
The Craft of Singing
... melody. The average bass range extends from d (below middle c'} to f' (above middle c'}, occasionally extending down to C, an octave below middle c'. Since one of the primary characteristics of barbershop music is its cone-shaped sound, the bass must sing with a heavier production than that used by ...
... melody. The average bass range extends from d (below middle c'} to f' (above middle c'}, occasionally extending down to C, an octave below middle c'. Since one of the primary characteristics of barbershop music is its cone-shaped sound, the bass must sing with a heavier production than that used by ...
CHAPTER 1 TONAL MODULATION WITH JUST
... scale is a source of materials, from which chords and melodies are drawn, and in which the scale as a scale appears only occasionally if at all.”4 The defining feature of Monophony is that it is not based upon equal divisions of the octave like the common twelve-tone equal tempered chromatic scale, ...
... scale is a source of materials, from which chords and melodies are drawn, and in which the scale as a scale appears only occasionally if at all.”4 The defining feature of Monophony is that it is not based upon equal divisions of the octave like the common twelve-tone equal tempered chromatic scale, ...
CH. 20 Musical Sounds - Stephen F. Austin State University
... frequencies that are in simple ratios to one another. •Octave: The eighth full tone (or 12th successive note in a scale) above or below a given tone. ...
... frequencies that are in simple ratios to one another. •Octave: The eighth full tone (or 12th successive note in a scale) above or below a given tone. ...
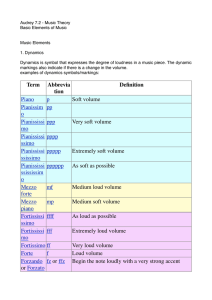
Basic Elements of Music
... large intervals called leaps. A step is for example from do to re, re to mi, and mi to fa and so on. A larger interval or leap is for example like from do to mi, do to sol, and so on. There is a variety of effects on how and when the melody tones are performed. They are called legato when they are p ...
... large intervals called leaps. A step is for example from do to re, re to mi, and mi to fa and so on. A larger interval or leap is for example like from do to mi, do to sol, and so on. There is a variety of effects on how and when the melody tones are performed. They are called legato when they are p ...
REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM 7th Grade General Music Major Scales - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ...
... REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM 7th Grade General Music Major Scales - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ...
Geometry of Harmony and Modes in Vaughan Williams` Romanza
... fugal combination of melodies played by the flutes, an oboe, clarinets in A, and English horn. These melodies are all in the E-Phrygian mode—due to emphasized starting notes of E and highest pitch notes of E. At measure 39, a very brief modal ambiguity occurs. This is where the harmony described in ...
... fugal combination of melodies played by the flutes, an oboe, clarinets in A, and English horn. These melodies are all in the E-Phrygian mode—due to emphasized starting notes of E and highest pitch notes of E. At measure 39, a very brief modal ambiguity occurs. This is where the harmony described in ...
File
... How long a note should be played/held. Note Values: see handout Silence also has value; a period of silence in music is called a REST. • Rests also have the same value as notes (whole, half, quarter, eighth, sixteenth, etc.) ...
... How long a note should be played/held. Note Values: see handout Silence also has value; a period of silence in music is called a REST. • Rests also have the same value as notes (whole, half, quarter, eighth, sixteenth, etc.) ...
MusicTheory Crossword - Music Express Magazine
... 1. How many lines are in a music sta ? [five] 2. Distance between two bar lines. [measure] 3. A special, separate ending. [Coda] 4. The line that connects two eighth notes. [beam] 6. The ________ signature shows us the meter of a piece. [time] 10. Major or minor [scale] 11. The term for performing a ...
... 1. How many lines are in a music sta ? [five] 2. Distance between two bar lines. [measure] 3. A special, separate ending. [Coda] 4. The line that connects two eighth notes. [beam] 6. The ________ signature shows us the meter of a piece. [time] 10. Major or minor [scale] 11. The term for performing a ...
