Twiddler`s syndrome: a rare cause of implantable cardioverter
... A St Jude Durata dual-coil active fixation ventricular lead was implanted via the left subclavian vein, attached to a St Jude Ellipse VR pulse generator buried in a pre-pectoral pocket (chest X-ray—Panel A). At 4-week review, it was noted that the pacing threshold on the ventricular lead had risen f ...
... A St Jude Durata dual-coil active fixation ventricular lead was implanted via the left subclavian vein, attached to a St Jude Ellipse VR pulse generator buried in a pre-pectoral pocket (chest X-ray—Panel A). At 4-week review, it was noted that the pacing threshold on the ventricular lead had risen f ...
Word version of this scenario
... Arrhythmias A 64 year old NZ European man is brought to the Emergency Department by ambulance. He had collapsed, temporarily lost consciousness and was observed to become pale at the time of collapse. When the ambulance crew arrived, it was noted that his pulse rate was very rapid. ...
... Arrhythmias A 64 year old NZ European man is brought to the Emergency Department by ambulance. He had collapsed, temporarily lost consciousness and was observed to become pale at the time of collapse. When the ambulance crew arrived, it was noted that his pulse rate was very rapid. ...
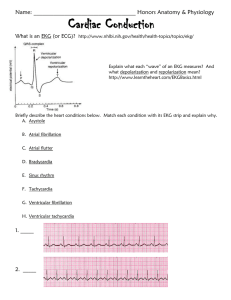
• ECG paper: small box = 0.04 seconds • Normal PR interval = 0.12
... Cardiac Monitor Technician Knowledge Assessment Examination: Study Guide Review basic facts and principles, such as: ...
... Cardiac Monitor Technician Knowledge Assessment Examination: Study Guide Review basic facts and principles, such as: ...
Ventricular Fibrillation and Cardiac Arrest
... veterinary hospital, very few patients are successfully resuscitated and live to leave the hospital. About 30% of people who are observed to have a cardiac arrest in the hospital are successfully resuscitated. Of that 30%, only about 10% ever leave the hospital. The most successful resuscitations ar ...
... veterinary hospital, very few patients are successfully resuscitated and live to leave the hospital. About 30% of people who are observed to have a cardiac arrest in the hospital are successfully resuscitated. Of that 30%, only about 10% ever leave the hospital. The most successful resuscitations ar ...
Cardiac Conduction Practice Worksheet
... Name: ____________________________________ Honors Anatomy & Physiology ...
... Name: ____________________________________ Honors Anatomy & Physiology ...
Comparison of Failure Rates for External and Implantable
... •Unless treatment is given in 5 to 10 minutes, ventricular fibrillation causes death. ...
... •Unless treatment is given in 5 to 10 minutes, ventricular fibrillation causes death. ...
Cardiac Pathology and Diagnosis
... Atherosclerosis (of the aorta in photo) This is the most common form of arteriosclerosis. This pathology is caused by the deposition of fatty yellowish plaques of cholesterol on the inner walls of the arteries. This photo features the plaque buildup on the walls of the aorta. Diagnosis may be perf ...
... Atherosclerosis (of the aorta in photo) This is the most common form of arteriosclerosis. This pathology is caused by the deposition of fatty yellowish plaques of cholesterol on the inner walls of the arteries. This photo features the plaque buildup on the walls of the aorta. Diagnosis may be perf ...
Time: Monday May 2nd, 2011 5:00pm Location: Buchanan A202
... Cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia (VT) and fibrillation (VF) can be fatal if left untreated. In two dimensions, these reentrant arrhythmias can be modeled as one or more spiral waves in a system of excitable media. The appearance of spiral waves due to structural inhomogeneities – ...
... Cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia (VT) and fibrillation (VF) can be fatal if left untreated. In two dimensions, these reentrant arrhythmias can be modeled as one or more spiral waves in a system of excitable media. The appearance of spiral waves due to structural inhomogeneities – ...
www.ipicd.com
... • Minimum ventricular fibrillation induction multiple (MinVFIM) lowest shock multiple that induced VF at least once. • Maximum safe multiple (MaxSM) the highest shock multiple that could be applied 3 times without induction of VF. • Ventricular fibrillation threshold (VFT) was defined as the average ...
... • Minimum ventricular fibrillation induction multiple (MinVFIM) lowest shock multiple that induced VF at least once. • Maximum safe multiple (MaxSM) the highest shock multiple that could be applied 3 times without induction of VF. • Ventricular fibrillation threshold (VFT) was defined as the average ...
Slide ()
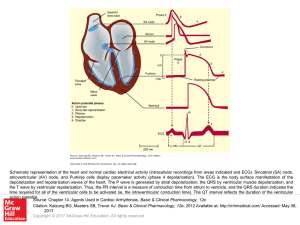
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
AED- Automated External Defibrillation
... • Each year approx 500,000 Americans die of cardiac arrest • 95% do not survive • Needs electric shock-defibrillators • AED-Automatic External Defibrillator • Result more cardiac arrest victims being saved ...
... • Each year approx 500,000 Americans die of cardiac arrest • 95% do not survive • Needs electric shock-defibrillators • AED-Automatic External Defibrillator • Result more cardiac arrest victims being saved ...
EKG
... ELECTROCARDIOGRAM An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a graphic representation of the heart’s electrical activity. ...
... ELECTROCARDIOGRAM An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a graphic representation of the heart’s electrical activity. ...
IV-29 9.01 R. Lidocaine Hydrochloride (Xylocaine®)
... A. Ventricular dysrhythmias, Cardiac arrest, Post cardioversion/defibrillation of ventricular rhythm [by online MD order only] •1 mg/kg slow IV/IO over 1 minute or 2 mg/kg ET. If no conversion, repeat 1 mg/kg IV/IO two times or 1 mg/kg ET one time in 3-5 minutes. (Maximum 3 mg/kg). VI ...
... A. Ventricular dysrhythmias, Cardiac arrest, Post cardioversion/defibrillation of ventricular rhythm [by online MD order only] •1 mg/kg slow IV/IO over 1 minute or 2 mg/kg ET. If no conversion, repeat 1 mg/kg IV/IO two times or 1 mg/kg ET one time in 3-5 minutes. (Maximum 3 mg/kg). VI ...
VERAPAMIL (CALAN)
... Blocks the entry of calcium into the cell Slows conduction through the AV node Negative chronotrope (slows heart rate) Negative inotrope (decreased force of cardiac contraction) To control the rate in hemodynamically stable atrial fibrillation or INDICATIONS atrial flutter with rapid ventric ...
... Blocks the entry of calcium into the cell Slows conduction through the AV node Negative chronotrope (slows heart rate) Negative inotrope (decreased force of cardiac contraction) To control the rate in hemodynamically stable atrial fibrillation or INDICATIONS atrial flutter with rapid ventric ...
Slide ()
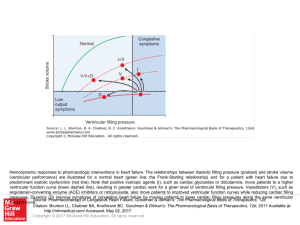
... Hemodynamic responses to pharmacologic interventions in heart failure. The relationships between diastolic filling pressure (preload) and stroke volume (ventricular performance) are illustrated for a normal heart (green line; the Frank-Starling relationship) and for a patient with heart failure due ...
... Hemodynamic responses to pharmacologic interventions in heart failure. The relationships between diastolic filling pressure (preload) and stroke volume (ventricular performance) are illustrated for a normal heart (green line; the Frank-Starling relationship) and for a patient with heart failure due ...
