Powerpoint
... the Baroque, were much less commonly used later Continuous movement in short note values without ‘periodic phrasing’ (i.e. without clearly-articulated two- and four-bar phrases) Fugal writing in parts of the Gigue – although similar contrapuntal styles were used before the Baroque period and were ne ...
... the Baroque, were much less commonly used later Continuous movement in short note values without ‘periodic phrasing’ (i.e. without clearly-articulated two- and four-bar phrases) Fugal writing in parts of the Gigue – although similar contrapuntal styles were used before the Baroque period and were ne ...
Texture and Melody
... any harmonies, although it may be played by more than one instrument or voice ...
... any harmonies, although it may be played by more than one instrument or voice ...
MUSICAL ACOUSTICS Tutorial 2: Solution Guide
... the square of the distance from the source. What does “isotropic” mean? If you stand 3 m from a bagpipe player on a flat moor and measure a Sound Pressure Level of 90 dB, what SPL will you measure at a distance of (a) 30 m; (b) 300 m? An isotropic sound source is one which radiates sound with equal ...
... the square of the distance from the source. What does “isotropic” mean? If you stand 3 m from a bagpipe player on a flat moor and measure a Sound Pressure Level of 90 dB, what SPL will you measure at a distance of (a) 30 m; (b) 300 m? An isotropic sound source is one which radiates sound with equal ...
Chpt. 3: 節奏Rhythm Flow of music (events) through time
... sounded at once • 和絃是一群同時發出聲響的音Chord is simultaneous tones • 旋律是一連串先後有致的單音Melody is series of individual tones • Progression: how chords follow each other 和諧與不和諧音Consonance and Dissonance • 數個音的組合穩定平和Stable, restful chords—consonant ...
... sounded at once • 和絃是一群同時發出聲響的音Chord is simultaneous tones • 旋律是一連串先後有致的單音Melody is series of individual tones • Progression: how chords follow each other 和諧與不和諧音Consonance and Dissonance • 數個音的組合穩定平和Stable, restful chords—consonant ...
No 6: Tonality
... dangerous and ensnaring. In the Renaissance and Baroque (1600– 1750), the Ionian mode became known as major and has continued to be popular today. The Aeolian mode was called natural minor and changed into harmonic minor by sharpening the seventh note, and this is still common today. For several hun ...
... dangerous and ensnaring. In the Renaissance and Baroque (1600– 1750), the Ionian mode became known as major and has continued to be popular today. The Aeolian mode was called natural minor and changed into harmonic minor by sharpening the seventh note, and this is still common today. For several hun ...
Notes - Stanford University
... frequency of the wave, measured in Hertz (Hz). For waves moving at the same speed, a longer wavelength implies a longer time for a single repetition of the pattern to move across any given point, and hence it implies a lower frequency. Indeed, we have the relationship frequency × wavelength = speed ...
... frequency of the wave, measured in Hertz (Hz). For waves moving at the same speed, a longer wavelength implies a longer time for a single repetition of the pattern to move across any given point, and hence it implies a lower frequency. Indeed, we have the relationship frequency × wavelength = speed ...
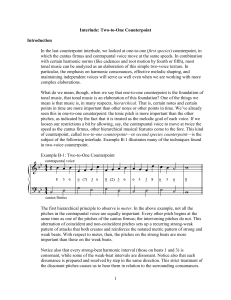
1 Interlude: Two-to-One Counterpoint Introduction In the last
... Interlude: Two-to-One Counterpoint Introduction In the last counterpoint interlude, we looked at one-to-one (first species) counterpoint, in which the cantus firmus and contrapuntal voice move at the same speeds. In combination with certain harmonic norms (like cadences and root motion by fourth or ...
... Interlude: Two-to-One Counterpoint Introduction In the last counterpoint interlude, we looked at one-to-one (first species) counterpoint, in which the cantus firmus and contrapuntal voice move at the same speeds. In combination with certain harmonic norms (like cadences and root motion by fourth or ...
standard music notation practice
... fast new processes for note-setting, this study was prepared by the Production Committee of the Music Publishers’ Association. It was evaluated by the editors of the majority of the members and represents o reasonable consensus, although it must be said that there was not unanimous agreement on some ...
... fast new processes for note-setting, this study was prepared by the Production Committee of the Music Publishers’ Association. It was evaluated by the editors of the majority of the members and represents o reasonable consensus, although it must be said that there was not unanimous agreement on some ...
Lesson_QQQ_-_Advance..
... Roman numerals are a useful, shorthand way of naming and analyzing chords, and of showing their relationships to a tonic. Conventional Roman numerals are adjusted to indicate chromaticism when harmonic practice becomes more advanced. Being able to recognize and use such adjustments is essential for ...
