Sample Grade 1 Theory Paper
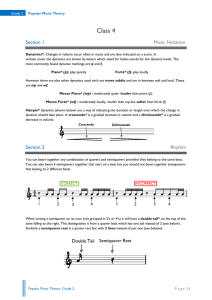
... 6.2 Write a chord symbol above the last note of this piece to show that the tonic triad should accompany it. 6.3 The rest in bar 4 lasts for how many crotchet beats? ...
... 6.2 Write a chord symbol above the last note of this piece to show that the tonic triad should accompany it. 6.3 The rest in bar 4 lasts for how many crotchet beats? ...
Popular Music Theory - The Academy Of Popular Music
... What bar or bars contain a crescendo?______________________________________________ Which bar is played loudly throughout?_____________________________________________ Which bar contains a diminuendo*?________________________________________________ Which bar is the quietest?________________________ ...
... What bar or bars contain a crescendo?______________________________________________ Which bar is played loudly throughout?_____________________________________________ Which bar contains a diminuendo*?________________________________________________ Which bar is the quietest?________________________ ...
File
... Rhythm: Rhythm is everywhere. If you hear basketball being dribbled, raindrops falling, or hands clapping there is a rhythm. Rhythm that makes music move and flow. Found in this website: http://www.sfskids.org/templates/musicLabF.asp?pageid=12 Tempo: Tempo is the speed of the music. Tempo can be fas ...
... Rhythm: Rhythm is everywhere. If you hear basketball being dribbled, raindrops falling, or hands clapping there is a rhythm. Rhythm that makes music move and flow. Found in this website: http://www.sfskids.org/templates/musicLabF.asp?pageid=12 Tempo: Tempo is the speed of the music. Tempo can be fas ...
DeiszPresentationQ2
... Creates an array of size that was input Follows the chord progression map for a major key to fill up the entire array with random new chords ...
... Creates an array of size that was input Follows the chord progression map for a major key to fill up the entire array with random new chords ...
Sample Grade 1 Theory Paper
... 6.2 Write a chord symbol above the last note of this piece to show that the tonic triad should accompany it. 6.3 The rest in bar 4 lasts for how many crotchet beats? ...
... 6.2 Write a chord symbol above the last note of this piece to show that the tonic triad should accompany it. 6.3 The rest in bar 4 lasts for how many crotchet beats? ...
AP Music Syllabus
... Sueta. Echo, then copy down short phrases in simple and compound meters! Go over quizzes. Introduce intervals - quantity and quality. Quiz/test strategies: what you should have in your head, and be able to write down: circle of 5ths, order of sharps/flats, be able to draw a piano keyboard and use it ...
... Sueta. Echo, then copy down short phrases in simple and compound meters! Go over quizzes. Introduce intervals - quantity and quality. Quiz/test strategies: what you should have in your head, and be able to write down: circle of 5ths, order of sharps/flats, be able to draw a piano keyboard and use it ...
notes and scales
... The keyboard is a good help to see the distance between notes. The smallest distance between keys is one semitone. So, between the white keys of C (do) and D (re) you have one tone because you have another key between both keys. This black key is the sharp C or flat D (therefore, you could call one ...
... The keyboard is a good help to see the distance between notes. The smallest distance between keys is one semitone. So, between the white keys of C (do) and D (re) you have one tone because you have another key between both keys. This black key is the sharp C or flat D (therefore, you could call one ...
Program Notes - Michael Harrison, composer and pianist
... Instead of avoiding them, Michael Harrison incorporates into his music the clashes that occur when completely pure (or "just") intervals are allowed to coexist in a piano’s tuning. In some ways, his vision represents the flip side of Arnold Schoenberg’s. Schoenberg broke down conventional harmonic m ...
... Instead of avoiding them, Michael Harrison incorporates into his music the clashes that occur when completely pure (or "just") intervals are allowed to coexist in a piano’s tuning. In some ways, his vision represents the flip side of Arnold Schoenberg’s. Schoenberg broke down conventional harmonic m ...
Document
... Since the Baroque period harmony had been progressing and became more and more complex. In the late Romantic period composers such as Wagner, Bruckner and Strauss (Richard) were using more chromatic notes and more dissonant chords. In France composers such as Debussy (1862-1918) were part of a new w ...
