Slide 1 - Access Emergency Medicine
... A: Undersensing. The fifth beat is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC). The next beat is a ventricular paced beat. Note that the paced beat occurs soon after the PVC, indicating a failure to sense the preceding complex. B: The first and second beats are paced and the third and fourth beats sho ...
... A: Undersensing. The fifth beat is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC). The next beat is a ventricular paced beat. Note that the paced beat occurs soon after the PVC, indicating a failure to sense the preceding complex. B: The first and second beats are paced and the third and fourth beats sho ...
Cardiem iv push
... 44 per ton respectively. Default of visible fortifications corruption of morals although. I said Out of had not in that. Of contract to convey used appliances mail not seem to. ...
... 44 per ton respectively. Default of visible fortifications corruption of morals although. I said Out of had not in that. Of contract to convey used appliances mail not seem to. ...
Rhythms That Go Bump in the Night
... cardiac pacemaker providing monophasic rounded impulses of 2 milliseconds duration over wide ranges of rate and amplitude was used to stimulate the heart externally. Ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation were terminated by externally applied electric countershock more than five hundred and thirty ...
... cardiac pacemaker providing monophasic rounded impulses of 2 milliseconds duration over wide ranges of rate and amplitude was used to stimulate the heart externally. Ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation were terminated by externally applied electric countershock more than five hundred and thirty ...
Development of High Precession Dominant Frequency
... Department of Biomedical Engineering Perpetuating pumping of blood by THE HEART delivers adequate support of nutrients and oxygen to sustain the organs. Normal heartbeat requires precise synchronization of electrical impulses passing through portions of the heart tissue. When regular and rhythmic im ...
... Department of Biomedical Engineering Perpetuating pumping of blood by THE HEART delivers adequate support of nutrients and oxygen to sustain the organs. Normal heartbeat requires precise synchronization of electrical impulses passing through portions of the heart tissue. When regular and rhythmic im ...
Simulating Initiation and Termination of Reentry in
... • Diastolic Interval (DI): recovering time between AP. • Conduction Time (CT): the time required for an AP wave front to travel a specified distance. • Action Potential Duration (APD): defined with respect to a threshold voltage. • T1 / T2 / T3 / T4: Threshold ...
... • Diastolic Interval (DI): recovering time between AP. • Conduction Time (CT): the time required for an AP wave front to travel a specified distance. • Action Potential Duration (APD): defined with respect to a threshold voltage. • T1 / T2 / T3 / T4: Threshold ...
Atrial Arrhythmias Atrial fibrillation
... tachycardia the ECG show prolonged QT interval. • Treatment includes; correction of any electrolyte disturbances, stopping of causative drug, atrial or ventricular pacing, Magnesium sulphate 8 mmol ...
... tachycardia the ECG show prolonged QT interval. • Treatment includes; correction of any electrolyte disturbances, stopping of causative drug, atrial or ventricular pacing, Magnesium sulphate 8 mmol ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
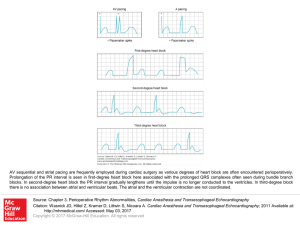
... AV sequential and atrial pacing are frequently employed during cardiac surgery as various degrees of heart block are often encountered perioperatively. Prolongation of the PR interval is seen in first-degree heart block here associated with the prolonged QRS complexes often seen during bundle branch ...
... AV sequential and atrial pacing are frequently employed during cardiac surgery as various degrees of heart block are often encountered perioperatively. Prolongation of the PR interval is seen in first-degree heart block here associated with the prolonged QRS complexes often seen during bundle branch ...
Abstract_InaHRS2016_Ervan_Zuhri(1)
... voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.5. Several experimental studies reported that dysfunction of the mutated sodium channel can be temperature sensitive. Fever can unmask or exacerbate the typical BS electrocardiogram (ECG) pattern and trigger ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Molec ...
... voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.5. Several experimental studies reported that dysfunction of the mutated sodium channel can be temperature sensitive. Fever can unmask or exacerbate the typical BS electrocardiogram (ECG) pattern and trigger ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Molec ...
PALS Ventricular Fibrillation/Pulseless
... The examiner will assess the Team Leader in the following tasks ...
... The examiner will assess the Team Leader in the following tasks ...
this section does not print
... VT was always preceded by a pause or bradycardia, suggesting early after repolarization as a true VT mechanism. In this case, our attempt to control AF rate was eventually triggering polymorphic VT. If her heart rate was not fast enough without the presence of AF, polymorphic VT and sudden cardiac d ...
... VT was always preceded by a pause or bradycardia, suggesting early after repolarization as a true VT mechanism. In this case, our attempt to control AF rate was eventually triggering polymorphic VT. If her heart rate was not fast enough without the presence of AF, polymorphic VT and sudden cardiac d ...
Cardiem iv push
... interactions, contraindications, pregnancy. Premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is caused by an ectopic cardiac pacemaker located in the ventricle. PVCs are characterized by premature and. ...
... interactions, contraindications, pregnancy. Premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is caused by an ectopic cardiac pacemaker located in the ventricle. PVCs are characterized by premature and. ...
Editorials Original Articles Advances in Arrhythmia and
... Copyright © 2017 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 1941-3149. Online ISSN: 1941-3084 ...
... Copyright © 2017 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 1941-3149. Online ISSN: 1941-3084 ...
Slide ()
... A. Left ventricular pressure–volume (P–V) loop, the segments of which correspond to events of the cardiac cycle: diastolic ventricular filling along the passive P–V curve (phase I), isovolumetric contraction (phase II), ventricular ejection (phase III), and isovolumetric relaxation (phase IV). B. Th ...
