supplementaryMaterial_08Dec15
... piano, beginning on C, form a Major scale (C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C). The scale degrees form a hierarchy of stability (the tonal hierarchy), enabling notes to be used for different structural purposes throughout a musical piece (e.g., highly stable notes are more likely to occur at boundaries than uns ...
... piano, beginning on C, form a Major scale (C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C). The scale degrees form a hierarchy of stability (the tonal hierarchy), enabling notes to be used for different structural purposes throughout a musical piece (e.g., highly stable notes are more likely to occur at boundaries than uns ...
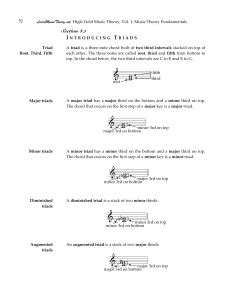
Introducing Triads - LearnMusicTheory.net
... LearnMusicTheory.net High-Yield Music Theory, Vol. 1: Music Theory Fundamentals ...
... LearnMusicTheory.net High-Yield Music Theory, Vol. 1: Music Theory Fundamentals ...
12 the lamb 2015 - My Music Classroom
... points in a set work -To apply improved knowledge of the elements of music to set work studies ...
... points in a set work -To apply improved knowledge of the elements of music to set work studies ...
Lewin, David “A Formal Theory of Generalized Tonal Functions”
... moves as well. A “Relative”-operation then takes you a minor third down from a major chord and a minor third up from a minor chord. The leap of a major third is called a “Leittone-exchange”. From a major chord a “L”-operation takes you a major third up, from a minor chord the “L”-operation takes you ...
... moves as well. A “Relative”-operation then takes you a minor third down from a major chord and a minor third up from a minor chord. The leap of a major third is called a “Leittone-exchange”. From a major chord a “L”-operation takes you a major third up, from a minor chord the “L”-operation takes you ...
Dynamics / louds and softs Fortissimo very loud Forte loud piano soft
... getting gradually slower getting gradually slower broadening out (getting louder and slower) flexible timing a note held for longer than normal ...
... getting gradually slower getting gradually slower broadening out (getting louder and slower) flexible timing a note held for longer than normal ...
HIGH FREQUENCY VOCABULARY WORDS AND DEFINITIONS
... A six-stringed instrument that is either plucked or strummed ; in 4/4 time, receives two beats Two or more pitches sounding at the same time Many-stringed instrument that is plucked in the string family Musical instrument with keys laid out in a row A special stick with a ball on one end to play a ...
... A six-stringed instrument that is either plucked or strummed ; in 4/4 time, receives two beats Two or more pitches sounding at the same time Many-stringed instrument that is plucked in the string family Musical instrument with keys laid out in a row A special stick with a ball on one end to play a ...
INTONATION FOR WINDS
... play much higher to be in tune. Of all the intervals, the minor 3rd needs the most adjustment by the musician in order to play in tune. So, to be in tune, the pitches are dependent on where in the scale they lie – and this will change in the music as the key changes! To make it even more challeng ...
... play much higher to be in tune. Of all the intervals, the minor 3rd needs the most adjustment by the musician in order to play in tune. So, to be in tune, the pitches are dependent on where in the scale they lie – and this will change in the music as the key changes! To make it even more challeng ...
Listening
... • Sequence - A repeating pattern which is transposed (moved up or down) a scale or round a cycle. • Imitation - A musical idea being passed around instruments or instrumental families. • Pedal - A sustained note which can be either either low in the bass, or high in the melody. • Ostinato - A repeat ...
... • Sequence - A repeating pattern which is transposed (moved up or down) a scale or round a cycle. • Imitation - A musical idea being passed around instruments or instrumental families. • Pedal - A sustained note which can be either either low in the bass, or high in the melody. • Ostinato - A repeat ...
Everything You Want to Know About the Music Category
... Barbershop is generally in the major mode with minor sections sometimes used for flavor; minor chords are more challenging for most singers to tune well, so major mode will be a more successful choice. The song should also imply a wide variety of chord progressions with dominant to tonic resolutions ...
... Barbershop is generally in the major mode with minor sections sometimes used for flavor; minor chords are more challenging for most singers to tune well, so major mode will be a more successful choice. The song should also imply a wide variety of chord progressions with dominant to tonic resolutions ...
Minor Pentatonic scale In music, notes are sometimes arranged into
... pattern should be played starting on a G note A minor pentatonic scale that has its root note as a B, would be ‘in the key of B minor’ or a ‘B minor pentatonic scale’ ...
... pattern should be played starting on a G note A minor pentatonic scale that has its root note as a B, would be ‘in the key of B minor’ or a ‘B minor pentatonic scale’ ...
Proficiencies—Piano Student Name: First Last Course Number
... ☐Interval of transposition is correct. Some incorrect notes may sound but flow of progression is not derailed. ☐Chord realization is correct with the occasional error which does not disrupt flow of exercise. ...
... ☐Interval of transposition is correct. Some incorrect notes may sound but flow of progression is not derailed. ☐Chord realization is correct with the occasional error which does not disrupt flow of exercise. ...
Minor Scales
... A scale is a series of notes dividing the octave, repeating each octave across the range of low to high pitches. According to the equal temperament tuning system, octaves are equally divided into twelve notes. A western scale is a series of notes selected among these twelve notes. Each of these note ...
... A scale is a series of notes dividing the octave, repeating each octave across the range of low to high pitches. According to the equal temperament tuning system, octaves are equally divided into twelve notes. A western scale is a series of notes selected among these twelve notes. Each of these note ...
