Chapter 3: The Nervous System
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. ▫ Works as an off switch. ...
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. ▫ Works as an off switch. ...
Central Nervous System
... They are called neurons And there are just three types Sensory is the first has receptors They respond to stimuli Association's in brain and spinal cord Interpreting the info and passing on To move the motor neurons carry to the body Bring it to the glands Bring it to the muscles...oh oh oh oh oh Ne ...
... They are called neurons And there are just three types Sensory is the first has receptors They respond to stimuli Association's in brain and spinal cord Interpreting the info and passing on To move the motor neurons carry to the body Bring it to the glands Bring it to the muscles...oh oh oh oh oh Ne ...
session1vocabulary
... Stimulus Anything/change in the environment that makes you react. Like feeling a burning stove Neurons The cells that carry information through your body/nervous system. Some of the cells in nerve tissues. Sensory, motor, and inter-neuron neurons. Nerve Impulse The messages carried by neurons. Cons ...
... Stimulus Anything/change in the environment that makes you react. Like feeling a burning stove Neurons The cells that carry information through your body/nervous system. Some of the cells in nerve tissues. Sensory, motor, and inter-neuron neurons. Nerve Impulse The messages carried by neurons. Cons ...
The Nervous System
... 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. 9e.Students know the roles of se ...
... 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. 9e.Students know the roles of se ...
Memories and your Brain
... • There are two basic types of cells in the brain, neurons and glial cells • Neurons do the transmitting • Glia do the support functions • There are many types of neurons and glial cells, but we don’t have to be too concerned about those ...
... • There are two basic types of cells in the brain, neurons and glial cells • Neurons do the transmitting • Glia do the support functions • There are many types of neurons and glial cells, but we don’t have to be too concerned about those ...
Memories and your Brain
... There are two basic types of cells in the brain, neurons and glial cells Neurons do the transmitting Glia do the support functions There are many types of neurons and glial cells, but we don’t have to be too concerned about those ...
... There are two basic types of cells in the brain, neurons and glial cells Neurons do the transmitting Glia do the support functions There are many types of neurons and glial cells, but we don’t have to be too concerned about those ...
Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... •Controls certain respiratory functions (autonomic functions) ...
... •Controls certain respiratory functions (autonomic functions) ...
Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 5:Spinal cord The
... Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 5: Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System In the previous section we saw that the neurons of the brain and spinal cord are centrally located in the body. Contrary to this, the neurons of peripheral nervous system are spread in the other zones of the body. This sy ...
... Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 5: Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System In the previous section we saw that the neurons of the brain and spinal cord are centrally located in the body. Contrary to this, the neurons of peripheral nervous system are spread in the other zones of the body. This sy ...
Nervous System
... internal conditions, vestibular (balance)) by the sensory neurons releasing neurotransmitters in the brain to the correct receiving neurons. Neurons for each senses are located in different areas of the brain. • The brain integrates this information to understand the whole picture by sending and rec ...
... internal conditions, vestibular (balance)) by the sensory neurons releasing neurotransmitters in the brain to the correct receiving neurons. Neurons for each senses are located in different areas of the brain. • The brain integrates this information to understand the whole picture by sending and rec ...
Human Body - TeacherTube
... brain and the rest of the body. • 31 pairs branch out from the spinal cord to connect the brain to the rest of the body. ...
... brain and the rest of the body. • 31 pairs branch out from the spinal cord to connect the brain to the rest of the body. ...
The Nervous System
... Today’s objectives… Identify and discuss the two main parts of the nervous system. Explain how the nervous system functions as the central control system of the body. Identify factors that may lead to disorders of the nervous system. ...
... Today’s objectives… Identify and discuss the two main parts of the nervous system. Explain how the nervous system functions as the central control system of the body. Identify factors that may lead to disorders of the nervous system. ...
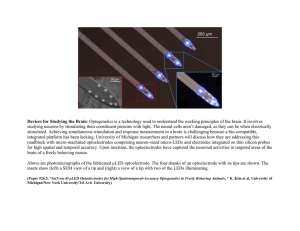
26-5 Devices for Studying the Brain
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
PSY 301 – Summer 2004
... Internal functioning E.g., Heartbeat, digestion, Sympathetic: Fight or flight (adrenalin) Parasympathetic: Resting and digesting (Back to baseline) (acetylcholine) ...
... Internal functioning E.g., Heartbeat, digestion, Sympathetic: Fight or flight (adrenalin) Parasympathetic: Resting and digesting (Back to baseline) (acetylcholine) ...
1. Receptor cells
... interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then transmitted to the brain. ...
... interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then transmitted to the brain. ...
Nervous System
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
Central Nervous System
... Axon: a single strand that extends away from the cell body and conducts impulses away from the cell body. Dendrites and axons are also called nerve fibers. Bundles of nerve fibers bound together by specialized tissues are called nerves. The junction between 2 neurons or between a neuron and a recept ...
... Axon: a single strand that extends away from the cell body and conducts impulses away from the cell body. Dendrites and axons are also called nerve fibers. Bundles of nerve fibers bound together by specialized tissues are called nerves. The junction between 2 neurons or between a neuron and a recept ...
Ch. 2 Practice
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
Nervous and Muscular System
... those that can be contracted or relaxed at will – Involuntary muscles are regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems ...
... those that can be contracted or relaxed at will – Involuntary muscles are regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems ...
Nervous system
... messages to the brain), others are descending (carrying messages from the brain). The spinal cord is also involved in reflexes that do not immediately involve the brain. ...
... messages to the brain), others are descending (carrying messages from the brain). The spinal cord is also involved in reflexes that do not immediately involve the brain. ...
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Glial Cells: (glia) cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons, they may also play a role in learning and thinking Temporal lobes: lies roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information from the opposite ear. Motor cortex: an area at the rear ...
... Glial Cells: (glia) cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons, they may also play a role in learning and thinking Temporal lobes: lies roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information from the opposite ear. Motor cortex: an area at the rear ...
Information Processing SG AK
... Learning Target #2: I can explain the location and function of brain parts. What are neurotransmitters? Describe three specific neurotransmitters and how they affect feelings and behavior. ...
... Learning Target #2: I can explain the location and function of brain parts. What are neurotransmitters? Describe three specific neurotransmitters and how they affect feelings and behavior. ...
The Human Nervous System
... 2. The cell body contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts messages away from the cell body. ...
... 2. The cell body contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts messages away from the cell body. ...
The Nervous System: Overview The nervous system Divisions of the
... within the CNS are interneurons Motor neurons – Relay instructions to muscles, organs, and ...
... within the CNS are interneurons Motor neurons – Relay instructions to muscles, organs, and ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.