irons.conroeisd.net
... A biochemical reaction that both humans and animals experience during intense stress or fear. The nervous system releases hormones causing changes to occur throughout the body. ...
... A biochemical reaction that both humans and animals experience during intense stress or fear. The nervous system releases hormones causing changes to occur throughout the body. ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... Nervous System Nervous system has three types of neurons: Sensory neurons - send info from tissues and organs toward CNS Motor neurons - how the CNS sends instructions out to body tissues. Interneurons - processes internal commincation in the CNS ...
... Nervous System Nervous system has three types of neurons: Sensory neurons - send info from tissues and organs toward CNS Motor neurons - how the CNS sends instructions out to body tissues. Interneurons - processes internal commincation in the CNS ...
Ch. 21.1 Nervous Lecture
... E. Brain Stem 1. Acts as a bridge between the brain and spinal cord 2. Coordinates involuntary activities such as heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, sneezing and vomitting ...
... E. Brain Stem 1. Acts as a bridge between the brain and spinal cord 2. Coordinates involuntary activities such as heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, sneezing and vomitting ...
Print › psych chapter 2 | Quizlet | Quizlet
... sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response. ...
... sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response. ...
Central Nervous System
... Central Nervous System • Consist of the brain and vertebrates and the spinal cord. ...
... Central Nervous System • Consist of the brain and vertebrates and the spinal cord. ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... – Sodium/Potassium pump in axon using ATP maintains this polarity (active transport);slower ...
... – Sodium/Potassium pump in axon using ATP maintains this polarity (active transport);slower ...
A1984SK79600002
... and adrenaline was obtained by bioassay of extracts of about 50 freshly dissected regions of the dog’s brain and spinal cord. The NA concentration ranged from 2.0 to 0.01 µg/g fresh tissue. [The SCI ® indicates that this paper has been cited in over 995 publications ...
... and adrenaline was obtained by bioassay of extracts of about 50 freshly dissected regions of the dog’s brain and spinal cord. The NA concentration ranged from 2.0 to 0.01 µg/g fresh tissue. [The SCI ® indicates that this paper has been cited in over 995 publications ...
The Nervous System
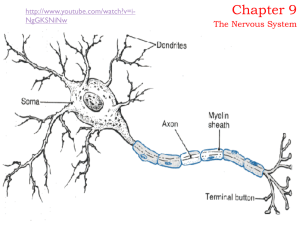
... Neuron – basic nerve cell (sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron) Cell body – control center of the cell containing the nucleus. Dendrites – projections branching from the cell body that bring impulses. Axon – thread-like extensions that carry impulses away from cell body. Two (2) divi ...
... Neuron – basic nerve cell (sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron) Cell body – control center of the cell containing the nucleus. Dendrites – projections branching from the cell body that bring impulses. Axon – thread-like extensions that carry impulses away from cell body. Two (2) divi ...
Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
... And there are just three types Sensory is the first has receptors They respond to stimuli Association's in brain and spinal cord Interpreting the info and passing on To move the motor neurons carry to the body Bring it to the glands Bring it to the muscles...oh oh oh oh oh Nervous System Spinal cord ...
... And there are just three types Sensory is the first has receptors They respond to stimuli Association's in brain and spinal cord Interpreting the info and passing on To move the motor neurons carry to the body Bring it to the glands Bring it to the muscles...oh oh oh oh oh Nervous System Spinal cord ...
Unit 3- Biological Psychology Study Guide
... Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between t ...
... Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between t ...
Brain Anatomy
... physical growth of connections between neurons. • Improve connections with ‘linking,’ emotion, repetition and practice ...
... physical growth of connections between neurons. • Improve connections with ‘linking,’ emotion, repetition and practice ...
36.1 The Nervous System Neurons: Basic units of
... Neurons: a long cell that consists of 3 regions a cell body, dendrites and axon and conducts an impulse. Dendrite - branch like extensions of the neuron that receive impulses and carry them to the cell body. White matter - Composed of myelin which coats the axons – this area of the brain is high in ...
... Neurons: a long cell that consists of 3 regions a cell body, dendrites and axon and conducts an impulse. Dendrite - branch like extensions of the neuron that receive impulses and carry them to the cell body. White matter - Composed of myelin which coats the axons – this area of the brain is high in ...
File
... are their functions? Answer: Sympathetic nervous system- “fight/flight”. Parasympathetic- “rest & digest”. ...
... are their functions? Answer: Sympathetic nervous system- “fight/flight”. Parasympathetic- “rest & digest”. ...
Document
... • _____________________________ – _______________- specialized for the transition of impulses from one part of the body to another. •Neurons _______________ _______________ –Cannot be replaced. If outside the brain and spinal cord may slowly grow back. Structure of a Neuron _______________ take in i ...
... • _____________________________ – _______________- specialized for the transition of impulses from one part of the body to another. •Neurons _______________ _______________ –Cannot be replaced. If outside the brain and spinal cord may slowly grow back. Structure of a Neuron _______________ take in i ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
Chapter 9 Nerves
... Integrative functions collect sensory information and make decisions that motor functions carry out ...
... Integrative functions collect sensory information and make decisions that motor functions carry out ...
lecture-4-post
... Neurons are cells that communicate within the nervous system 10-100 billion in the brain alone, each communicating with thousands of others ...
... Neurons are cells that communicate within the nervous system 10-100 billion in the brain alone, each communicating with thousands of others ...
Nervous System
... Why are spinal injuries that result in paralysis often permanent? Sensory and motor nerves can heal completely but it is slow. The spinal nerves can also grow but not well enough to repair significant damage. ...
... Why are spinal injuries that result in paralysis often permanent? Sensory and motor nerves can heal completely but it is slow. The spinal nerves can also grow but not well enough to repair significant damage. ...
Nervous System Test Review
... the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
... the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
Nervous Systems
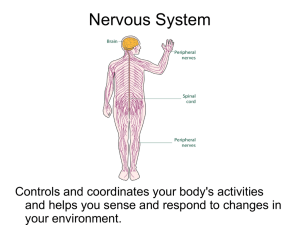
... Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body Sensory receptors: collect info Sensory neurons: body CNS Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons Nerves = bundles of neurons C ...
... Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body Sensory receptors: collect info Sensory neurons: body CNS Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons Nerves = bundles of neurons C ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.