Name: and Physiology Test #2
... 16) What structure permits adjacent cardiac cells to depolarize each other a) Actin b) Troponin c) Gap Junctions d) Voltage-gated sodium channels 17) A ______degree heart block would occur if a P-wave came before all QRS-complexs, but some Pwaves were not associated with a QRS complex. a) First b) S ...
... 16) What structure permits adjacent cardiac cells to depolarize each other a) Actin b) Troponin c) Gap Junctions d) Voltage-gated sodium channels 17) A ______degree heart block would occur if a P-wave came before all QRS-complexs, but some Pwaves were not associated with a QRS complex. a) First b) S ...
The Shocking Truth
... Larger currents, around 1 Amp stop the heart completely! When the current stops, the heart usually starts beating again But larger currents also cause burns and tissue damage, especially with voltages around 500-1000 volts ...
... Larger currents, around 1 Amp stop the heart completely! When the current stops, the heart usually starts beating again But larger currents also cause burns and tissue damage, especially with voltages around 500-1000 volts ...
INTRODUCTION It gives us great pleasure to
... It is known that failing heart is the main problem of cardiovascular medicine today. Heart failure due to cardiovascular disease is associated with contractile dysfunction and high risk of lifethreatening arrhythmias, with up to 50% of mortality attributable to sudden cardiac death. Sudden cardiac d ...
... It is known that failing heart is the main problem of cardiovascular medicine today. Heart failure due to cardiovascular disease is associated with contractile dysfunction and high risk of lifethreatening arrhythmias, with up to 50% of mortality attributable to sudden cardiac death. Sudden cardiac d ...
Dias nummer 1
... Sudden cardiac death (SCD) in young adults is often caused by inherited heart disease. Until now the genetic diagnostic tools in patients with SCD or survivors after cardiac arrest have targeted the presumed phenotype which often can be difficult to define. We aimed to overcome these limitations by ...
... Sudden cardiac death (SCD) in young adults is often caused by inherited heart disease. Until now the genetic diagnostic tools in patients with SCD or survivors after cardiac arrest have targeted the presumed phenotype which often can be difficult to define. We aimed to overcome these limitations by ...
AED Safety Tip Flyer Final.pub - PMA
... deaths (250 000 to 500 000) are sudden and unexpected. Most of these sudden deaths occur outside the hospital and could occur at the workplace. Survival rates have traditionally been poor—only 1% to 5% of these patients are estimated to survive to hospital discharge ...
... deaths (250 000 to 500 000) are sudden and unexpected. Most of these sudden deaths occur outside the hospital and could occur at the workplace. Survival rates have traditionally been poor—only 1% to 5% of these patients are estimated to survive to hospital discharge ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... 2. Name the five cardiac cycle activities starting with excitation and ending with regulation of blood flow and volume. ...
... 2. Name the five cardiac cycle activities starting with excitation and ending with regulation of blood flow and volume. ...
Position of the Heart and Associated Structures Coronary trivia
... Purkinje fibers Depolarization of sarcolemma opens voltage-gated fast Na+ channels causing rapid depolarization Prolonged depolarization called the “plateau” involves opening of voltage-gated slow Ca2+ channels ...
... Purkinje fibers Depolarization of sarcolemma opens voltage-gated fast Na+ channels causing rapid depolarization Prolonged depolarization called the “plateau” involves opening of voltage-gated slow Ca2+ channels ...
5-Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis
... Combination of clinical presentation and laboratory/imaging studies ESR: elevated. Cardiac Enzymes: rise over several days as opposed to hours in AMI. Endomyocardial Biopsy: definitive diagnosis. CBC: Mild leukocytosis Echocardiography: Dilated chambers with focal wall motion defects. ECG: Low Volta ...
... Combination of clinical presentation and laboratory/imaging studies ESR: elevated. Cardiac Enzymes: rise over several days as opposed to hours in AMI. Endomyocardial Biopsy: definitive diagnosis. CBC: Mild leukocytosis Echocardiography: Dilated chambers with focal wall motion defects. ECG: Low Volta ...
BIOL 424 Circulation 1 I. Circulation A. Open
... c. slow conduction rate 2. bundle fibers a. very large b. in ventricular septum c. fast conduction system 3. cardiomyocytes -bulk of heart D. Heart wall 1. epicardium 2. myocardium e. endocardium III. Cardiac Cycle A. Systole 1. atrial 2. ventricular B. Diastole C. Ventricular Systole 1. atria relax ...