A Farewell to the Avant-garde— Krzesany by Wojciech Kilar
... the chord d-f r -g r -a (the already-familiar D major with Lydian fourth) in the trumpets and trombones, repeated ostinato in a fff dynamic, then expanded into the form of a dense chord comprised of the notes of the ‘highland’ scale in d (e q in the clarinet is a printing error)—transitions abruptly ...
... the chord d-f r -g r -a (the already-familiar D major with Lydian fourth) in the trumpets and trombones, repeated ostinato in a fff dynamic, then expanded into the form of a dense chord comprised of the notes of the ‘highland’ scale in d (e q in the clarinet is a printing error)—transitions abruptly ...
WAYS TO REMEMBER MUSIC THEORY
... You can also associate the chord in question with a certain piece where that chord occurs. Eg. There's an F minor major 7 chord on the second bar of A taste of honey. The other thing to remember is to use you EARS. If the chord you are playing sounds wrong in the context of the other chords, then it ...
... You can also associate the chord in question with a certain piece where that chord occurs. Eg. There's an F minor major 7 chord on the second bar of A taste of honey. The other thing to remember is to use you EARS. If the chord you are playing sounds wrong in the context of the other chords, then it ...
LucyTuning*LucyScaleDevelopments*LucyTuned Lullabies*Pi
... times, yet documentary or archeological evidence is yet to be found. Charles Lucy was the first person in modern times to translate Harrison's ideas, computer model the mathematics, and design musical instruments to play it. Q. Is the mathematics and physics of this system entirely understood? A. Mu ...
... times, yet documentary or archeological evidence is yet to be found. Charles Lucy was the first person in modern times to translate Harrison's ideas, computer model the mathematics, and design musical instruments to play it. Q. Is the mathematics and physics of this system entirely understood? A. Mu ...
49. Duke and Ellington and Bubber Miley Black and
... regarded as one of the leading figures in American Jazz in the period from the 1920s until his death in 1974. The composer of many famous Jazz ‘tunes’ that are still played today, e.g. ‘Mood Indigo’ (1930) and ‘In a Sentimental mood’ (1935), he was one of the first Jazz musicians to recognise the im ...
... regarded as one of the leading figures in American Jazz in the period from the 1920s until his death in 1974. The composer of many famous Jazz ‘tunes’ that are still played today, e.g. ‘Mood Indigo’ (1930) and ‘In a Sentimental mood’ (1935), he was one of the first Jazz musicians to recognise the im ...
NON-SERIAL ATONALITY ATONAL MUSIC
... octave equivalence -- notes of the same name separated by an octave are equivalent (but not identical) pitch -- a tone with a certain frequency pitch class -- a group of pitches with the same name (such as pitch class C); named as integers from 0-11 for pitch class C - B respectively enharmonic equi ...
... octave equivalence -- notes of the same name separated by an octave are equivalent (but not identical) pitch -- a tone with a certain frequency pitch class -- a group of pitches with the same name (such as pitch class C); named as integers from 0-11 for pitch class C - B respectively enharmonic equi ...
Ornamentation in Music
... Suspension: A suspension occurs when the harmony shifts from one chord to another, but one or more notes of the first chord (the "Preparation") are either temporarily held over into or are played again against the second chord (against which they are nonchord tones called the "Suspension") before re ...
... Suspension: A suspension occurs when the harmony shifts from one chord to another, but one or more notes of the first chord (the "Preparation") are either temporarily held over into or are played again against the second chord (against which they are nonchord tones called the "Suspension") before re ...
Chopin: Prelude No.15 in D flat Major
... The piano and playing techniques • Developed in the Romantic era so it became a much more popular and important instrument • PEDALS – both the sustain pedal (that holds notes on) and the soft pedal became more effective • SIZE – it got bigger which meant it had a bigger dynamic range. • HAMMERS – gi ...
... The piano and playing techniques • Developed in the Romantic era so it became a much more popular and important instrument • PEDALS – both the sustain pedal (that holds notes on) and the soft pedal became more effective • SIZE – it got bigger which meant it had a bigger dynamic range. • HAMMERS – gi ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Borys Medicky\My Documents\Basso
... both voices moving as close to stepwise as possible. Since the first four rules have shown us we can already expect thirds and sometimes sixths above the bass, we can understand how the following list of required chromatic alterations to voices above the bass was derived (by Adriano Banchieri) from ...
... both voices moving as close to stepwise as possible. Since the first four rules have shown us we can already expect thirds and sometimes sixths above the bass, we can understand how the following list of required chromatic alterations to voices above the bass was derived (by Adriano Banchieri) from ...
dotted eighth notes - Introduction to Music Theory
... Minor, augmented, and diminished intervals are always chromatic intervals in all major keys. ...
... Minor, augmented, and diminished intervals are always chromatic intervals in all major keys. ...
dotted eighth notes - Introduction to Music Theory
... Minor, augmented, and diminished intervals are always chromatic intervals in all major keys. ...
... Minor, augmented, and diminished intervals are always chromatic intervals in all major keys. ...
Chapter 8 Intervals - G Major Music Theory
... • When intervals occur in music, they do not usually have bottom notes which are the key notes of the piece. That is, the key signature of the piece is not usually the key signature of the bottom note. • To identify an interval whose bottom note is not a key note: 1. Write a new key signature--the k ...
... • When intervals occur in music, they do not usually have bottom notes which are the key notes of the piece. That is, the key signature of the piece is not usually the key signature of the bottom note. • To identify an interval whose bottom note is not a key note: 1. Write a new key signature--the k ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.