... Since the Baroque period harmony had been progressing and became more and more complex. In the late Romantic period composers such as Wagner, Bruckner and Strauss (Richard) were using more chromatic notes and more dissonant chords. In France composers such as Debussy (1862-1918) were part of a new w ...
Slides
... →C8 (8433.5 Hz) → (go down 7 octaves) →C1 (65.8868 Hz) Wait a minute!!!! The frequency (pitch) is high by a factor of ...
... →C8 (8433.5 Hz) → (go down 7 octaves) →C1 (65.8868 Hz) Wait a minute!!!! The frequency (pitch) is high by a factor of ...
Musical Elements - eddleman1301wc03
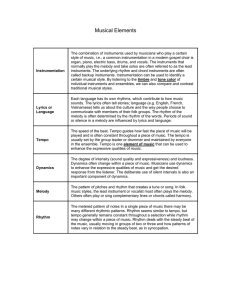
... The degree of intensity (sound quality and expressiveness) and loudness. Dynamics often change within a piece of music. Musicians use dynamics to enhance the expressive qualities of music and get the desired response from the listener. The deliberate use of silent intervals is also an important comp ...
... The degree of intensity (sound quality and expressiveness) and loudness. Dynamics often change within a piece of music. Musicians use dynamics to enhance the expressive qualities of music and get the desired response from the listener. The deliberate use of silent intervals is also an important comp ...
Prolongation of Seventh Chords in Tonal Music, by Yosef Goldenberg
... the problematic status of the intervallic step between the chordal seventh and root, contravening triadic tonality’s clear systemic distinction between the roles of steps (voice leading) and skips/leaps (arpeggiation). Schenker’s normative view, of course, was that the seventh chord is not an indepe ...
... the problematic status of the intervallic step between the chordal seventh and root, contravening triadic tonality’s clear systemic distinction between the roles of steps (voice leading) and skips/leaps (arpeggiation). Schenker’s normative view, of course, was that the seventh chord is not an indepe ...
Modal Jazz - Jonathan Dimond
... Classic modal jazz compositions contain very few chords, allowing each individual mode to be used for a long period of time. An example of this is “So What” by Miles Davis, from the album Kind of Blue (1959). This only uses two chords during its 32 measure duration – Dm and Ebm. Due to the repetitio ...
... Classic modal jazz compositions contain very few chords, allowing each individual mode to be used for a long period of time. An example of this is “So What” by Miles Davis, from the album Kind of Blue (1959). This only uses two chords during its 32 measure duration – Dm and Ebm. Due to the repetitio ...
Lecture 6
... notes making up the song’s melody, chords, and bassline are all derived from that group of notes. Similarly, a piece of music can be in a minor key and revolve around a natural minor scale. For example, a song in the ‘key of D minor’ uses the notes of the D minor scale – D, E, F, G, A, Bb, and C. ...
... notes making up the song’s melody, chords, and bassline are all derived from that group of notes. Similarly, a piece of music can be in a minor key and revolve around a natural minor scale. For example, a song in the ‘key of D minor’ uses the notes of the D minor scale – D, E, F, G, A, Bb, and C. ...
PPT
... Publication we are going to study: •The Local Boundary Detection Model (LBDM) and its Application in the Study of ...
... Publication we are going to study: •The Local Boundary Detection Model (LBDM) and its Application in the Study of ...
history of barbershop
... This is also the first overtone, and the first harmony (polyphony) the Gregorians began to sing. They probably decided to sing it because they heard the overtone. The next most natural intervals are the perfect fifth, which is the ratio 3:2, and the perfect fourth, with ratio 4:3. These were the nex ...
... This is also the first overtone, and the first harmony (polyphony) the Gregorians began to sing. They probably decided to sing it because they heard the overtone. The next most natural intervals are the perfect fifth, which is the ratio 3:2, and the perfect fourth, with ratio 4:3. These were the nex ...
Powerpoint
... slower tempo and was an early form of reggae. The word ‘reggae’ is probably derived from patois for a ‘regular’ beat. The three styles share some principal characteristics: Heavy, repetitive chord rhythms on the second half of the beat. The guitar often uses a heavy downward ‘chop’ stroke, immedia ...
