1. Receptor cells
... interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then transmitted to the brain. ...
... interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting – touching). receive various types of stimulation from environment, which are then transmitted to the brain. ...
NEUROCHEMICAL TRANSMISSION
... controls simple reflexes, eye and ear orientation movements superior colliculi (“little hills”)—relay visual information inferior colliculi—relay auditory information ...
... controls simple reflexes, eye and ear orientation movements superior colliculi (“little hills”)—relay visual information inferior colliculi—relay auditory information ...
The Nervous System
... nervous system (CNS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The PNS gathers information from inside and outside the body. The CNS receives and analyzes this information and initiates responses. The PNS then picks up and carries the response signals. This information is transmitted throughout the ...
... nervous system (CNS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The PNS gathers information from inside and outside the body. The CNS receives and analyzes this information and initiates responses. The PNS then picks up and carries the response signals. This information is transmitted throughout the ...
Chapter 2: Brain Development
... • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
... • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
The Biological Perspective - Klicks-IBPsychology-Wiki
... • Basic units of the nervous system • Act like a wire passing an electric signal called a nerve impulse • Key components of neurons – Dendrites- small branches that receive and transmit info between neurons – Axon-cable like structure on which messages travel through neurons – Myelin- insulating she ...
... • Basic units of the nervous system • Act like a wire passing an electric signal called a nerve impulse • Key components of neurons – Dendrites- small branches that receive and transmit info between neurons – Axon-cable like structure on which messages travel through neurons – Myelin- insulating she ...
Unit 4 Test Nervous System
... a. One direction: From dendrites to axon terminals b. One direction: From axon terminals to dendrites c. Two directions: Can travel up or down the neuron d. Any direction: Whichever direction the impulse is stronger ...
... a. One direction: From dendrites to axon terminals b. One direction: From axon terminals to dendrites c. Two directions: Can travel up or down the neuron d. Any direction: Whichever direction the impulse is stronger ...
Nervous System Nervous system
... The axons in spinal cord allow the brain to communicate with PNS The axons of sensory neurons in skin and muscles carry impulses to the spinal cord The spinal cord relays these impulses to the brain The brain interprets these impulses as pain, temperature, or other sensations and responds to the sit ...
... The axons in spinal cord allow the brain to communicate with PNS The axons of sensory neurons in skin and muscles carry impulses to the spinal cord The spinal cord relays these impulses to the brain The brain interprets these impulses as pain, temperature, or other sensations and responds to the sit ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory because decreased amounts of it in the brain are associated with the disease, Alzheimers. Neurotransmit ...
... neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory because decreased amounts of it in the brain are associated with the disease, Alzheimers. Neurotransmit ...
Unit 5- Nervous
... - I can Identify the major anatomical components of the brain and spinal cord and briefly comment in the function of each. - I can Identify and discuss the coverings and fluid spaces of the brain and spinal cord. - I can discuss spinal and cranial nerves - I can discuss the anatomical and functional ...
... - I can Identify the major anatomical components of the brain and spinal cord and briefly comment in the function of each. - I can Identify and discuss the coverings and fluid spaces of the brain and spinal cord. - I can discuss spinal and cranial nerves - I can discuss the anatomical and functional ...
Unit 2-Week 1 Notes Sheets
... Unit 2: Nervous System Week 1 Notes Topic: ___________________________________________ ...
... Unit 2: Nervous System Week 1 Notes Topic: ___________________________________________ ...
Chapter 3
... Neuroscience Deals with the biological bases of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors Where are memories stored in the brain? How do we experience joy, anger, or desire? Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses ...
... Neuroscience Deals with the biological bases of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors Where are memories stored in the brain? How do we experience joy, anger, or desire? Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses ...
Neuroscience
... Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles. Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. ...
... Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles. Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. ...
Students know
... • Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. • Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
... • Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. • Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
Unit 3 Cerqueira guide
... AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. • Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake m ...
... AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. • Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake m ...
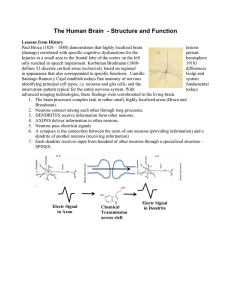
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... Injuries to a small area in the frontal lobe of the cortex on the left hemisphere only resulted in speech impairment. Korbinian Brodmann (18681918) defines 52 discrete cortical areas exclusively based on regional differences in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi a ...
... Injuries to a small area in the frontal lobe of the cortex on the left hemisphere only resulted in speech impairment. Korbinian Brodmann (18681918) defines 52 discrete cortical areas exclusively based on regional differences in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi a ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... Main steps of brain development The human brain is a complex structure which undergoes many changes from its formation in the embryonic phase till its full development in late adolescence. In this essay/presentation I would like to introduce the major steps of this process. It all starts with the fo ...
... Main steps of brain development The human brain is a complex structure which undergoes many changes from its formation in the embryonic phase till its full development in late adolescence. In this essay/presentation I would like to introduce the major steps of this process. It all starts with the fo ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... Analyze how nerve impulses travel within the nervous system. Interpret the functions of the major parts of the nervous system. Compare voluntary responses and involuntary ...
... Analyze how nerve impulses travel within the nervous system. Interpret the functions of the major parts of the nervous system. Compare voluntary responses and involuntary ...
Review
... transmission of a signal between neurons. Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and functions. Recount historic and contemporary research strategies and technologies that s ...
... transmission of a signal between neurons. Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and functions. Recount historic and contemporary research strategies and technologies that s ...
Module 04
... (for example, the bricks) that make up a structure (for example, a house). The structure of our nervous system, or neural information system, is made up of neurons (they are its building blocks). To fathom our thoughts and actions, memories and moods, we must first understand how neurons work and co ...
... (for example, the bricks) that make up a structure (for example, a house). The structure of our nervous system, or neural information system, is made up of neurons (they are its building blocks). To fathom our thoughts and actions, memories and moods, we must first understand how neurons work and co ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.