I. The Cold War
... more than 12 million people, including 6 million European Jews, during WWII Genocide • Mass murder of people because of their race, religion, ethnicity, politics, or culture ...
... more than 12 million people, including 6 million European Jews, during WWII Genocide • Mass murder of people because of their race, religion, ethnicity, politics, or culture ...
Cold War Quiz
... the world. First, 31.___________, the world’s most populous nation, became communist. Second, the 32._________ __________ exploded an atomic bomb. Many Americans feared that communist spies held important positions in the federal government, because of the trials of 33.________ ________ and 34._____ ...
... the world. First, 31.___________, the world’s most populous nation, became communist. Second, the 32._________ __________ exploded an atomic bomb. Many Americans feared that communist spies held important positions in the federal government, because of the trials of 33.________ ________ and 34._____ ...
Chapter 28: Cold War and a New Western World 1945-1970
... Responsible and in power during the Cuban Missile Crisis, the tensest year of the Cold War. ...
... Responsible and in power during the Cuban Missile Crisis, the tensest year of the Cold War. ...
From World War to Cold War Sec. 5
... them was attacked. In 1955, the Soviet union responded by forming its own military alliance, the Warsaw Pact. It included the USSR and seven satellite states in Eastern Europe. Unlike NATO, however, the Warsaw Pact was a weapon used by Soviets to keep its satellites in order. ...
... them was attacked. In 1955, the Soviet union responded by forming its own military alliance, the Warsaw Pact. It included the USSR and seven satellite states in Eastern Europe. Unlike NATO, however, the Warsaw Pact was a weapon used by Soviets to keep its satellites in order. ...
Chapter 36 1. Explain the causes and consequences of the post
... d. Term for the dramatic rise in U.S. births that began immediately after World War II e. Big Three wartime conference that later became the focus of charges that Roosevelt had "sold out" Eastern Europe to the Soviet communists f. The extended post-World War II confrontation between the United State ...
... d. Term for the dramatic rise in U.S. births that began immediately after World War II e. Big Three wartime conference that later became the focus of charges that Roosevelt had "sold out" Eastern Europe to the Soviet communists f. The extended post-World War II confrontation between the United State ...
C29 Khrushchev to British retreat from Empire
... United States refuses to Soviet Union protest about the military intervention, but also do not intervene result was Egypt maintains control of the canal, while United States and the Soviet Union show constraint in attempting to avoid war ...
... United States refuses to Soviet Union protest about the military intervention, but also do not intervene result was Egypt maintains control of the canal, while United States and the Soviet Union show constraint in attempting to avoid war ...
CHAPTER 1: FROM WORLD WAR TO COLD WAR
... defeat fascism. Churchill deemed it a “deal with the devil.” If history had taken a different turn, the United States could have aligned with Hitler against Stalin. This unlikely alliance was forced when Hitler reneged on the Molotov-Rippendorp Pact—the non-aggression agreement signed by Germany and ...
... defeat fascism. Churchill deemed it a “deal with the devil.” If history had taken a different turn, the United States could have aligned with Hitler against Stalin. This unlikely alliance was forced when Hitler reneged on the Molotov-Rippendorp Pact—the non-aggression agreement signed by Germany and ...
BELL QUIZ: USE PAGES 605-608
... though they were allies in WWII. WHY? 1) Soviets upset about not being invited to Treaty of Versailles (peace treaty ending WWI). 2) Soviets were stripped of their colonies in Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. 3) Soviets resent the U.S. delay in attacking Germany in Europe. (didn’t happen unt ...
... though they were allies in WWII. WHY? 1) Soviets upset about not being invited to Treaty of Versailles (peace treaty ending WWI). 2) Soviets were stripped of their colonies in Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. 3) Soviets resent the U.S. delay in attacking Germany in Europe. (didn’t happen unt ...
CHAPTER 29 – THE COLD WAR ERA AND THE EMERGENCE OF
... VI. The Turmoil of French Decolonization A. France and Algeria B. France and Vietnam C. Vietnam Drawn into the Cold War D. Direct United States Involvement VII. The Collapse of European Communism A. Gorbachev Attempts to Reform the Soviet Union B. 1989: Revolution in Eastern Europe C. The Collapse ...