Playing the Piano
... between two tones played at the same time. There are several ways of classifying them. One of them is known as a major interval, and it is determined by measuring a major second, third, sixth or seventh, by matching the second, third, sixth, or seventh notes on the major scale, and counting half st ...
... between two tones played at the same time. There are several ways of classifying them. One of them is known as a major interval, and it is determined by measuring a major second, third, sixth or seventh, by matching the second, third, sixth, or seventh notes on the major scale, and counting half st ...
FIGURED BASS Figured bass symbols indicate intervals above the
... of thorough bass: composers wrote bass line and figures. The part was played by the cello player and the keyboard (continuo) player who realized the chords, filling in the harmonies. RULES: 1. Figures (the arabic numbers below the bass note) tell the intervals above the bass note. ...
... of thorough bass: composers wrote bass line and figures. The part was played by the cello player and the keyboard (continuo) player who realized the chords, filling in the harmonies. RULES: 1. Figures (the arabic numbers below the bass note) tell the intervals above the bass note. ...
Lesson_LLL_-_Mixture..
... degrees 3, 6, and 7, so it is at these points that mixture will occur. In both major and minor keys, chords borrowed from the parallel key can intensify the drama of a musical texture. Some instances of mixture can be seen as a result of strengthening the basic interval progressions governing the vo ...
... degrees 3, 6, and 7, so it is at these points that mixture will occur. In both major and minor keys, chords borrowed from the parallel key can intensify the drama of a musical texture. Some instances of mixture can be seen as a result of strengthening the basic interval progressions governing the vo ...
Paige Studlack Malone Middle School Ms
... second) labeled in Hertz. When you hear different, overlapping notes that sound good together, it is because their frequencies are consonant and the sound waves meet and cross at regular intervals. This produces a pleasing sound (harmony). For example, a piano's middle C's second wave and the 3rd wa ...
... second) labeled in Hertz. When you hear different, overlapping notes that sound good together, it is because their frequencies are consonant and the sound waves meet and cross at regular intervals. This produces a pleasing sound (harmony). For example, a piano's middle C's second wave and the 3rd wa ...
1 VIRGIN MUSIC (By Peter L.P. Simpson) Post Modernism Among
... If the rishi's notes had been subjected to this music from Bach, they would now all be dead and a great deal of retuning and replaying would be needed to revive them. I will take these notes of the rishi as representative of what I shall call virgin music, not only because these notes are personifie ...
... If the rishi's notes had been subjected to this music from Bach, they would now all be dead and a great deal of retuning and replaying would be needed to revive them. I will take these notes of the rishi as representative of what I shall call virgin music, not only because these notes are personifie ...
Music Vocabulary - Phoenix Symphony
... Tempo. The pace at which music moves according to the speed of the underlying beat. Ternary. A musical form consisting of three main sections. Texture. The character of the different layers of horizontal and vertical sounds. Theme and variation. A compositional form in which a theme is clearly state ...
... Tempo. The pace at which music moves according to the speed of the underlying beat. Ternary. A musical form consisting of three main sections. Texture. The character of the different layers of horizontal and vertical sounds. Theme and variation. A compositional form in which a theme is clearly state ...
Mathematical Properties of the Melodic M[...]
... searching the Lydian Dominant or 4th mode of the melodic minor uncovered a wealth of information. This mode of the scale (a dominant 7th scale with a raised 4th, so giving a feeling of excitement and tension) was used exensively by 19th century composers such as Liszt, Debussy, Stravinsky and Bartok ...
... searching the Lydian Dominant or 4th mode of the melodic minor uncovered a wealth of information. This mode of the scale (a dominant 7th scale with a raised 4th, so giving a feeling of excitement and tension) was used exensively by 19th century composers such as Liszt, Debussy, Stravinsky and Bartok ...
2015 Chorus Midterm Review Sheet
... and a rhythmic pattern. Two or more melodies sounding together is called counterpoint. b. harmony – the simultaneous sounding of tones “vertically,” as opposed to melody, which is “horizontal.” c. rhythm – a pattern of sounds conforming to a regularity of pulses or beats. The pattern is created by a ...
