Chapter 8: The Nervous System
... Ans: A nerve impulse is a wave of depolarization and repolarization, during which sodium ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, neurotransmitter substances are released int ...
... Ans: A nerve impulse is a wave of depolarization and repolarization, during which sodium ions first move into a neuron and then potassium ions move out of a neuron. This is called an action potential. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, neurotransmitter substances are released int ...
Cover page
... neuronal regeneration in the context of neurodegenerative disease of the cortical output circuitry. The neocortex contains an unparalleled diversity of neuronal subtypes, each defined by distinct traits that are developmentally acquired under the control of several neuron subtype-specific and pan-ne ...
... neuronal regeneration in the context of neurodegenerative disease of the cortical output circuitry. The neocortex contains an unparalleled diversity of neuronal subtypes, each defined by distinct traits that are developmentally acquired under the control of several neuron subtype-specific and pan-ne ...
theta oscillation in the hippocampus
... Theta frequency field oscillation reflects synchronized synaptic potentials that entrain the discharge of neuronal populations within the D100–200 ms range. The cellular-synaptic generation of theta activity in the hippocampus was investigated by intracellular recordings from the somata and dendrite ...
... Theta frequency field oscillation reflects synchronized synaptic potentials that entrain the discharge of neuronal populations within the D100–200 ms range. The cellular-synaptic generation of theta activity in the hippocampus was investigated by intracellular recordings from the somata and dendrite ...
Hypothalamus
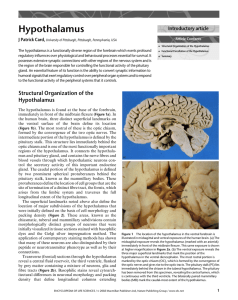
... entrained oscillatory output of the SCN is transmitted to other cells groups through axonal projections of SCN neurons. The synaptic targets of these projections are found largely within the hypothalamus, but the temporal information is distributed to a number of cell groups in the central and perip ...
... entrained oscillatory output of the SCN is transmitted to other cells groups through axonal projections of SCN neurons. The synaptic targets of these projections are found largely within the hypothalamus, but the temporal information is distributed to a number of cell groups in the central and perip ...
Integration of Perspective and Disparity Cues in Surface
... Masato Taira. Integration of perspective and disparity cues in surface-orientation–selective neurons of area CIP. J Neurophysiol 86: 2856 –2867, 2001. We investigated the effects of linear perspective and binocular disparity, as monocular and binocular depth cues, respectively, on the response of su ...
... Masato Taira. Integration of perspective and disparity cues in surface-orientation–selective neurons of area CIP. J Neurophysiol 86: 2856 –2867, 2001. We investigated the effects of linear perspective and binocular disparity, as monocular and binocular depth cues, respectively, on the response of su ...
Circadian Plasticity of Mammalian Inhibitory Interneurons
... In vertebrates, the majority of interneurons are inhibitory and they mainly release GABA. However, GABA can also act as an excitatory neurotransmitter. During brain development, GABA is the main excitatory neurotransmitter acting by GABA A receptors and cooperating with glutamate [12–16]. The effect ...
... In vertebrates, the majority of interneurons are inhibitory and they mainly release GABA. However, GABA can also act as an excitatory neurotransmitter. During brain development, GABA is the main excitatory neurotransmitter acting by GABA A receptors and cooperating with glutamate [12–16]. The effect ...
Can we conquer pain?
... expectancy, but are accompanied by a rise in the cumulative incidence of tumor-related pain syndromes as well as of pain associated with therapy, such as chemotherapy-induced painful polyneuropathy. The unmet clinical need, the personal suffering and societal economic costs of pain are substantial. ...
... expectancy, but are accompanied by a rise in the cumulative incidence of tumor-related pain syndromes as well as of pain associated with therapy, such as chemotherapy-induced painful polyneuropathy. The unmet clinical need, the personal suffering and societal economic costs of pain are substantial. ...
PDF
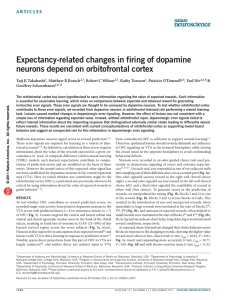
... simple loss of information regarding expected value. Instead, without orbitofrontal input, dopaminergic error signals failed to reflect internal information about the impending response that distinguished externally similar states leading to differently valued future rewards. These results are consi ...
... simple loss of information regarding expected value. Instead, without orbitofrontal input, dopaminergic error signals failed to reflect internal information about the impending response that distinguished externally similar states leading to differently valued future rewards. These results are consi ...
Stochastic neural network dynamics: synchronisation and control
... from different dendritic branches almost simultaneously. Consequently, inputs must arrive within a short time period to significantly raise the electrical potential at the soma; the timing within this interval affects the magnitude of contribution from each input. When the overall electrical input f ...
... from different dendritic branches almost simultaneously. Consequently, inputs must arrive within a short time period to significantly raise the electrical potential at the soma; the timing within this interval affects the magnitude of contribution from each input. When the overall electrical input f ...