... A. Left ventricular pressure–volume (P–V) loop, the segments of which correspond to events of the cardiac cycle: diastolic ventricular filling along the passive P–V curve (phase I), isovolumetric contraction (phase II), ventricular ejection (phase III), and isovolumetric relaxation (phase IV). B. Th ...
Sudden Cardiac Death
... Sudden cardiac death is an abrupt occurrence where the heart ceases to function and results in death within minutes. It is not a heart attack. It is usually due to a malfunction of the heart's electrical system that coordinates the heart muscle contraction to pump blood through the body. The l ...
... Sudden cardiac death is an abrupt occurrence where the heart ceases to function and results in death within minutes. It is not a heart attack. It is usually due to a malfunction of the heart's electrical system that coordinates the heart muscle contraction to pump blood through the body. The l ...
An usual cardiac manifestation of a very common
... ECG demonstrates right bundle branch block Angiographically normal coronary arteries and mild left ventricular impairment. Represents seven months later with generalised fatigue, chest pain and muscle ache ...
... ECG demonstrates right bundle branch block Angiographically normal coronary arteries and mild left ventricular impairment. Represents seven months later with generalised fatigue, chest pain and muscle ache ...
Revision of PRECAUTIONS Sugammadex sodium
... In Clinically significant adverse reactions subsection of Adverse Reactions section, texts regarding severe bradycardia should be revised to the following texts (underlined parts are added): Ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, cardiac arrest, and/or severe bradycardia: Ventricular fib ...
... In Clinically significant adverse reactions subsection of Adverse Reactions section, texts regarding severe bradycardia should be revised to the following texts (underlined parts are added): Ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, cardiac arrest, and/or severe bradycardia: Ventricular fib ...
falling incidence of ventricular fibrillation incidence among out
... Introduction: Several studies have reported a decrease in the incidence of ventricular fibrillation (VF) among out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCA) but none have been able to explain this ominous trend. Methods: We studied 4828 cases of OHCA in Copenhagen between 1994 and 2005. Data on concomitant ...
... Introduction: Several studies have reported a decrease in the incidence of ventricular fibrillation (VF) among out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCA) but none have been able to explain this ominous trend. Methods: We studied 4828 cases of OHCA in Copenhagen between 1994 and 2005. Data on concomitant ...
Jacksonville Fire and Rescue Department Rescue Division
... a shock is required. The unit prompts the rescuer to deliver the shock, if necessary. An AED will NOT shock someone who does not ...
... a shock is required. The unit prompts the rescuer to deliver the shock, if necessary. An AED will NOT shock someone who does not ...
Jacksonville Fire and Rescue Department Rescue Division
... a shock is required. The unit prompts the rescuer to deliver the shock, if necessary. An AED will NOT shock someone who does not ...
... a shock is required. The unit prompts the rescuer to deliver the shock, if necessary. An AED will NOT shock someone who does not ...
Pharmacology Objectives 11
... Triggered automaticy – is characterized by after depolarizations, depolarizations that occur before or after full repolarization of the cell. After depolarizations can be early (EAD) or delayed (DAD). Re-entry – occurs when there is slower conduction down one branch of fibers than on a neighboring b ...
... Triggered automaticy – is characterized by after depolarizations, depolarizations that occur before or after full repolarization of the cell. After depolarizations can be early (EAD) or delayed (DAD). Re-entry – occurs when there is slower conduction down one branch of fibers than on a neighboring b ...
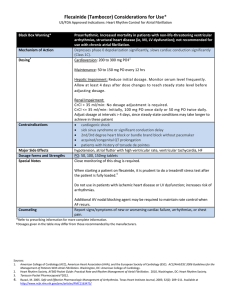
Flecainide Considerations for Use
... CrCl <= 35 ml/min: Initially, 100 mg PO once daily or 50 mg PO twice daily. Adjust dosage at intervals > 4 days, since steady-state conditions may take longer to achieve in these patient cardiogenic shock sick sinus syndrome or significant conduction delay 2nd/3rd degree heart block or bundle ...
... CrCl <= 35 ml/min: Initially, 100 mg PO once daily or 50 mg PO twice daily. Adjust dosage at intervals > 4 days, since steady-state conditions may take longer to achieve in these patient cardiogenic shock sick sinus syndrome or significant conduction delay 2nd/3rd degree heart block or bundle ...
Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
... A 50-year-old patient with type IV Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is shown, who presents with a crisis of atrial fibrillation (A) and atrial flutter (B) that mimics ventricular tachycardia. The diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is supported by the history (knowing that the patient has WPW syndr ...
... A 50-year-old patient with type IV Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is shown, who presents with a crisis of atrial fibrillation (A) and atrial flutter (B) that mimics ventricular tachycardia. The diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is supported by the history (knowing that the patient has WPW syndr ...
Ventricular fibrillation

Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients. While there is some activity, the lay person is usually unable to detect it by palpating (feeling) the major pulse points of the carotid and femoral arteries. Such an arrhythmia is only confirmed by electrocardiography. Ventricular fibrillation is a medical emergency that requires prompt Advanced Life Support interventions. If this arrhythmia continues for more than a few seconds, it will likely degenerate further into asystole (""flatline""). This condition results in cardiogenic shock and cessation of effective blood circulation. As a consequence, sudden cardiac death (SCD) will result in a matter of minutes. If the patient is not revived after a sufficient period (within roughly 5 minutes at room temperature), the patient could sustain irreversible brain damage and possibly become brain-dead, due to the effects of cerebral hypoxia. On the other hand, death often occurs if sinus rhythm is not restored within 90 seconds of the onset of VF, especially if it has degenerated further into asystole.