brainbeebootcamp 2017
... http://www.madrimasd.org/cienciaysociedad/patrimonio/personajes/santiago_ramon_ycajal/Default.asp ...
... http://www.madrimasd.org/cienciaysociedad/patrimonio/personajes/santiago_ramon_ycajal/Default.asp ...
HUMAN ANATOMY
... • Axon – is the long (sometimes up to the 1 m or more) extension, which sends outgoing signals to the cells. ...
... • Axon – is the long (sometimes up to the 1 m or more) extension, which sends outgoing signals to the cells. ...
013368718X_CH31_483
... neuron’s cell body that carry impulses from other neurons to the cell body ...
... neuron’s cell body that carry impulses from other neurons to the cell body ...
No Slide Title
... In action potential when the sodium gates are open and sodium ions move inside the axon, this stage is called ___________. ...
... In action potential when the sodium gates are open and sodium ions move inside the axon, this stage is called ___________. ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
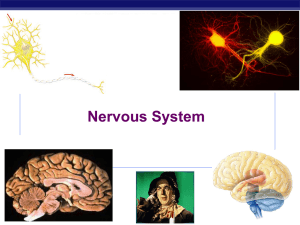
Nervous System
... • Once the neuron’s membrane is depolarized to the threshold level, an action potential occurs. • An electrical signal travels via the axon to the next neuron. – At the end of the axon, the signal causes the release of neurotransmitters that jump the space between cells called the synapse ...
... • Once the neuron’s membrane is depolarized to the threshold level, an action potential occurs. • An electrical signal travels via the axon to the next neuron. – At the end of the axon, the signal causes the release of neurotransmitters that jump the space between cells called the synapse ...
Nervous System - cloudfront.net
... Part of the PNS that regulates the functions of internal organs such as the heart, stomach and intestines. 2 parts: Sympathetic Nervous System Parasympathetic Nervous System ...
... Part of the PNS that regulates the functions of internal organs such as the heart, stomach and intestines. 2 parts: Sympathetic Nervous System Parasympathetic Nervous System ...
Andrea Sookchan Jasmine Hodge Billy Chang
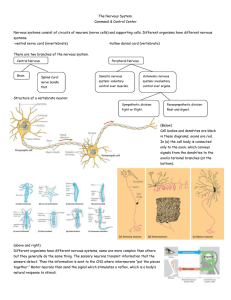
... •These cells carry messages (impulse) throughout the nervous system. ...
... •These cells carry messages (impulse) throughout the nervous system. ...
Nervous system Nervous system
... • Nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. • Nervous tissue consists of neurons; whereas the brain and spinal cord contain all parts of neurons, nerves contain only axons. ...
... • Nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. • Nervous tissue consists of neurons; whereas the brain and spinal cord contain all parts of neurons, nerves contain only axons. ...
The Nervous System
... electrical signals from your brain out to your body. These signals can travel up to 220 miles per hour! The space between neurons is called a synapse. ...
... electrical signals from your brain out to your body. These signals can travel up to 220 miles per hour! The space between neurons is called a synapse. ...
Nociceptive sensation. Somatic sensory analyzer
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 12. __________________________ are chemicals found in the synaptic vesicles which, when released, has an effect on the next cell. 13. The ______________________ neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to fire. 14. The __________________ _______________ a long bundle of neurons that carries messag ...
... 12. __________________________ are chemicals found in the synaptic vesicles which, when released, has an effect on the next cell. 13. The ______________________ neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to fire. 14. The __________________ _______________ a long bundle of neurons that carries messag ...
chapter the nervous system and the effects of drugs
... Study the Diagram Read the paragraph in the box and study the diagram. Then answer the questions. The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up ...
... Study the Diagram Read the paragraph in the box and study the diagram. Then answer the questions. The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up ...
nervous system divisions cns, pns 1
... 3. Reaction/Response: – Motor output. – response to information processed through stimulation of effectors • muscle contraction, glandular secretion The activation of muscles or glands (typically via the release of neurotransmitters (NTs)) ...
... 3. Reaction/Response: – Motor output. – response to information processed through stimulation of effectors • muscle contraction, glandular secretion The activation of muscles or glands (typically via the release of neurotransmitters (NTs)) ...
chapter 3 study guide
... Neurons: Identify and locate the fundamental components and functions that form the biological bases of communication and behavior within the nervous system, including: ...
... Neurons: Identify and locate the fundamental components and functions that form the biological bases of communication and behavior within the nervous system, including: ...
Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior
... GABA(gamma-aminobutyric acid)-major inhibitory transmitter in the brain-neuron loss after stroke ...
... GABA(gamma-aminobutyric acid)-major inhibitory transmitter in the brain-neuron loss after stroke ...
The Nervous System
... Central Nervous System The Brain • 100 billion neurons • Protected by skull bones • Wrapped in three layers of connective tissue called meninges. • Bathed in cerebrospinal fluid which acts as a shock absorber. ...
... Central Nervous System The Brain • 100 billion neurons • Protected by skull bones • Wrapped in three layers of connective tissue called meninges. • Bathed in cerebrospinal fluid which acts as a shock absorber. ...
nervous system
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
BOX 2.1 THE NEURON DOCTRINE The cell theory, which states
... In 1897, Charles Sherrington postulated that neurons establish functional contact with one another and with other cell types via a theoretical structure he called the synapse (Greek synaptein, to fasten together). It was not until 50 years later that the structural existence of synapses was demonstr ...
... In 1897, Charles Sherrington postulated that neurons establish functional contact with one another and with other cell types via a theoretical structure he called the synapse (Greek synaptein, to fasten together). It was not until 50 years later that the structural existence of synapses was demonstr ...
The Nervous System - Centennial Christian School
... • You had the maximum number of neurons when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often become forgetful ...
... • You had the maximum number of neurons when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often become forgetful ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.