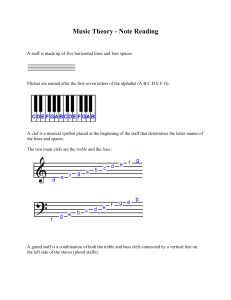
Study Guide for Music 1000 1 Music Organization of Sound and
... o Text is the mistress of music o The mistress of music is the text o Creation of musical instruments o Dance o Fugue: Music a contrapuntal composition in which a short melody or phrase (the subject) is introduced by one part and successively taken up by others and developed by interweaving the part ...
... o Text is the mistress of music o The mistress of music is the text o Creation of musical instruments o Dance o Fugue: Music a contrapuntal composition in which a short melody or phrase (the subject) is introduced by one part and successively taken up by others and developed by interweaving the part ...
Scales
... as time. The meter or time signature in a musical composition is indicated by a fraction, and located at the beginning of a piece of music. The lower number of the fraction tells what kind of note receives one beat. The upper number tells how many beats are in a measure. In Western music there are t ...
... as time. The meter or time signature in a musical composition is indicated by a fraction, and located at the beginning of a piece of music. The lower number of the fraction tells what kind of note receives one beat. The upper number tells how many beats are in a measure. In Western music there are t ...
A PRACTICAL GLOSSARY for Twentieth
... or during the performance. Examples include rolling dice to determine pitches or instructing a performer to play three melodic figures in any order. The term is closely associated with John Cage, but many composers have included a degree of aleatory in their music. all-combinatorial row — a row that ...
... or during the performance. Examples include rolling dice to determine pitches or instructing a performer to play three melodic figures in any order. The term is closely associated with John Cage, but many composers have included a degree of aleatory in their music. all-combinatorial row — a row that ...
lesson 1 - john p birchall
... White note scales, without sharps or flats, starting on notes other than C are called MODES and because they have the semitone steps In DIFFERENT PLACES their characteristic sound is different. These modes all have Greek names and were used extensively in early period music to create a variety of d ...
... White note scales, without sharps or flats, starting on notes other than C are called MODES and because they have the semitone steps In DIFFERENT PLACES their characteristic sound is different. These modes all have Greek names and were used extensively in early period music to create a variety of d ...
ap® music theory 2013 scoring guidelines
... II. Chord Symbols (8 points) A. Award 1 point for each chord symbol correct in both Roman and Arabic numerals. B. Award ½ point for each correct Roman numeral that has incorrect or missing Arabic numerals. C. Accept the correct Roman numeral regardless of its case. D. Accept “ii” (or “II”) as a corr ...
... II. Chord Symbols (8 points) A. Award 1 point for each chord symbol correct in both Roman and Arabic numerals. B. Award ½ point for each correct Roman numeral that has incorrect or missing Arabic numerals. C. Accept the correct Roman numeral regardless of its case. D. Accept “ii” (or “II”) as a corr ...
Key Terms and Definitions a cappella Vocal singing that involves no
... regulated by the speed of the beat or pulse to ...
... regulated by the speed of the beat or pulse to ...
Intonation, Tuning, and Blending
... ◦ Also known as Resonance or Ghost Tones ◦ The faint presence of a tone whose frequency is equal to the difference between the frequencies of the two notes actually being played. Usually an octave or two lower. ◦ The pitches being played must be adjusted so the fundamental sounds in tune. Trio for ...
... ◦ Also known as Resonance or Ghost Tones ◦ The faint presence of a tone whose frequency is equal to the difference between the frequencies of the two notes actually being played. Usually an octave or two lower. ◦ The pitches being played must be adjusted so the fundamental sounds in tune. Trio for ...
MTO 18.2: Sly, Review of Damschroder
... [9] The apposition of Damschroder’s and Beach’s readings of the opening movement of the “Trout” Quintet is particularly engaging, in part because the main issue of contention—the movement’s subdominant recapitulation—is so closely circumscribed. For Beach 1993, the central issue is how this harmony ...
... [9] The apposition of Damschroder’s and Beach’s readings of the opening movement of the “Trout” Quintet is particularly engaging, in part because the main issue of contention—the movement’s subdominant recapitulation—is so closely circumscribed. For Beach 1993, the central issue is how this harmony ...