Formation of Neuronal Pathways in the lmaginal Discs of Drosophila
... discs start to evaginate. The cell bodies at the center of the disc, Al, A2, A3, and Pl , move with the future tip of the leg whereas their axons simply elongate. By 1 hr after puparium formation (APF) (Fig. 26), the leg begins to assume a tubular shape; these four neurons are now located at the ver ...
... discs start to evaginate. The cell bodies at the center of the disc, Al, A2, A3, and Pl , move with the future tip of the leg whereas their axons simply elongate. By 1 hr after puparium formation (APF) (Fig. 26), the leg begins to assume a tubular shape; these four neurons are now located at the ver ...
Circuit Architecture of VTA Dopamine Neurons Revealed by
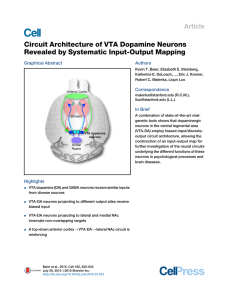
... Figure 1. Rabies-Mediated Trans-synaptic Tracing Reveals Inputs to VTA-DA and -GABA Neurons (A) Schematic of rabies tracing, shown for DAT-Cre. Left, diagrams of the injection site (blue box highlights the VTA) and the viruses used. (1) Injections of AAVs expressing Cre-dependent TVA-mCherry (TC) a ...
... Figure 1. Rabies-Mediated Trans-synaptic Tracing Reveals Inputs to VTA-DA and -GABA Neurons (A) Schematic of rabies tracing, shown for DAT-Cre. Left, diagrams of the injection site (blue box highlights the VTA) and the viruses used. (1) Injections of AAVs expressing Cre-dependent TVA-mCherry (TC) a ...
Orcokinin peptides in developing and adult crustacean
... individual sensory and descending neurons that project into the STG acquire their full complement of neurotransmitters sequentially (Fénelon et al., 1998, 1999; Kilman et al., 1999; Le Feuvre et al., 2001). The timing of appearance of the orcokinins in development has not been previously studied. T ...
... individual sensory and descending neurons that project into the STG acquire their full complement of neurotransmitters sequentially (Fénelon et al., 1998, 1999; Kilman et al., 1999; Le Feuvre et al., 2001). The timing of appearance of the orcokinins in development has not been previously studied. T ...
Clonal analysis of the mushroom bodies
... derived from this GMC will be labeled in the whole lineage (lower). In addition, mitotic recombination in a dividing GMC can generate a single cell clone independently (lower). (E) Composite confocal images of an adult MB Nb clone demonstrate five axonal bundles, three projecting medially and two pr ...
... derived from this GMC will be labeled in the whole lineage (lower). In addition, mitotic recombination in a dividing GMC can generate a single cell clone independently (lower). (E) Composite confocal images of an adult MB Nb clone demonstrate five axonal bundles, three projecting medially and two pr ...
UNIT II - Elsevier Health
... passing to the right. As long as the electrode is outside the nerve membrane, the recorded potential is zero, which is the potential of the extracellular fluid. Then, as the recording electrode passes through the voltage change area at the cell membrane (called the electrical dipole layer), the pote ...
... passing to the right. As long as the electrode is outside the nerve membrane, the recorded potential is zero, which is the potential of the extracellular fluid. Then, as the recording electrode passes through the voltage change area at the cell membrane (called the electrical dipole layer), the pote ...
Maruska & Tricas 2011
... also varied across the year, suggesting seasonal changes in GnRH influence of auditory processing. Exogenous application of GnRH (sGnRH and cGnRHII) caused a primarily inhibitory effect on auditory-evoked single neuron responses in the torus semicircularis. In the majority of neurons, GnRH caused a l ...
... also varied across the year, suggesting seasonal changes in GnRH influence of auditory processing. Exogenous application of GnRH (sGnRH and cGnRHII) caused a primarily inhibitory effect on auditory-evoked single neuron responses in the torus semicircularis. In the majority of neurons, GnRH caused a l ...
The Structure of Spatial Receptive Fields of Neurons in Primary
... were used, and sound-source directions were referred to the same spherical coordinate system centered on the cat’s interaural plane that covered 3608 in azimuth and 1268 in elevation. Measurements were not made at elevations below 2368 (Musicant et al., 1990) and thus were not represented in our VAS ...
... were used, and sound-source directions were referred to the same spherical coordinate system centered on the cat’s interaural plane that covered 3608 in azimuth and 1268 in elevation. Measurements were not made at elevations below 2368 (Musicant et al., 1990) and thus were not represented in our VAS ...
Glia–Neuron Interactions in Nervous System Function
... be possible, in principle, to generate glia harboring mutations that aVect neuronal function but not survival. Although these approaches have proven quite informative, it is yet unclear how relevant these studies are to the functioning of the nervous system in vivo. Glial alterations leading to obvi ...
... be possible, in principle, to generate glia harboring mutations that aVect neuronal function but not survival. Although these approaches have proven quite informative, it is yet unclear how relevant these studies are to the functioning of the nervous system in vivo. Glial alterations leading to obvi ...
