Namely, having black and ...
... The mentioned addition of the sus = s main value as 4 can be obtained by replacing s with s/4. Placing our imaginary capo or cape anywhere, will create a possible key choice on the guitar. The rule for basic chords is to use only three kinds from the seven basic notes above. Namely, having black and ...
here
... - Polychords – simultaneous use of two or more simple chords (common in 20th century compositions) - Tone Cluster – truly simultaneous musical chord comprised of consecutive tones separated chromatically: sound very dissonant - Open fifths – the tonic and dominant note of the chord, without the medi ...
... - Polychords – simultaneous use of two or more simple chords (common in 20th century compositions) - Tone Cluster – truly simultaneous musical chord comprised of consecutive tones separated chromatically: sound very dissonant - Open fifths – the tonic and dominant note of the chord, without the medi ...
A2 2, Part 2: Written Examination (MS)
... • first attempt at total serialism and is based on 12 pitches, 12 different types of attack, 12 different durations • ordered into four scales of 12 notes each, one for each musical element, assigning order numbers to each • use of retrograde, inversion, transposition of the pitch series up ...
... • first attempt at total serialism and is based on 12 pitches, 12 different types of attack, 12 different durations • ordered into four scales of 12 notes each, one for each musical element, assigning order numbers to each • use of retrograde, inversion, transposition of the pitch series up ...