... c. slow conduction rate 2. bundle fibers a. very large b. in ventricular septum c. fast conduction system 3. cardiomyocytes -bulk of heart D. Heart wall 1. epicardium 2. myocardium e. endocardium III. Cardiac Cycle A. Systole 1. atrial 2. ventricular B. Diastole C. Ventricular Systole 1. atria relax ...
PDF - Circulation
... assumes a unimodal distribution and it is clear from the amount of deviation that considerable scatter is present. It was for this very reason that we stated clearly in our paper that no a priori prediction of the effect of digitalis could be made. The direction and magnitude of change observed depe ...
... assumes a unimodal distribution and it is clear from the amount of deviation that considerable scatter is present. It was for this very reason that we stated clearly in our paper that no a priori prediction of the effect of digitalis could be made. The direction and magnitude of change observed depe ...
RECENT TRENDS IN TREATMENT OF ARRHYTHMIAS
... The aim. of a surgical approach in supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) are to excise or isolate the origin of a tachycardia, to interrupt a reentrant path way necessary for maintainance of the tachycardia, and to induce AV block in patients with (SVT) that cause rapid ventricular responses. In ventr ...
... The aim. of a surgical approach in supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) are to excise or isolate the origin of a tachycardia, to interrupt a reentrant path way necessary for maintainance of the tachycardia, and to induce AV block in patients with (SVT) that cause rapid ventricular responses. In ventr ...
Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
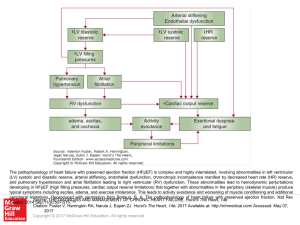
... The pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is complex and highly interrelated, involving abnormalities in left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic reserve, arterial stiffening, endothelial dysfunction, chronotropic incompetence manifest by decreased heart rate ...
... The pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is complex and highly interrelated, involving abnormalities in left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic reserve, arterial stiffening, endothelial dysfunction, chronotropic incompetence manifest by decreased heart rate ...
Atrial_Fibrillation
... usually at at atrial rate greater than 350 beats per minute. As a result, there is no concerted contraction of the atria. No P-waves are observed in the EKG due to the chaotic atrial depolarization. The chaotic atrial depolarization waves penetrate the AV node in an irregular manner, resulting in ir ...
... usually at at atrial rate greater than 350 beats per minute. As a result, there is no concerted contraction of the atria. No P-waves are observed in the EKG due to the chaotic atrial depolarization. The chaotic atrial depolarization waves penetrate the AV node in an irregular manner, resulting in ir ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... Sinus rhythm with ventricular bigeminy due to digitalis toxicity. Ventricular premature complexes follow each sinus-conducted QRS at a fixed coupling interval. ST-segment depression and T wave inversion in the sinus-conducted beats is seen in V6; however, since each sinus-conducted beat is a postext ...
... Sinus rhythm with ventricular bigeminy due to digitalis toxicity. Ventricular premature complexes follow each sinus-conducted QRS at a fixed coupling interval. ST-segment depression and T wave inversion in the sinus-conducted beats is seen in V6; however, since each sinus-conducted beat is a postext ...
Placement of a left ventricular assist device in a patient with
... pulmonary arterial system. Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium, passes through the morphologic tricuspid valve, into the right ventricle which then pumps systemically to the aorta. More than 2/3 of ccTGA patients also have associated cardiac anomalies such as VSD, which dictate the natural h ...
... pulmonary arterial system. Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium, passes through the morphologic tricuspid valve, into the right ventricle which then pumps systemically to the aorta. More than 2/3 of ccTGA patients also have associated cardiac anomalies such as VSD, which dictate the natural h ...
Ethical Scenario - My Surgery Website
... £70000. The life expectancy after implantation is around 5 years. Cardiac ablation is generally used for patients with AF and a reduced quality of life (normally younger/active patients) who have not responded well to conservative treatment. The costs of cardiac ablation are around £5000 per patient ...
... £70000. The life expectancy after implantation is around 5 years. Cardiac ablation is generally used for patients with AF and a reduced quality of life (normally younger/active patients) who have not responded well to conservative treatment. The costs of cardiac ablation are around £5000 per patient ...
Adult Medical –Surgical Nursing 1
... Radiofrequency, cryoablation or electrical ablation used ...