Atrial Fibrillation as A Complication of Congestive Heart Failure in
... Heart failure (HF) is a clinical syndrome that present when the heart is unable to pump blood forward at a sufficient rate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. HF results in a clinical syndrome of dyspnea, fatigue, peripheral edema and rales. In CHF patient often occurs ventricular remodeling ...
... Heart failure (HF) is a clinical syndrome that present when the heart is unable to pump blood forward at a sufficient rate to meet the metabolic demands of the body. HF results in a clinical syndrome of dyspnea, fatigue, peripheral edema and rales. In CHF patient often occurs ventricular remodeling ...
Familial Arrhythmia
... Familial Arrhythmia Cardiac arrhythmias are generally characterized by abnormal electrical activity in the heart that puts patients at high risk for embolic stroke and/or sudden cardiac death (SCD). Commonly recognized arrhythmic disorders include atrial fibrillation (AF), long QT syndrome (LQTS), c ...
... Familial Arrhythmia Cardiac arrhythmias are generally characterized by abnormal electrical activity in the heart that puts patients at high risk for embolic stroke and/or sudden cardiac death (SCD). Commonly recognized arrhythmic disorders include atrial fibrillation (AF), long QT syndrome (LQTS), c ...
Athero Arteriosclorsis
... Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of atria. It can be a chronic condition, usually treated with anticoagulation and sometimes with conversion to normal sinus rhythm. In this condition the normal electrical pulses coming from the sinoatrial node a ...
... Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of atria. It can be a chronic condition, usually treated with anticoagulation and sometimes with conversion to normal sinus rhythm. In this condition the normal electrical pulses coming from the sinoatrial node a ...
Emergency Department use of Esmolol in Refractory Ventricular
... difficult to treat and carries a high mortality rate • Treatment with epinephrine: – Activates α-1 receptors: this is probably helpful – Activates β-1 and β-2 receptors: this is probably harmful ...
... difficult to treat and carries a high mortality rate • Treatment with epinephrine: – Activates α-1 receptors: this is probably helpful – Activates β-1 and β-2 receptors: this is probably harmful ...
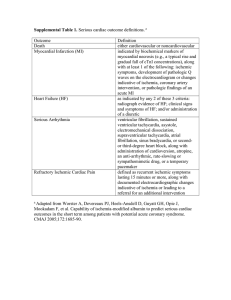
Supplemental Table 1
... indicated by biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis (e.g., a typical rise and gradual fall of cTnI concentrations), along with at least 1 of the following: ischemic symptoms, development of pathologic Q waves on the electrocardiogram or changes indicative of ischemia, coronary artery interventio ...
... indicated by biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis (e.g., a typical rise and gradual fall of cTnI concentrations), along with at least 1 of the following: ischemic symptoms, development of pathologic Q waves on the electrocardiogram or changes indicative of ischemia, coronary artery interventio ...
Defibrillators
... condition which can lead to asystole. • It is usually preceded by ventricular tachycardia (fast heart rhythm). ...
... condition which can lead to asystole. • It is usually preceded by ventricular tachycardia (fast heart rhythm). ...
Ventricular fibrillation

Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients. While there is some activity, the lay person is usually unable to detect it by palpating (feeling) the major pulse points of the carotid and femoral arteries. Such an arrhythmia is only confirmed by electrocardiography. Ventricular fibrillation is a medical emergency that requires prompt Advanced Life Support interventions. If this arrhythmia continues for more than a few seconds, it will likely degenerate further into asystole (""flatline""). This condition results in cardiogenic shock and cessation of effective blood circulation. As a consequence, sudden cardiac death (SCD) will result in a matter of minutes. If the patient is not revived after a sufficient period (within roughly 5 minutes at room temperature), the patient could sustain irreversible brain damage and possibly become brain-dead, due to the effects of cerebral hypoxia. On the other hand, death often occurs if sinus rhythm is not restored within 90 seconds of the onset of VF, especially if it has degenerated further into asystole.