... Roman numerals are a useful, shorthand way of naming and analyzing chords, and of showing their relationships to a tonic. Conventional Roman numerals are adjusted to indicate chromaticism when harmonic practice becomes more advanced. Being able to recognize and use such adjustments is essential for ...
Elements of Music
... b. Tones in a melody may repeat or change. c. When tones in a melody change they may go up or down in a regular succession of half steps, whole steps, or leaps. 2. Musical notation is a set of visual symbols that show the relationships that can exist among tones. 3. The movement of a melody is not o ...
... b. Tones in a melody may repeat or change. c. When tones in a melody change they may go up or down in a regular succession of half steps, whole steps, or leaps. 2. Musical notation is a set of visual symbols that show the relationships that can exist among tones. 3. The movement of a melody is not o ...
C - WordPress.com
... Do the same with the Ionian mode and move throughout all the keys. Know the names of all notes as you play them. Know the relationship each note has with the root you are playing over. In the Ionian mode you would have these relationships ...
... Do the same with the Ionian mode and move throughout all the keys. Know the names of all notes as you play them. Know the relationship each note has with the root you are playing over. In the Ionian mode you would have these relationships ...
ANP_Paper3_MathofMusic
... Notes with the symbol “#” are called “sharp” while notes with the symbol “b” are called “flat”. A# and Bb have the same frequency, as do the other notes with two different names. (1) There are many different types of twelve-tone temperaments, or methods by which an octave can be split into twelve no ...
... Notes with the symbol “#” are called “sharp” while notes with the symbol “b” are called “flat”. A# and Bb have the same frequency, as do the other notes with two different names. (1) There are many different types of twelve-tone temperaments, or methods by which an octave can be split into twelve no ...
Music 231 Second Species Counterpoint, Two Parts
... B. The two half notes create a strong beat (first) and a weak beat (second) II. Uses of the second half note A. Passing tone 1. Moves stepwise in the same direction between two consonant verticals 2. May be consonant (CPT) or dissonant (DPT) B. Neighbor (auxiliary) tone 1. Moves stepwise away from a ...
... B. The two half notes create a strong beat (first) and a weak beat (second) II. Uses of the second half note A. Passing tone 1. Moves stepwise in the same direction between two consonant verticals 2. May be consonant (CPT) or dissonant (DPT) B. Neighbor (auxiliary) tone 1. Moves stepwise away from a ...
The demise of number ratios in music theory
... and just) that lie within a continuous range of acceptable tunings, so neither is “correct”. Ratios only make psychological sense if the numbers correspond to audible harmonics in complex tones (8:9 is ok but 64:81 is misleading). In fact, musical intervals are approximate psychological distances on ...
... and just) that lie within a continuous range of acceptable tunings, so neither is “correct”. Ratios only make psychological sense if the numbers correspond to audible harmonics in complex tones (8:9 is ok but 64:81 is misleading). In fact, musical intervals are approximate psychological distances on ...
CADENCES AND PHRASES
... A musical paragraph is called a period. A period is a collection of phrases with the last phrase having the strongest (most conclusive) authentic cadence. Like the “bite-sized” notion behind cadences and phrases, the organization of a period helps to serve the larger sense of direction in music. By ...
... A musical paragraph is called a period. A period is a collection of phrases with the last phrase having the strongest (most conclusive) authentic cadence. Like the “bite-sized” notion behind cadences and phrases, the organization of a period helps to serve the larger sense of direction in music. By ...
isomorphic tessellations for musical keyboards
... of harmonies that can be achieved through any number of discrete tones. In music theory, there are several harmonic combinations that are found in the music of all ages. These are the octave, the dominant triad, and the dominant seventh. The octave is an interval between two musical notes where one ...
... of harmonies that can be achieved through any number of discrete tones. In music theory, there are several harmonic combinations that are found in the music of all ages. These are the octave, the dominant triad, and the dominant seventh. The octave is an interval between two musical notes where one ...
playing the organ works of mendelssohn
... the last measure, right hand builds up a five-note chord; I can see only one real solution for this. ...
... the last measure, right hand builds up a five-note chord; I can see only one real solution for this. ...
Bringing some science to music
... one hears the “chromatic” scale. Each tone is separated by a “semitione” Also “half tone” or “half step”. ...
... one hears the “chromatic” scale. Each tone is separated by a “semitione” Also “half tone” or “half step”. ...
Analysis of ``Kol Nidrei
... Jewish descent. The first theme is featured in the opening melody and throughout the D minor section of the piece. It is based on the Kol Nidre prayer, which is an old Hebrew prayer of atonement that is recited on the Jewish holiday of Yom Kippur. The melody of this theme is meant to imitate the voi ...
... Jewish descent. The first theme is featured in the opening melody and throughout the D minor section of the piece. It is based on the Kol Nidre prayer, which is an old Hebrew prayer of atonement that is recited on the Jewish holiday of Yom Kippur. The melody of this theme is meant to imitate the voi ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.