Brumberg - QC Queens College
... individual elements of a cortical circuit and how they interact brings us a step closer to understanding the function of the circuit as a whole and ultimately its behavior in response to environmental stimuli. While the analogy applies to the neocortex, deciphering the cortical microcircuit is much ...
... individual elements of a cortical circuit and how they interact brings us a step closer to understanding the function of the circuit as a whole and ultimately its behavior in response to environmental stimuli. While the analogy applies to the neocortex, deciphering the cortical microcircuit is much ...
Nervous_System_Neurons
... carry impulses “in between” sensory neurons and motor neurons found in the spinal cord ...
... carry impulses “in between” sensory neurons and motor neurons found in the spinal cord ...
Name
... 2. tumors formed by over-reproduction of glial cells; commonly known as brain tumors 3. whitish, fatty covering which protects and insulates nerve fibers 4. short, branched afferent process of a neuron 5. bundles of neuron processes in the CNS 6. long, slender, efferent process of a neuron 7. nerve ...
... 2. tumors formed by over-reproduction of glial cells; commonly known as brain tumors 3. whitish, fatty covering which protects and insulates nerve fibers 4. short, branched afferent process of a neuron 5. bundles of neuron processes in the CNS 6. long, slender, efferent process of a neuron 7. nerve ...
E1 – Stimulus and response - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... transmit nerve impulse within the CNS from sensory to motor neuron ...
... transmit nerve impulse within the CNS from sensory to motor neuron ...
Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now
... What is a stimulus? How do your senses work? Homework: 594-602 #1-5 ...
... What is a stimulus? How do your senses work? Homework: 594-602 #1-5 ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
Invariant selectivity of auditory neurons due to predictive coding
... The model can account for nonlinear contextual effects such as two-tone and forward suppression. The model neurons adapt rapidly to new input statistics (such as behaviorally relevant tones). The model can be used to explain neuronal and behavioral responses. ...
... The model can account for nonlinear contextual effects such as two-tone and forward suppression. The model neurons adapt rapidly to new input statistics (such as behaviorally relevant tones). The model can be used to explain neuronal and behavioral responses. ...
Technical Definitions
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
Estimating Dynamic Neural Interactions in Awake Behaving Animals
... Neurons embedded in a network are correlated, and can produce synchronous spiking activities with millisecond precision. It is likely that the correlated activity organizes dynamically during behavior and cognition, and this may be independent from spike rates of individual neurons. Consequently cur ...
... Neurons embedded in a network are correlated, and can produce synchronous spiking activities with millisecond precision. It is likely that the correlated activity organizes dynamically during behavior and cognition, and this may be independent from spike rates of individual neurons. Consequently cur ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... synaptic cleft, a microscopic gap between the terminal button of one neuron and the cell membrane of another neuron. • The arrival of an action potential at an axon’s terminal buttons triggers the release of neurotransmitters- chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. • The che ...
... synaptic cleft, a microscopic gap between the terminal button of one neuron and the cell membrane of another neuron. • The arrival of an action potential at an axon’s terminal buttons triggers the release of neurotransmitters- chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. • The che ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... 30. The reticular formation or reticular __________________ system functions in regulating ________________ and __________________. 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the ap ...
... 30. The reticular formation or reticular __________________ system functions in regulating ________________ and __________________. 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the ap ...
Neural Development - Peoria Public Schools
... Synapses that are not used do not persist • Synapses can be formed at any stage in life. • When used: a. Chemical markers are left that strengthen a synapse. • When not used: a. Synapse is weak due to no chemical markers. ...
... Synapses that are not used do not persist • Synapses can be formed at any stage in life. • When used: a. Chemical markers are left that strengthen a synapse. • When not used: a. Synapse is weak due to no chemical markers. ...
Slide ()
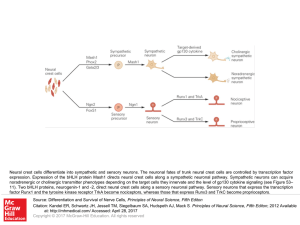
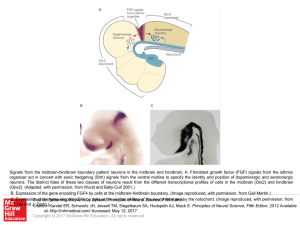
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
The Brain and Behavior
... the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the skin or muscle. ...
... the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the skin or muscle. ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
... Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
Neuron_Exercises_HPsychAY10
... will complete the following “stations” and/or projects in whatever order seems best to you: 1. Create a diagram of the structure of the neuron using construction paper and crayons or pencils. 2. Answer the following on a separate piece of paper: a. what are the three major tasks of neurons? b. give ...
... will complete the following “stations” and/or projects in whatever order seems best to you: 1. Create a diagram of the structure of the neuron using construction paper and crayons or pencils. 2. Answer the following on a separate piece of paper: a. what are the three major tasks of neurons? b. give ...
The Biology of Mind
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...