* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Rhythm - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
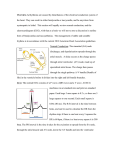
Cardiac Rhythm • “Until the day Jesus returns, I will live in a body which does not function as God originally intended. My brain, which is a key, central, integral part of my body, will not function correctly. Chemicals will become imbalanced. Serotonin will not be properly absorbed. Norepinephrine will be unevenly distributed. Synapses won’t fire correctly. My brain, just like every other part of my body, is prone to illness.” Sinus Rhythm - 6 second strip qrs times 10 = heart rayr Sinus Rhythm Atrial Fibrillation A-Fib – no p wave Atrial Flutter – fluttering of p waves Supra Ventricular – heart is beating fast and the heart can’t fill and the heart can’t pump First Degree Atrioventricular block 1° AV Block – p waves are far away from qrs Third Degree Atrio Ventricular Block 3° AV Block – p waves completely dissociated from qrs complexes Ventricular Tachycardia V-Tach – qrs complexes are wide, one ventricle must be stimulating the other Ventricular Fibrillation V-Fib VF – no qrs complexes, common rhythm in cardiac arrest Cardiac Muscle Cell • The cardiac muscle cell can repeatedly contract or beat by itself Cardiac Muscle Cell • Na+ Ca2+ K+ Cl• The cardiac muscle cell requires these ions and their membrane channel Charged and Ready • • • • • • • The Na+/K+ pump creates: - sodium concentration gradient - more outside than inside - potassium concentration gradient - more inside than outside The Na/Ca pump creates - calcium concentration gradient Action Potential • Step 1 sodium channels open • Sodium rushes in, causing a voltage change across the membrane Action Potential • Step 2 calcium channels open • Calcium rushes in, causing muscle contraction • Na channels are closing now Action Potential • Step 3 potassium channels open • Potassium ‘resets’ the membrane by rushing out until the membrane is charged and ready for another action potential Cardiac muscle cell • Each separate cardiac muscle cell can repeatedly contract or beat by itself, at it’s own pace. Fibrillation • When the cells beat separately and on their own, this is called fibrillation Fibrillation • When the ventricles, the main pumps, are fibrillating there can be no heart beat Synchrony • It is important that the cells work together Conduction Pathway • Certain specialized heart muscles help conduct the signals and maintain synchrony Conducting System of the Heart Picture Atrio-Ventricular Node R-Atrium Picture • Sympathetic Neuron • NE – norepinephrine • Increased HR • Parasympathetic Neuron • Ach • Decreased HR • • • • • • P wave – atrial excitation - think of it as lighting the fuse QRS wave – ventricular excitation - think of it as the BANG! T wave – ventricular repolarization - think of it as the RESET What do we do in V-fib? • Chest compressions is the first round of treatment for V-fib • 100 beats/minute Pulseless arrest • • • • BLS Algorithm: Call for help, give CPR Give oxygen when available Attach monitor/defibrillator when available Allow for full recoil using chest compressions • Oxygen is a drug • - most important drug in pediatric arrhythmia • Use Bag valve mask or ambu bag Bag Valve Ambu Bag VF/VT – pulseless • Give 1 shock • Manual biphasic: device specific (typically 120 to 200J) • AED: device specific – automatic external defibrillator • Monophasic: 360J • Resume CPR immediately • Stand clear • Shock! Fibrillation • By applying a large electrical shock sometimes we can convert fibrillation into a perfusing rhythm – synchrony • So must do chest compressions, oxygen, electricity Defibrillation • Applying a shock to the heart is called defibrillation • V-fib – oxygen is one of the greatest antiarrhythmic drugs • Resume CPR immediately after the shock • When the IV is available, give vasopressin during the procedure (before or after the shock) • Epinephrine 1mg IV • Repeat every 3 to 5 mins or may give 1 dose of vasopressin 40IV to replace first or second dose of epinephrine • Epinephrine produces beneficial effects in patients during cardiac arrest primarily because of it’s α-adrenergic stimulating vasoconstrictive properties • Vasopressin – is a nonadrenergic vasoconstrictor • Vasopressin is also called Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH) and is released by the posterior pituitary of the brain • Resume CPR immediately after the shock • Consider antiarrhythimics, give during CPR (before or after the shock) • - amiodarone • - lidocaine • Lidocaine is a “Class 1” antiarrhythmic • It is a sodium channel blocker in heart muscle slowing down heart contraction • Amiodarone • Is a “Class 3” antiarrhythmic • It is a: sodium channel blocker, potassium channel blocker, calcium channel blocker, α & β adrenergic blocker V-Fib interventions • Chest compressions • Oxygen • Shock! V-Fib Drugs • • • • Epinephrine Vasopressin (ADH) Lidocaine Amiodarone Do not confuse • Ventricular fibrillation – cardiac arrest • Atrial fibrillation – the ventricles are still beating – will have a pulse, irregularly irregular ECG, will have tachycardia – you may call this as atrial fibrillation with rapid response A-fib • Major cause of strokes • Major reason to give coumadin • Don’t want to convert A-fib to SR (sinus rhythm) until we know there is no thrombus A-Fib • Stable • Unstable Digoxin Lanoxin • Digitalis glycoside • Blocks Na/K ATPase increasing calcium availability • Antiarrhythmic • Positive Inotrope • Negative Chronotrope • Slows AV conduction Digoxin Risks • Arrythmia • Toxicity with hypokalemia Supra Ventricular Tachycardia ECG Picture SVT • • • • • • A-Fib RVR – rapid ventricular rate - Control ventricular rate - Β-blockers (Class 2) - Calcium channel blokcers (Class 4) - verapamil - diltiazem Adenosine • Endogenous nucleotides which slows conduction through the AV node • IV antidysrythmic used in PSVT – paroxysmal supra ventricular tachycardia SVT • • • • • • Adenosine - safe - “reset” AV node - stops heart beat for about 6 secs - 6 very long seconds…… Will not reverse a-fib a-flut • Atrial flutter – treat the same as a-fib First Degree AV Block ECG Picture Third Degree AV Block ECG Picture – p waves completely dissociated from qrs complexes Bradycardia • Bradycardia means low heart rate • Bradycardia is heart rate less than 60 • Relative bradycardia means heart is beating too slow just to keep up with demand Bradycadia • Stable • Unstable Bradycardia • Atropine • - cholinergic blocker • Epinephrine • - adrenaline Procaine – similar to Lidocaine • • • • Procainamide - sodium channel blocker - watch for hypertension - lupus-like adverse effects when taken chronically