Music Theory & Ear Training for Busy Adults
... E.g., The C major scale and the A natural minor scale are relative major and minor, respectively. (By the way, the C major and A natural minor scales are special cases in that they use only white keys.) 7. Modes are scales which use the same menu of notes as major and minor scales, but have other ro ...
... E.g., The C major scale and the A natural minor scale are relative major and minor, respectively. (By the way, the C major and A natural minor scales are special cases in that they use only white keys.) 7. Modes are scales which use the same menu of notes as major and minor scales, but have other ro ...
Other Chords of the Major Key
... a major third interval as the lower interval and a minor third upper interval. Minor Chords are made up of a minor third interval as the lower interval and a major third upper interval. The viio chord, however, is made up a two minor third intervals, thus a diminished chord. Examples of the Leading ...
... a major third interval as the lower interval and a minor third upper interval. Minor Chords are made up of a minor third interval as the lower interval and a major third upper interval. The viio chord, however, is made up a two minor third intervals, thus a diminished chord. Examples of the Leading ...
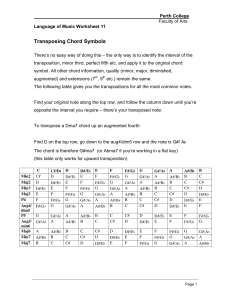
Transposing Chord Symbols
... We discussed compound intervals, that is intervals of more than an octave, in an earlier lesson. How might we notate the addition of these as extensions to a chord? The first point to make is that extensions of the tenth and twelve are just thirds and fifths plus an octave. The extensions of real in ...
... We discussed compound intervals, that is intervals of more than an octave, in an earlier lesson. How might we notate the addition of these as extensions to a chord? The first point to make is that extensions of the tenth and twelve are just thirds and fifths plus an octave. The extensions of real in ...
simpler list of musical terminology
... of music its tune. The melody line is the most prominent line of the music. It is the line you hum or remember most vividly. A hymn gets its identity from its melody. Although a hymn’s chords and harmonic movement may be similar to other hymns, its melody will be unique. The hymn melody is usually i ...
... of music its tune. The melody line is the most prominent line of the music. It is the line you hum or remember most vividly. A hymn gets its identity from its melody. Although a hymn’s chords and harmonic movement may be similar to other hymns, its melody will be unique. The hymn melody is usually i ...
ANP_Paper3_MathofMusic
... systems used today. In general, a sound of a specific frequency is designated with a letter. As another example, let “A” be a sound of frequency 100 Hz (we’ll call this an A note from now on). We designate all sounds of frequency 100 Hz * 2x, with “x” being any integer, as A notes as well, so sounds ...
... systems used today. In general, a sound of a specific frequency is designated with a letter. As another example, let “A” be a sound of frequency 100 Hz (we’ll call this an A note from now on). We designate all sounds of frequency 100 Hz * 2x, with “x” being any integer, as A notes as well, so sounds ...
Music for Small Ensemble
... Galliard is rhythmically more complex, especially in the opening section, with its syncopations (see line 4) Texture Contrapuntal – somewhat like a civilised conversation between the five players: each part has a melodic line of its own Imitation between the parts Lines cross over each other ...
... Galliard is rhythmically more complex, especially in the opening section, with its syncopations (see line 4) Texture Contrapuntal – somewhat like a civilised conversation between the five players: each part has a melodic line of its own Imitation between the parts Lines cross over each other ...
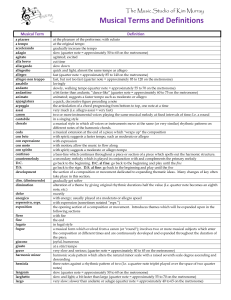
Musical Terms and Definitions
... the opening section of a composition or movement. Introduces themes which will be expanded upon in the following sections with fire the end in fugal style a musical form which evolved from a canon (or "round"); involves two or more musical subjects which enter the composition at different times and ...
... the opening section of a composition or movement. Introduces themes which will be expanded upon in the following sections with fire the end in fugal style a musical form which evolved from a canon (or "round"); involves two or more musical subjects which enter the composition at different times and ...
