The Neuron: Building Block of the Nervous System
... The Action Potential All-or-None Principle – Refers to the fact that the ...
... The Action Potential All-or-None Principle – Refers to the fact that the ...
NEURONS
... EX- light, gravity, food, etc. *The ability to RESPOND to a stimulus is common to _______ living things !!! ...
... EX- light, gravity, food, etc. *The ability to RESPOND to a stimulus is common to _______ living things !!! ...
vocabulary worksheet
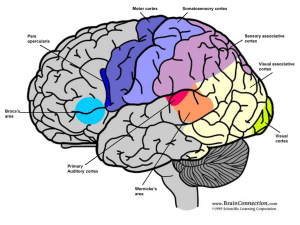
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
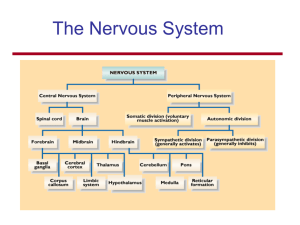
The Nervous System
... • In order to maintain homeostasis, organisms must be able to respond to internal and external stimuli. • In order to be able to respond to stimuli, the human body needs the nervous system to bring messages from one place to another. • Nerve cells (neurons) are the basic fundamental unit of the ner ...
... • In order to maintain homeostasis, organisms must be able to respond to internal and external stimuli. • In order to be able to respond to stimuli, the human body needs the nervous system to bring messages from one place to another. • Nerve cells (neurons) are the basic fundamental unit of the ner ...
Characterization of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
eating spaghetti!
... nerve impulse in the second neuron. The electrical signal is changing from positive to negative, and it moves the nerve impulse along a neuron. Neurons are in a fiber-like bundle called a nerve, and the impulses are all traveling in the same direction. ...
... nerve impulse in the second neuron. The electrical signal is changing from positive to negative, and it moves the nerve impulse along a neuron. Neurons are in a fiber-like bundle called a nerve, and the impulses are all traveling in the same direction. ...
Textbook PowerPoint
... Relative Refractory Period Neuron would only respond to very strong impulse ...
... Relative Refractory Period Neuron would only respond to very strong impulse ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excitatory potentials may be needed before a postsynaptic ...
... • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excitatory potentials may be needed before a postsynaptic ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... neural impulses; the allor-nothing electrical bursts that begin at one end of the axon of a neuron and move along the axon to the other end ...
... neural impulses; the allor-nothing electrical bursts that begin at one end of the axon of a neuron and move along the axon to the other end ...
A neuron receives input from other neurons
... The brain contains over 100 billion specialized cells called neurons. Neurons can be thought of as the basic processing units of the brain and convey signals by passing electrical impulses called action potentials from one end of themselves to another. Action potentials are generated by the o ...
... The brain contains over 100 billion specialized cells called neurons. Neurons can be thought of as the basic processing units of the brain and convey signals by passing electrical impulses called action potentials from one end of themselves to another. Action potentials are generated by the o ...
Text S2: Conflicting demands of localization and pattern
... However, in order to achieve invariance with respect to x and µ in the central pattern neuron, we can make use of the subtraction of the peripheries. For any given ∆x this means that rper(x+µ+∆x) - rper(x+µ-∆x) = rdir(∆x). After differentiating this equation with respect to (x+µ) and rearranging we ...
... However, in order to achieve invariance with respect to x and µ in the central pattern neuron, we can make use of the subtraction of the peripheries. For any given ∆x this means that rper(x+µ+∆x) - rper(x+µ-∆x) = rdir(∆x). After differentiating this equation with respect to (x+µ) and rearranging we ...
Tutorial 10: Temporal and Spatial Summation Figure 10: Temporal
... separate points of the dendritic tree (Kogo & Ariel, 1999). Two distinct responses are distinguished based on the interval between the time of stimulation at each of the two sites of postsynaptic membrane. Surprisingly, a facilitation of response was never observed. This could be a unique characteri ...
... separate points of the dendritic tree (Kogo & Ariel, 1999). Two distinct responses are distinguished based on the interval between the time of stimulation at each of the two sites of postsynaptic membrane. Surprisingly, a facilitation of response was never observed. This could be a unique characteri ...
lec12
... • Every atomic vector and every association is stored in the clean-up memory. – The memory can take a degraded vector and return the closest stored vector, plus a goodness of fit. – It needs to be a matrix memory (or something similar) that can store many different vectors accurately. • Each time a ...
... • Every atomic vector and every association is stored in the clean-up memory. – The memory can take a degraded vector and return the closest stored vector, plus a goodness of fit. – It needs to be a matrix memory (or something similar) that can store many different vectors accurately. • Each time a ...
Psychology`s biological roots: neurons and neural communication
... When the action is over, the positive sodium, is pumped back out until next time ...
... When the action is over, the positive sodium, is pumped back out until next time ...