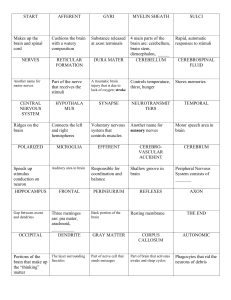
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... 1. What role does the Central Nervous System play? The decision maker 2. What role does the peripheral nervous system play? Gathers information and transmits decisions made by CNS to other parts of body 3. What role do nerves play? Electrical cables made up of millions of axons connecting the ...
... 1. What role does the Central Nervous System play? The decision maker 2. What role does the peripheral nervous system play? Gathers information and transmits decisions made by CNS to other parts of body 3. What role do nerves play? Electrical cables made up of millions of axons connecting the ...
The Nervous System
... Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure **”Runner’s High” is an example of endorphin release ...
... Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure **”Runner’s High” is an example of endorphin release ...
neuron and nervous system
... Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure ...
... Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure ...
Unit 3 Essential Vocabulary File - District 196 e
... motor neurons brainstem frontal lobes parietal lobes acetylcholine amygdala hippocampus plasticity sensory cortex heritability ...
... motor neurons brainstem frontal lobes parietal lobes acetylcholine amygdala hippocampus plasticity sensory cortex heritability ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... 2- ALL behavior is controlled by the nervous system 3- The nervous system is one of the smallest but most complex of the 11 organ systems. The nervous system (brain and nerve) has a total mass of about 2 kg or about 3% of body weight. The nervous system is divided into two sections a- ...
... 2- ALL behavior is controlled by the nervous system 3- The nervous system is one of the smallest but most complex of the 11 organ systems. The nervous system (brain and nerve) has a total mass of about 2 kg or about 3% of body weight. The nervous system is divided into two sections a- ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... oculomotor, facial, auditory, trigeminal, etc. - cervical nerves (8 pairs) - spinal nerves (many pairs) + thoracic, lumber, sacral, coccygeal ...
... oculomotor, facial, auditory, trigeminal, etc. - cervical nerves (8 pairs) - spinal nerves (many pairs) + thoracic, lumber, sacral, coccygeal ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Afferent Nerves (sensory nerves) - Carry information to the spinal cord and brain Efferent Nerves (motor nerves) - Carry information to the muscles ...
... Afferent Nerves (sensory nerves) - Carry information to the spinal cord and brain Efferent Nerves (motor nerves) - Carry information to the muscles ...
Key Learning Guide - City Vision University
... 4. Chemical messengers are called______________________. 5. Neurons have a central body with wispy tendrils called ___________________. ...
... 4. Chemical messengers are called______________________. 5. Neurons have a central body with wispy tendrils called ___________________. ...
Nervous System
... Nerve Impulse- an electrical signal is sent from the dendrite, along the axon, to the terminal. A chemical message, called a neurotransmitter is released from the axon terminals into the synapse, where it travels to the next cell. ...
... Nerve Impulse- an electrical signal is sent from the dendrite, along the axon, to the terminal. A chemical message, called a neurotransmitter is released from the axon terminals into the synapse, where it travels to the next cell. ...
The Brain
... • Somatic nervous system (SNS) soma means body ANS- includes nerves that originate in the CNS and stop at the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscle tissue and glands. Runs on autopilot. SNS- Includes the afferent and efferent nerves that bring sensory info in and motor info out of the CNS ...
... • Somatic nervous system (SNS) soma means body ANS- includes nerves that originate in the CNS and stop at the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscle tissue and glands. Runs on autopilot. SNS- Includes the afferent and efferent nerves that bring sensory info in and motor info out of the CNS ...
Introduction to the Nervous System Guided Notes are masses of
... (2) ___________________________– monitor the position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints (3) __________________________ – Monitor internal environment and provide sensations of taste, deep pressure, and pain (2) _____________ neurons - Efferent neurons that make up efferent component of the ...