... slower tempo and was an early form of reggae. The word ‘reggae’ is probably derived from patois for a ‘regular’ beat. The three styles share some principal characteristics: Heavy, repetitive chord rhythms on the second half of the beat. The guitar often uses a heavy downward ‘chop’ stroke, immedia ...
View printable PDF of 6.3 Analyzing Diatonic Modes
... STEP 3: Because there are seven notes (don't count E twice), and because the accidentals fit a diatonic key signature for three sharps (F#, C#, and G#), this is a diatonic mode (see 6.2 The Diatonic Modes). When analyzing diatonic modes, find the answer using a relative OR parallel approach (NOT bot ...
... STEP 3: Because there are seven notes (don't count E twice), and because the accidentals fit a diatonic key signature for three sharps (F#, C#, and G#), this is a diatonic mode (see 6.2 The Diatonic Modes). When analyzing diatonic modes, find the answer using a relative OR parallel approach (NOT bot ...
Harmonic Techniques in Maurice Ravel`s Opera L
... While this research has been incredibly fruitful, the desire to uncover more about this mysterious individual may distract us from a rigorous analysis of his ingenious music itself. Undoubtedly, Ravel led a secretive and solitary life, and much is left to unearth about this unusual composer. Ravel i ...
... While this research has been incredibly fruitful, the desire to uncover more about this mysterious individual may distract us from a rigorous analysis of his ingenious music itself. Undoubtedly, Ravel led a secretive and solitary life, and much is left to unearth about this unusual composer. Ravel i ...
Musical Terms and Concepts
... modified strophic: simply means that the repetitions of the sections are varied slightly, but not so much that they are a significant variation or the original. bar form: two sections of music, with only the first section A repeated. Many hymns use the far form. binary form: two sections of music, u ...
... modified strophic: simply means that the repetitions of the sections are varied slightly, but not so much that they are a significant variation or the original. bar form: two sections of music, with only the first section A repeated. Many hymns use the far form. binary form: two sections of music, u ...
NGFL_Shost_movt_4_analysis
... 2nd and the 4th beats). TEXTURE: Apart from the A# pedal note held low in violin 1 which lasts here for 21 bars, the chords are a key feature –but also significant is the unison playing by the lower three parts of the triadic motif from the cello concerto. THEMES: Theme a is heard in the lower 3 par ...
... 2nd and the 4th beats). TEXTURE: Apart from the A# pedal note held low in violin 1 which lasts here for 21 bars, the chords are a key feature –but also significant is the unison playing by the lower three parts of the triadic motif from the cello concerto. THEMES: Theme a is heard in the lower 3 par ...
Pythagoras and His Vibrating Strings
... the 12 notes of the chromatic scale. Also, we do not use a pure fifth causing it to be slightly out of tune. This difference is not detectable by the untrained ear. If we were to tune using the pure fifth as Pythagoras did, notes that we today know to sound the same, such as, G# and Ab, would not s ...
... the 12 notes of the chromatic scale. Also, we do not use a pure fifth causing it to be slightly out of tune. This difference is not detectable by the untrained ear. If we were to tune using the pure fifth as Pythagoras did, notes that we today know to sound the same, such as, G# and Ab, would not s ...
A Mathematical and Musical Analogy in Microtonal Systems
... means of organizing pitch relationships. “The basic principle of the keyboard is that any key that is twelve half steps [the interval between any two adjacent keys] above another key produces a pitch whose frequency is exactly double that of the lower key. To the ear, these two sounds seem related, ...
... means of organizing pitch relationships. “The basic principle of the keyboard is that any key that is twelve half steps [the interval between any two adjacent keys] above another key produces a pitch whose frequency is exactly double that of the lower key. To the ear, these two sounds seem related, ...
The Syntax of Music
... • Scale: 7 tones (scale degrees) per octave with an asymmetric pa^ern of pitch spacing (intervals) between them. • The different tones take on different roles in the fabric of music, with one tone ...
... • Scale: 7 tones (scale degrees) per octave with an asymmetric pa^ern of pitch spacing (intervals) between them. • The different tones take on different roles in the fabric of music, with one tone ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.