... Radiofrequency, cryoablation or electrical ablation used ...
Ventricular Ectopic Beats: How Many is Too Much?
... Paradoxically, trained athletes with the smallest extent of LV remodeling demonstrated a tendency to more frequent VA ...
... Paradoxically, trained athletes with the smallest extent of LV remodeling demonstrated a tendency to more frequent VA ...
ECG Lecture Chapter 3
... • No P wave you have fibrillatory “f” waves • Chaotic firing of the atria. No organized contraction = Quivering. • Contribution of atria contraction to ventricular filling is not achieved. • Randon AV conduction so the QRS is normal. ...
... • No P wave you have fibrillatory “f” waves • Chaotic firing of the atria. No organized contraction = Quivering. • Contribution of atria contraction to ventricular filling is not achieved. • Randon AV conduction so the QRS is normal. ...
Gabie Gomez - Labmongers2
... flutter to normal sinus rhythm. Class IV:(Calan) Antiarrhymic drug that inhibit the movement of calcium through channels across the myocardial cell membrane and vascular smooth muscle. By reducing the calcium flow, conduction through the (SA) node and (AV) nodes is slowed and the refractory period i ...
... flutter to normal sinus rhythm. Class IV:(Calan) Antiarrhymic drug that inhibit the movement of calcium through channels across the myocardial cell membrane and vascular smooth muscle. By reducing the calcium flow, conduction through the (SA) node and (AV) nodes is slowed and the refractory period i ...
Morte cardiaca improvvisa - Informazioni
... Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a life-threating heart condition, and if not treated within minutes, can lead to death. SCA results from an irregular or abnormal heart rhythm, due to a problem with the electrical system of the heart. There are generally two types of abnormal rhythms: • Ventricular ta ...
... Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a life-threating heart condition, and if not treated within minutes, can lead to death. SCA results from an irregular or abnormal heart rhythm, due to a problem with the electrical system of the heart. There are generally two types of abnormal rhythms: • Ventricular ta ...
Plötzlicher Herztod - Hintergrundinformationen
... Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a life-threating heart condition, and if not treated within minutes, can lead to death. SCA results from an irregular or abnormal heart rhythm, due to a problem with the electrical system of the heart. There are generally two types of abnormal rhythms: • Ventricular ta ...
... Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a life-threating heart condition, and if not treated within minutes, can lead to death. SCA results from an irregular or abnormal heart rhythm, due to a problem with the electrical system of the heart. There are generally two types of abnormal rhythms: • Ventricular ta ...
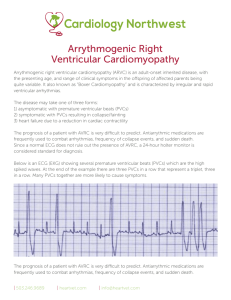
Arrythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC, Boxer
... the presenting age, and range of clinical symptoms in the offspring of affected parents being quite variable. It also known as “Boxer Cardiomyopathy” and is characterized by irregular and rapid ventricular arrhythmias. The disease may take one of three forms: 1) asymptomatic with premature ventricul ...
... the presenting age, and range of clinical symptoms in the offspring of affected parents being quite variable. It also known as “Boxer Cardiomyopathy” and is characterized by irregular and rapid ventricular arrhythmias. The disease may take one of three forms: 1) asymptomatic with premature ventricul ...
Cover - Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology
... Copyright © 2017 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 1941-3149. Online ISSN: 1941-3084 ...
... Copyright © 2017 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 1941-3149. Online ISSN: 1941-3084 ...
Ventricular fibrillation

Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients. While there is some activity, the lay person is usually unable to detect it by palpating (feeling) the major pulse points of the carotid and femoral arteries. Such an arrhythmia is only confirmed by electrocardiography. Ventricular fibrillation is a medical emergency that requires prompt Advanced Life Support interventions. If this arrhythmia continues for more than a few seconds, it will likely degenerate further into asystole (""flatline""). This condition results in cardiogenic shock and cessation of effective blood circulation. As a consequence, sudden cardiac death (SCD) will result in a matter of minutes. If the patient is not revived after a sufficient period (within roughly 5 minutes at room temperature), the patient could sustain irreversible brain damage and possibly become brain-dead, due to the effects of cerebral hypoxia. On the other hand, death often occurs if sinus rhythm is not restored within 90 seconds of the onset of VF, especially if it has degenerated further into asystole.