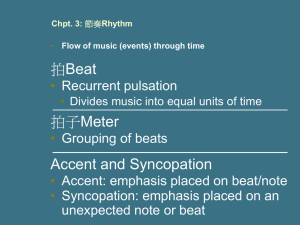
Chpt. 3: 節奏Rhythm Flow of music (events) through time
... • Appears again later if meter changes ...
... • Appears again later if meter changes ...
Harmonic Language in The Legend of Zelda: Ocarina of Time
... III chord also contains scale degree 1, but is less commonly found in traditional Common Practice progressions. These chords usually begin and end the harmonic phrase model, and contribute to a sense of stability. The second category, dominant, is defined by the prominence of scale degree 7, which s ...
... III chord also contains scale degree 1, but is less commonly found in traditional Common Practice progressions. These chords usually begin and end the harmonic phrase model, and contribute to a sense of stability. The second category, dominant, is defined by the prominence of scale degree 7, which s ...
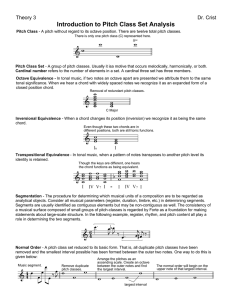
Introduction to Pitch Class Set Analysis
... Segments are usually identified as contiguous elements but may be non-contiguous as well. The consistency of a musical surface composed of small groups of pitch-classes is regarded by Forte as a foundation for making statements about large-scale structure. In the following example, register, rhythm, ...
... Segments are usually identified as contiguous elements but may be non-contiguous as well. The consistency of a musical surface composed of small groups of pitch-classes is regarded by Forte as a foundation for making statements about large-scale structure. In the following example, register, rhythm, ...
The Lydian Mode - Fundamental Changes
... When forming chord progressions to highlight the characteristics of the Lydian mode, some varying techniques are used. Often in rock it is played over a static vamp, and sometimes even the tonic Major 7#11 chord is sustained: Example 14b ...
... When forming chord progressions to highlight the characteristics of the Lydian mode, some varying techniques are used. Often in rock it is played over a static vamp, and sometimes even the tonic Major 7#11 chord is sustained: Example 14b ...
Proficiencies—Piano Student Name: First Last Course Number
... not continual. ☐Correct chords in progression occur only intermittently. ...
... not continual. ☐Correct chords in progression occur only intermittently. ...
lesson 1 - john p birchall
... semitones between any note and its OCTAVE is a CHROMATIC SCALE. The chromatic scale divides the octave into 12 EQUAL SEMITONES. See Example 1. Play this over on your instrument and listen to the sound. This scale contains ALL the notes in the octave; there are no other notes in the sound system that ...
... semitones between any note and its OCTAVE is a CHROMATIC SCALE. The chromatic scale divides the octave into 12 EQUAL SEMITONES. See Example 1. Play this over on your instrument and listen to the sound. This scale contains ALL the notes in the octave; there are no other notes in the sound system that ...
On the Slow Movement of Brahms`s F-Minor Clarinet Sonata
... Cohn has argued that such major-thirds cycles are “paradoxical from a Schenkerian/linear perspective” since they depart from the underlying Diatonie of Schenker’s framework.3 Howard Cinnamon (1984, 1986) notes that such cycles appear to arpeggiate an augmented triad, a harmony that is ineligible for ...
... Cohn has argued that such major-thirds cycles are “paradoxical from a Schenkerian/linear perspective” since they depart from the underlying Diatonie of Schenker’s framework.3 Howard Cinnamon (1984, 1986) notes that such cycles appear to arpeggiate an augmented triad, a harmony that is ineligible for ...
dotted eighth notes - Introduction to Music Theory
... are in. When a melody is rewritten into another key with the exact same sequence of notes and intervals, it is called TRANSPOSITION. This raises or lowers the notes to make a melody easier to sing or play, or so it can be played by an instrument in a different key. The easiest way to transpose i ...
... are in. When a melody is rewritten into another key with the exact same sequence of notes and intervals, it is called TRANSPOSITION. This raises or lowers the notes to make a melody easier to sing or play, or so it can be played by an instrument in a different key. The easiest way to transpose i ...
dotted eighth notes - Introduction to Music Theory
... are in. When a melody is rewritten into another key with the exact same sequence of notes and intervals, it is called TRANSPOSITION. This raises or lowers the notes to make a melody easier to sing or play, or so it can be played by an instrument in a different key. The easiest way to transpose i ...