Name: Motina Barracks Course: Music 101 Report Summary A scale
... Name: Motina Barracks Course: Music 101 Report Summary A scale is a group of eight note which is arrange in a particular order. Every Major scale has eight tones which is called an octave. The numbers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 are called degrees. While the musical alphabet is A B C D E FG and the first and ei ...
... Name: Motina Barracks Course: Music 101 Report Summary A scale is a group of eight note which is arrange in a particular order. Every Major scale has eight tones which is called an octave. The numbers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 are called degrees. While the musical alphabet is A B C D E FG and the first and ei ...
Chapter Five: Baroque Art and Music
... • Two elements remain constant – Expressive, sometimes extravagant melody – Strong supporting bass ...
... • Two elements remain constant – Expressive, sometimes extravagant melody – Strong supporting bass ...
General Principles of Harmony by Alan Belkin
... surface contrast. Except in the case where the two are placed side by side for comparison or otherwise "pointed out" to the listener, the pitch similarity between them is thus relatively unimportant. Note that to make the listener's job easier I have used the same pitch classes. Imagine if I had als ...
... surface contrast. Except in the case where the two are placed side by side for comparison or otherwise "pointed out" to the listener, the pitch similarity between them is thus relatively unimportant. Note that to make the listener's job easier I have used the same pitch classes. Imagine if I had als ...
Music Theory Unplugged Functional Harmony
... the original tonic chord CMa7 in fact the upper three notes ‘E’, ‘G’, ‘B’. The chord built on the sixth degree Am7 also contains three of the four notes found in the original tonic chord CMa7, this time the three lower notes ‘C’, ‘E’, ‘G’ actually the ‘C’ Major Triad. What this means is that these t ...
... the original tonic chord CMa7 in fact the upper three notes ‘E’, ‘G’, ‘B’. The chord built on the sixth degree Am7 also contains three of the four notes found in the original tonic chord CMa7, this time the three lower notes ‘C’, ‘E’, ‘G’ actually the ‘C’ Major Triad. What this means is that these t ...
Benward Chapter 3
... Always placed after the name of the note – example, F# Sharp – raises a pitch by a half step Flat – lowers a pitch by a half step Double Flat – lowers a pitch by two half steps Double Sharp – raises a pitch by two half steps Natural – cancels the preceding accidental for the same pitch. ...
... Always placed after the name of the note – example, F# Sharp – raises a pitch by a half step Flat – lowers a pitch by a half step Double Flat – lowers a pitch by two half steps Double Sharp – raises a pitch by two half steps Natural – cancels the preceding accidental for the same pitch. ...
Slide 1
... published version. Each measure was studied and a color-coded system was used to note differences in articulation, dynamics, and the notes themselves. This example is in the first movement, measures 37-45. This transition section is leading up to an F major chord, which is V in B-flat major, the key ...
... published version. Each measure was studied and a color-coded system was used to note differences in articulation, dynamics, and the notes themselves. This example is in the first movement, measures 37-45. This transition section is leading up to an F major chord, which is V in B-flat major, the key ...
Antecedent-Consequent Phrases», Part 1
... b7 to 3 resolution Jazz players understand the importance of being able to improvise on the «changes». That is, the ability to effectively delineate chords during a solo improvisation. Chord arpeggiation or change running, as it is sometimes called, is a fundamental technique required from every jaz ...
... b7 to 3 resolution Jazz players understand the importance of being able to improvise on the «changes». That is, the ability to effectively delineate chords during a solo improvisation. Chord arpeggiation or change running, as it is sometimes called, is a fundamental technique required from every jaz ...
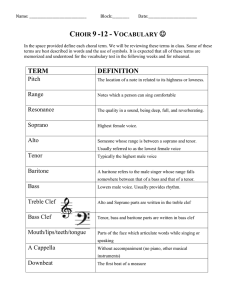
Choir 9 -12 - Vocabulary J - Fleetwoodpark
... Musical improve of a melodic line. Usually done by a soloist or small group. Pop music use this frequently. ...
... Musical improve of a melodic line. Usually done by a soloist or small group. Pop music use this frequently. ...
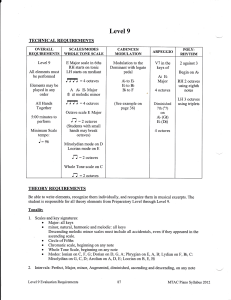
Level 9 - The Music Makers
... Know the four periods of music history in order. Know at least three composers from each period. A list of composers is on pages 161-169. When asked to name a composer from a particular period, students may use any composer's name from that period. The following composers may appear on the test: ...
