2222222222222222222 System • Responsible for coordinating the
... Elements of the nervous system • ______________ o Any organ that picks up stimulus o Ex. eye, nose, skin • Effectors o Any organ that _________________ o Ex. Muscle gland • Conductors o Transmit information about __________ between the receptor and an effector o Ex. neurons (include those in the bra ...
... Elements of the nervous system • ______________ o Any organ that picks up stimulus o Ex. eye, nose, skin • Effectors o Any organ that _________________ o Ex. Muscle gland • Conductors o Transmit information about __________ between the receptor and an effector o Ex. neurons (include those in the bra ...
Overview of the Day
... between neurons is a small space (1 millionth of an inch thick) called synaptic cleft when action potential reaches knob-like terminals at axon's end, it triggers release of neurotransmitter they cross synaptic cleft and bind to receptor cites on dendrites of next neuron: receptor cites are spe ...
... between neurons is a small space (1 millionth of an inch thick) called synaptic cleft when action potential reaches knob-like terminals at axon's end, it triggers release of neurotransmitter they cross synaptic cleft and bind to receptor cites on dendrites of next neuron: receptor cites are spe ...
Module 04
... A wrongheaded theory . . . Even though phrenology was without any scientific merit (wrongheaded), the theory did suggest the idea that different parts of the brain influence a variety of functions and behaviors. Neural Communication For scientists, it is a happy fact of nature that the information s ...
... A wrongheaded theory . . . Even though phrenology was without any scientific merit (wrongheaded), the theory did suggest the idea that different parts of the brain influence a variety of functions and behaviors. Neural Communication For scientists, it is a happy fact of nature that the information s ...
Slide ()
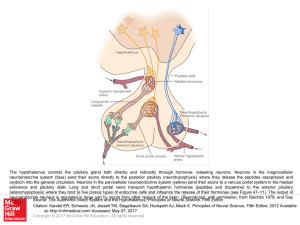
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
Neurotransmisson Practice
... some of these extensions are insulated by a layer of fatty cells called the ______________, which help speed the neuron’s impulses. 3. The neural impulse, or ______________________-, is a brief electrical charge that travels down a neuron. 4. The junction between two neurons is called a ____________ ...
... some of these extensions are insulated by a layer of fatty cells called the ______________, which help speed the neuron’s impulses. 3. The neural impulse, or ______________________-, is a brief electrical charge that travels down a neuron. 4. The junction between two neurons is called a ____________ ...
2. Peripheral Nervous System
... This is all-or-none, meaning a stimulus must exceed a threshold for the action potential to occur ...
... This is all-or-none, meaning a stimulus must exceed a threshold for the action potential to occur ...
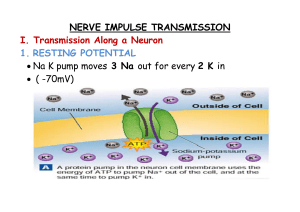
steps in nerve impulse transmission
... Increasing the intensity of the stimuli above threshold will not produce an increased response. Neurons either fire maximally or not at all. ...
... Increasing the intensity of the stimuli above threshold will not produce an increased response. Neurons either fire maximally or not at all. ...
Neurons
... Ex. Ach (role in memory, learning, and is also the messenger at every junction between motor neurons (which carry info from the brain and spinal cord to the body’s tissues) and skeletal muscles If ACh transmission is blocked then your muscles cannot contract --leading to paralysis ...
... Ex. Ach (role in memory, learning, and is also the messenger at every junction between motor neurons (which carry info from the brain and spinal cord to the body’s tissues) and skeletal muscles If ACh transmission is blocked then your muscles cannot contract --leading to paralysis ...
Neurons - Scott Melcher
... tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving cell is called a synapse. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft. When neurons are firing and action potentials are traveling down an axon, neurotransmitters are send through the synapse. Neurotransmi ...
... tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving cell is called a synapse. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft. When neurons are firing and action potentials are traveling down an axon, neurotransmitters are send through the synapse. Neurotransmi ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... 20. If a neuron can only send an ON or OFF signal, how can information about stimulus intensity be contained in that signal? (11.3) 21. How does an action potential from one neuron create a graded potential in a target neuron? (11.5) 22. Explain how a neurotransmitter can be excitatory (meaning what ...
... 20. If a neuron can only send an ON or OFF signal, how can information about stimulus intensity be contained in that signal? (11.3) 21. How does an action potential from one neuron create a graded potential in a target neuron? (11.5) 22. Explain how a neurotransmitter can be excitatory (meaning what ...
neurons
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal. • Positive Potassium (K) is pumped out AS THE PROCESS OCCURS DOWN THE AXON and now the neuron is in a state of ...
... • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal. • Positive Potassium (K) is pumped out AS THE PROCESS OCCURS DOWN THE AXON and now the neuron is in a state of ...
Brain 1
... (a) A particular experience causes a neuron to fire and transmitter to be released. The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the syna ...
... (a) A particular experience causes a neuron to fire and transmitter to be released. The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the syna ...
Slide ()
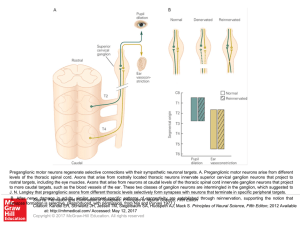
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
Re-examining the debate about the functional role of motor cortex
... motor cortical neurons to movement direction precipitated a protracted debate on the function of motor cortex. The success of the population vector approach led some to speculate that high level kinematic details of movement are represented by the firing rates of these neurons. Others more firmly ro ...
... motor cortical neurons to movement direction precipitated a protracted debate on the function of motor cortex. The success of the population vector approach led some to speculate that high level kinematic details of movement are represented by the firing rates of these neurons. Others more firmly ro ...
Name: Date: Period:
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
... human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
Sparse coding in the primate cortex
... especially in infero-temporal cortex (IT). Cells’ preferences in IT are often difficult to account for by reference to simple stimulus features, such as orientation, motion, position, or color, and they appear to lie in the domain of shape (Gross, Rocha-Miranda, and Bender, 1972; Perrett et al., 198 ...
... especially in infero-temporal cortex (IT). Cells’ preferences in IT are often difficult to account for by reference to simple stimulus features, such as orientation, motion, position, or color, and they appear to lie in the domain of shape (Gross, Rocha-Miranda, and Bender, 1972; Perrett et al., 198 ...
Bridging Rate Coding and Temporal Spike Coding
... Firing rates of spikes in the brain are thought to represent information in external stimuli. However, calculation in the brain often seems to complete in a shorter time scale than the time required for temporal averaging of spike signals necessary for obtaining firing rates. Actually, precisely tim ...
... Firing rates of spikes in the brain are thought to represent information in external stimuli. However, calculation in the brain often seems to complete in a shorter time scale than the time required for temporal averaging of spike signals necessary for obtaining firing rates. Actually, precisely tim ...
Neural Basis of the Oblique Effect
... – There are more cells tuned for cardinal orientations and these cells exhibit a narrower tuning width at horizontal angles. – The slopes of the tuning curves are also steeper for horizontal orientations. ...
... – There are more cells tuned for cardinal orientations and these cells exhibit a narrower tuning width at horizontal angles. – The slopes of the tuning curves are also steeper for horizontal orientations. ...
Assignment 2 - Gordon State College
... These questions can be answered from your textbook, class notes, and/or lecture slides. Complete this sheet and turn it in for 5 points extra credit on Test 1. It will not be graded but will be scanned for completeness and reasonable answers. 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via __ ...
... These questions can be answered from your textbook, class notes, and/or lecture slides. Complete this sheet and turn it in for 5 points extra credit on Test 1. It will not be graded but will be scanned for completeness and reasonable answers. 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via __ ...