... are in. When a melody is rewritten into another key with the exact same sequence of notes and intervals, it is called TRANSPOSITION. This raises or lowers the notes to make a melody easier to sing or play, or so it can be played by an instrument in a different key. The easiest way to transpose i ...
Song leaders tools
... As the notes are written closer to the top of these clefs their pitch increases giving them a higher sound. Conversely, as notes are written closer to the bottom of the clefs the pitch decreases giving them a lower sound. The treble clef contains notes that are higher in pitch than the bass clef and ...
... As the notes are written closer to the top of these clefs their pitch increases giving them a higher sound. Conversely, as notes are written closer to the bottom of the clefs the pitch decreases giving them a lower sound. The treble clef contains notes that are higher in pitch than the bass clef and ...
Twelve Tone Serialism - Mathematics and Computer Science
... incorporation of three, four, or even six voices. Eventually instruments were included as well. Although, they were originally used as a background noise, a drone that would enhance certain notes but not add anything on its own (Forney, 75). As more instruments were used in composition, music gained ...
... incorporation of three, four, or even six voices. Eventually instruments were included as well. Although, they were originally used as a background noise, a drone that would enhance certain notes but not add anything on its own (Forney, 75). As more instruments were used in composition, music gained ...
- MusicTeachers.co.uk
... evident in his mature piano works written after 1900, with their exploration of the instrument's percussive bell- and gong-like sonorities. Harmonically, Debussy's music incorporates both modality and tonality (earlier French composers such as Fauré had used modal aspects in their works) and he is r ...
... evident in his mature piano works written after 1900, with their exploration of the instrument's percussive bell- and gong-like sonorities. Harmonically, Debussy's music incorporates both modality and tonality (earlier French composers such as Fauré had used modal aspects in their works) and he is r ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 23 Enharmonic Spellings and Enharmonic
... So far, all enharmonic discussed so far is intended primarily for the eye, not the ear There are FOUR sonorities used in tonal music can be reinterpreted enharmonically in a different key ( NOT in enharmonic keys, like Gb and F#) 1. Major-minor seventh: can be serve either as a V7 OR as a Ger+6 ...
... So far, all enharmonic discussed so far is intended primarily for the eye, not the ear There are FOUR sonorities used in tonal music can be reinterpreted enharmonically in a different key ( NOT in enharmonic keys, like Gb and F#) 1. Major-minor seventh: can be serve either as a V7 OR as a Ger+6 ...
Slides - UMD Physics
... C, C#/Db, D, D#/Eb, E, E#, Fb, F, F#/Gb, G, G#/Ab, A, A#/Bb, B or do, do#/re b, re, re#/mi b, mi, mi#/fa b, fa, fa#, sol, sol#/la b, la, la#/sib, si ...
... C, C#/Db, D, D#/Eb, E, E#, Fb, F, F#/Gb, G, G#/Ab, A, A#/Bb, B or do, do#/re b, re, re#/mi b, mi, mi#/fa b, fa, fa#, sol, sol#/la b, la, la#/sib, si ...
The Triad in First Inversion: Tonic, Subdominant, and Dominant Triads
... The use of an inversion of a triad makes possible better voice leading in the bass. An inverted triad coming between the strong root positions of triads increases the musical interest of a composition. The first inversions of major and minor triads may be found as early as the 13 th century. Th ...
... The use of an inversion of a triad makes possible better voice leading in the bass. An inverted triad coming between the strong root positions of triads increases the musical interest of a composition. The first inversions of major and minor triads may be found as early as the 13 th century. Th ...
Jazz Piano Quartal Voicing Workshop
... only did the content (the actual chord voicings) change, but the context (the way that the voicings were used and the forms within which they appeared) was also dramatically altered. First, the music moved from being tonal to being also modal. Most of what pianists played in the harmony up until tha ...
... only did the content (the actual chord voicings) change, but the context (the way that the voicings were used and the forms within which they appeared) was also dramatically altered. First, the music moved from being tonal to being also modal. Most of what pianists played in the harmony up until tha ...