... (2) ___________________________– monitor the position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints (3) __________________________ – Monitor internal environment and provide sensations of taste, deep pressure, and pain (2) _____________ neurons - Efferent neurons that make up efferent component of the ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... – Single process arises from body – Branches into an axon and dendrite – e.g., Present in spinal and cranial ganglia (sensory neuron) Bipolar: – Single axon and single dendrite on opposite ends of the soma. e.g., interneuron Multipolar; – Single axon & multiple dendrites – Most common type in men – ...
... – Single process arises from body – Branches into an axon and dendrite – e.g., Present in spinal and cranial ganglia (sensory neuron) Bipolar: – Single axon and single dendrite on opposite ends of the soma. e.g., interneuron Multipolar; – Single axon & multiple dendrites – Most common type in men – ...
Chapter 03: Neuroscience and behaviour PowerPoint
... – concentration of ions inside and outside cell ...
... – concentration of ions inside and outside cell ...
Central Nervous System
... (the brain and spinal cord) to serve the limbs and organs. Unlike the central nervous system, however, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), it is not protected by bone, leaving it exposed to toxins and mechanical injuries. ...
... (the brain and spinal cord) to serve the limbs and organs. Unlike the central nervous system, however, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), it is not protected by bone, leaving it exposed to toxins and mechanical injuries. ...
Nervous System 4/28/09
... 1. Receiving info – inside and outside body 2. Responding to info – reaction to stimulus (change/signal) 3. Maintaining homeostasis ...
... 1. Receiving info – inside and outside body 2. Responding to info – reaction to stimulus (change/signal) 3. Maintaining homeostasis ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... 5. Draw a concept diagram and place these terms in boxes: PNS, autonomic, somatic, CNS, motor, sympathetic, parasympathetic. Be sure to link the boxes with terms describing the relationship between systems inside the boxes. (sl 2, 11.1 are examples) 6. Afferent nerves are found in the ______________ ...
... 5. Draw a concept diagram and place these terms in boxes: PNS, autonomic, somatic, CNS, motor, sympathetic, parasympathetic. Be sure to link the boxes with terms describing the relationship between systems inside the boxes. (sl 2, 11.1 are examples) 6. Afferent nerves are found in the ______________ ...
The nervous system
... a) the Somatic Nervous System – nerves which communicate with the skin and muscles and b) the Autonomic Nervous System – nerves which control the involuntary muscles, internal organs (heart, lungs, stomach, etc.) and glands ...
... a) the Somatic Nervous System – nerves which communicate with the skin and muscles and b) the Autonomic Nervous System – nerves which control the involuntary muscles, internal organs (heart, lungs, stomach, etc.) and glands ...
Study Guide
... 2. Distinguish between sensation and perception. 3. Recognize or explain sensory adaptation. 4. Locate the epineurium, perineurium and endoneurium. 5. Describe the basics of nerve regeneration. 6. Know the name, number, and whether the cranial nerves are sensory, motor or mixed, and functions that a ...
... 2. Distinguish between sensation and perception. 3. Recognize or explain sensory adaptation. 4. Locate the epineurium, perineurium and endoneurium. 5. Describe the basics of nerve regeneration. 6. Know the name, number, and whether the cranial nerves are sensory, motor or mixed, and functions that a ...
Communication and Control-The Nervous System chp 25-1
... • A spinal cord injury may block all information to and from the brain. • Each year, thousands of people are paralyzed by spinal cord injuries. • Severed axons in the PNS can be regenerated but if the axon is severed in the CNS it cannot be regenerated (paralysis or loss of sensation may occur) ...
... • A spinal cord injury may block all information to and from the brain. • Each year, thousands of people are paralyzed by spinal cord injuries. • Severed axons in the PNS can be regenerated but if the axon is severed in the CNS it cannot be regenerated (paralysis or loss of sensation may occur) ...
Nervous System
... world: sights, sounds, smells, feel, etc … • Taking in all the stimuli and reacting to it • The brain is generally (very, very generally) divided into 3 main sections – Cerebrum – Cerebellum – Medulla ...
... world: sights, sounds, smells, feel, etc … • Taking in all the stimuli and reacting to it • The brain is generally (very, very generally) divided into 3 main sections – Cerebrum – Cerebellum – Medulla ...
Notes Outline I (Part I)
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.