... and a rhythmic pattern. Two or more melodies sounding together is called counterpoint. b. harmony – the simultaneous sounding of tones “vertically,” as opposed to melody, which is “horizontal.” c. rhythm – a pattern of sounds conforming to a regularity of pulses or beats. The pattern is created by a ...
Name of general study
... Musical feature 1: Melody (Use of Intervals – Long & Short) • B. Jaws • A much smaller interval used • Bass part repeats the interval of a semitone (half-step) between notes. • Incredibly small in comparison but is still very effective & memorable to the listener. ...
... Musical feature 1: Melody (Use of Intervals – Long & Short) • B. Jaws • A much smaller interval used • Bass part repeats the interval of a semitone (half-step) between notes. • Incredibly small in comparison but is still very effective & memorable to the listener. ...
Why is Music Healing?
... In the first experiments they mounted a camera on top of the microscope to photograph the inside structure of each cell as it reacted to the different sounds they produced. In the second group of experiments they used Kirlian photography in order to record the changes in the electromagnetic field of ...
... In the first experiments they mounted a camera on top of the microscope to photograph the inside structure of each cell as it reacted to the different sounds they produced. In the second group of experiments they used Kirlian photography in order to record the changes in the electromagnetic field of ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 1 Elements of Pitch
... A harmonic interval results when the notes are performed at the same time A melodic interval occurs when the notes are played successively The method of measuring for both type of intervals are the same Two parts to any interval name: o Numerical name: how far apart regardless of what accide ...
... A harmonic interval results when the notes are performed at the same time A melodic interval occurs when the notes are played successively The method of measuring for both type of intervals are the same Two parts to any interval name: o Numerical name: how far apart regardless of what accide ...
Int 2 concept booklet
... before major & minor keys were developed a change from minor to major key with the same key signature ...
... before major & minor keys were developed a change from minor to major key with the same key signature ...
Notes for Class 3 - Midcoast Senior College
... concentrated listening by a knowledgeable elite. In fact, it may be intentionally “difficult” (to perform AND to hear). The above traits could be said to characterize Beethoven (!), or Beethoven’s 19th century followers Schubert, Schumann, Brahms, Wagner, Liszt, etc. The Post-Wagnerians, in fact, ex ...
... concentrated listening by a knowledgeable elite. In fact, it may be intentionally “difficult” (to perform AND to hear). The above traits could be said to characterize Beethoven (!), or Beethoven’s 19th century followers Schubert, Schumann, Brahms, Wagner, Liszt, etc. The Post-Wagnerians, in fact, ex ...
2 Chants Ancient Roo.. - Paul Ayick Vintage Brass
... between divisions of a vibrating string and sound intervals define the very musical divisions we use to this day. “These were discovered by means of the monochord. The monochord, as the name implies, is a one-stringed instrument. By stopping the string at one point, plucking it, then stopping it at ...
... between divisions of a vibrating string and sound intervals define the very musical divisions we use to this day. “These were discovered by means of the monochord. The monochord, as the name implies, is a one-stringed instrument. By stopping the string at one point, plucking it, then stopping it at ...
Absolute music. Music that makes no intentional reference to a non
... renowned collection of canons is contained in J.S. Bach's Musical Offering. "Row, Row, your Boat" is a familiar example of a simple canon. Cantabile. [kahn-tah-bee-lay] (Italian) "Singing" Music performed in a singing style. The term can be added to a tempo marking (andante cantabile, for example) o ...
... renowned collection of canons is contained in J.S. Bach's Musical Offering. "Row, Row, your Boat" is a familiar example of a simple canon. Cantabile. [kahn-tah-bee-lay] (Italian) "Singing" Music performed in a singing style. The term can be added to a tempo marking (andante cantabile, for example) o ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.













![Mathematical Properties of the Melodic M[...]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010878245_1-bf479fc29436337f034bfd616c268c91-300x300.png)