The medial geniculate, not the amygdala, as the root of auditory fear
... The AMYG model has been presented in numerous reviews (e.g., Fanselow and LeDoux, 1999; LeDoux, 1990, 1992, 1993a, 1994, 1995, 2000; LeDoux and Muller, 1997; Maren, 2001; Maren and Quirk, 2004; Phelps and LeDoux, 2005; Rodrigues et al., 2009). The major findings on which the AMYG model is based are s ...
... The AMYG model has been presented in numerous reviews (e.g., Fanselow and LeDoux, 1999; LeDoux, 1990, 1992, 1993a, 1994, 1995, 2000; LeDoux and Muller, 1997; Maren, 2001; Maren and Quirk, 2004; Phelps and LeDoux, 2005; Rodrigues et al., 2009). The major findings on which the AMYG model is based are s ...
A Hebbian learning rule gives rise to mirror neurons and links them
... that a simple eligibility-weighted Hebbian learning rule, operating within a sensorimotor loop during motor explorations and stabilized by heterosynaptic competition, naturally gives rise to mirror neurons as well as control theoretic inverse models encoded in the synaptic weights from sensory to mo ...
... that a simple eligibility-weighted Hebbian learning rule, operating within a sensorimotor loop during motor explorations and stabilized by heterosynaptic competition, naturally gives rise to mirror neurons as well as control theoretic inverse models encoded in the synaptic weights from sensory to mo ...
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Directly Activates Noradrenergic
... activation of LC neurons is unknown. Moreover, given the apparent absence of mRNA for CRH receptors in LC neurons, the exact location of action of CRH within the cerulear region is debated. Using in vitro intracellular recordings from rat brainstem, we examined whether CRH exerts a direct effect on ...
... activation of LC neurons is unknown. Moreover, given the apparent absence of mRNA for CRH receptors in LC neurons, the exact location of action of CRH within the cerulear region is debated. Using in vitro intracellular recordings from rat brainstem, we examined whether CRH exerts a direct effect on ...
Use of lipophilic dyes in studies of axonal pathfinding in vivo
... distribution is mainly by lateral diffusion in the plasma membrane rather than by axonal transport. Therefore, DiI can be used to trace axonal tracts over extremely long distances in fixed tissue that can be kept for weeks to allow sufficient time for the diffusion of the dye (Godement et al., 1987) ...
... distribution is mainly by lateral diffusion in the plasma membrane rather than by axonal transport. Therefore, DiI can be used to trace axonal tracts over extremely long distances in fixed tissue that can be kept for weeks to allow sufficient time for the diffusion of the dye (Godement et al., 1987) ...
Mapping Horizontal Spread of Activity in Monkey Motor
... Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China ...
... Qiushi Academy for Advanced Studies, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China ...
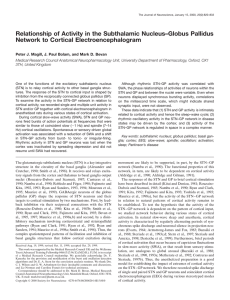
Relationship of Activity in the Subthalamic Nucleus–Globus Pallidus
... Essex, UK). This protocol was used to perform single or double recordings of neurons. Spikes were often several millivolts in amplitude and always exhibited a biphasic waveform with an initial positive deflection. Recordings of spontaneous activity typically lasted for 4 –25 min. The EEG was recorde ...
... Essex, UK). This protocol was used to perform single or double recordings of neurons. Spikes were often several millivolts in amplitude and always exhibited a biphasic waveform with an initial positive deflection. Recordings of spontaneous activity typically lasted for 4 –25 min. The EEG was recorde ...
Optogenetic drive of neocortical pyramidal neurons generates fMRI
... signal is higher for 40 relative to 8 Hz. Quantifying this result (Fig. 2B), firing rate (MUA) was elevated (n=2 animals) for 40 Hz compared to 8 Hz (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, P=5.78e-12), the LFP power ratio (n=3) decreased with increased stimulation frequency (P=0.0134) and the dcLFP (n=3) average v ...
... signal is higher for 40 relative to 8 Hz. Quantifying this result (Fig. 2B), firing rate (MUA) was elevated (n=2 animals) for 40 Hz compared to 8 Hz (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, P=5.78e-12), the LFP power ratio (n=3) decreased with increased stimulation frequency (P=0.0134) and the dcLFP (n=3) average v ...
Macrophages Promote Axon Regeneration with Concurrent Neurotoxicity
... conditions, DRG neurons were killed or their ability to extend axons was dramatically impaired. The concurrent induction of proregenerative and neurotoxic functions in zymosan-activated macrophages (ZAMs) was confirmed in vitro using DRG and cortical neurons. Importantly, the ability of ZAMs to stim ...
... conditions, DRG neurons were killed or their ability to extend axons was dramatically impaired. The concurrent induction of proregenerative and neurotoxic functions in zymosan-activated macrophages (ZAMs) was confirmed in vitro using DRG and cortical neurons. Importantly, the ability of ZAMs to stim ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.