... Know the four periods of music history in order. Know at least three composers from each period. A list of composers is on pages 161-169. When asked to name a composer from a particular period, students may use any composer's name from that period. The following composers may appear on the test: ...
"Tonal Organization in Schoenberg`s Six Little Piano Pieces, Op. 19"
... piece begins. Here its role is that of a third-less submediant seventh chord functioning as a suggested tonic triad with added sixth. The tonic triad is termed "suggested" because, although the tonic function may be perceived aurally, the root is not present except perhaps via combination tones (Ex. ...
... piece begins. Here its role is that of a third-less submediant seventh chord functioning as a suggested tonic triad with added sixth. The tonic triad is termed "suggested" because, although the tonic function may be perceived aurally, the root is not present except perhaps via combination tones (Ex. ...
Blues basics, Style basics the musical background of rock
... iii. Called a tonic pitch iv. Tonic pitch first note of scale upon which piece is built – E. Harmony 1. Sounds that provide support for a melody a. Melody = horizontal aspect of music b. Harmony = vertical aspect 2. Can also think of as simultaneous combination of notes – relationships of intervals ...
... iii. Called a tonic pitch iv. Tonic pitch first note of scale upon which piece is built – E. Harmony 1. Sounds that provide support for a melody a. Melody = horizontal aspect of music b. Harmony = vertical aspect 2. Can also think of as simultaneous combination of notes – relationships of intervals ...
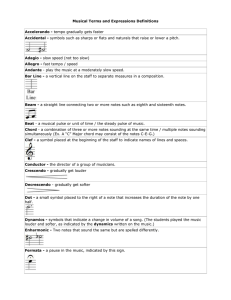
Musical Terms and Expressions Definitions
... Pizzicato - pluck strings instead of bowing Presto - very fast tempo or speed Recorder - an end-blown flute-like instrument that has a whistle mouthpiece, available in soprano, alto, tenor and bass. (The teacher told the students to play the recorder by blowing more softly.) Refrain - the melody of ...
... Pizzicato - pluck strings instead of bowing Presto - very fast tempo or speed Recorder - an end-blown flute-like instrument that has a whistle mouthpiece, available in soprano, alto, tenor and bass. (The teacher told the students to play the recorder by blowing more softly.) Refrain - the melody of ...
The Motown Beat
... about harmony – We hear harmonies from the bass up – I, IV and V are the three basic chords of the blues—and of early rock – The change from one chord to the next creates a rhythm ...
... about harmony – We hear harmonies from the bass up – I, IV and V are the three basic chords of the blues—and of early rock – The change from one chord to the next creates a rhythm ...
Reharmonization as Process in Fauré`s Prelude Op. 103, No. 3
... transposed up by half step. The melody of each pattern combines the top tetrachord of one minor scale with the bottom tetrachord of the minor scale a half step higher; as a result, the melody of each pattern contains seven out of eight notes of an octatonic scale. In the first pattern, for instance, ...
... transposed up by half step. The melody of each pattern combines the top tetrachord of one minor scale with the bottom tetrachord of the minor scale a half step higher; as a result, the melody of each pattern contains seven out of eight notes of an octatonic scale. In the first pattern, for instance, ...
Establishing the Elements of Music Groundwork
... the next cycle then another cycle at a higher range. In reality, there are only 12 unique notes, or pitches. The cycle allows me to introduce the concept of an octave. An octave is defined as and interval that is the distance between one note and itself, either one full cycle up, or a full cycle dow ...
... the next cycle then another cycle at a higher range. In reality, there are only 12 unique notes, or pitches. The cycle allows me to introduce the concept of an octave. An octave is defined as and interval that is the distance between one note and itself, either one full cycle up, or a full cycle dow ...
Establishing the Elements of Music Groundwork
... the next cycle then another cycle at a higher range. In reality, there are only 12 unique notes, or pitches. The cycle allows me to introduce the concept of an octave. An octave is defined as and interval that is the distance between one note and itself, either one full cycle up, or a full cycle dow ...
... the next cycle then another cycle at a higher range. In reality, there are only 12 unique notes, or pitches. The cycle allows me to introduce the concept of an octave. An octave is defined as and interval that is the distance between one note and itself, either one full cycle up, or a full cycle dow ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.