... VI. The Turmoil of French Decolonization A. France and Algeria B. France and Vietnam C. Vietnam Drawn into the Cold War D. Direct United States Involvement VII. The Collapse of European Communism A. Gorbachev Attempts to Reform the Soviet Union B. 1989: Revolution in Eastern Europe C. The Collapse ...
PowerPoint
... cooperated to win WWII but conflicts in ways of thinking and mutual distrust led to the development of the Cold War. – Containment – What is the difference between a “cold war” and a “hot war” ...
... cooperated to win WWII but conflicts in ways of thinking and mutual distrust led to the development of the Cold War. – Containment – What is the difference between a “cold war” and a “hot war” ...
Cold War
... cooperated to win WWII but conflicts in ways of thinking and mutual distrust led to the development of the Cold War. – Containment – What is the difference between a “cold war” and a “hot war” ...
... cooperated to win WWII but conflicts in ways of thinking and mutual distrust led to the development of the Cold War. – Containment – What is the difference between a “cold war” and a “hot war” ...
The Cold War
... Union and the rest of the world was what? The Berlin Wall- November 9, 1989 30 years after the wall had been put up. ...
... Union and the rest of the world was what? The Berlin Wall- November 9, 1989 30 years after the wall had been put up. ...
Cold War
... and other needed supplies like medicine and food from entering West Berlin. •The United States and the UN flew planes and dropped these needed supplies into West Berlin. ...
... and other needed supplies like medicine and food from entering West Berlin. •The United States and the UN flew planes and dropped these needed supplies into West Berlin. ...
End of the Cold War - Scott County Schools
... • Once the door to criticism was cracked open, it couldn’t be cut off again – Glasnost (openness) ...
... • Once the door to criticism was cracked open, it couldn’t be cut off again – Glasnost (openness) ...
THE EARLY COLD WAR
... Truman Doctrine • Truman Doctrine: Truman declared that the United States would support any nation resisting a Communist takeover. • Containment: The belief that Communism should be contained and not allowed to spread. ...
... Truman Doctrine • Truman Doctrine: Truman declared that the United States would support any nation resisting a Communist takeover. • Containment: The belief that Communism should be contained and not allowed to spread. ...
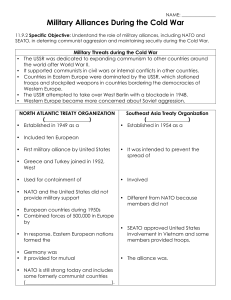
Military Alliances
... The USSR was dedicated to expanding communism to other countries around the world after World War II. It supported communists in civil wars or internal conflicts in other countries. Countries in Eastern Europe were dominated by the USSR, which stationed troops and stockpiled weapons in countries bor ...
... The USSR was dedicated to expanding communism to other countries around the world after World War II. It supported communists in civil wars or internal conflicts in other countries. Countries in Eastern Europe were dominated by the USSR, which stationed troops and stockpiled weapons in countries bor ...
Ch. 10 Review
... between the United States, Great Britain, France and Canada • Warsaw Pact- Soviet Union alliance system with Eastern European satellite countries after creation of NATO • Countries choosing sides after WWII ...
... between the United States, Great Britain, France and Canada • Warsaw Pact- Soviet Union alliance system with Eastern European satellite countries after creation of NATO • Countries choosing sides after WWII ...
Early Cold War Events
... Western allies control West Germany. The Soviets control East Germany. West Germany has a democratic government while East Germany has a communist government. The Western Allies also control a part of Berlin, which is surrounded by East Germany, which will cause problems for decades. ...
... Western allies control West Germany. The Soviets control East Germany. West Germany has a democratic government while East Germany has a communist government. The Western Allies also control a part of Berlin, which is surrounded by East Germany, which will cause problems for decades. ...
The Cold War - Reading Community Schools
... between the two countries during the Cold War led to serious situations that could escalate to nuclear war (Cuban Missile Crisis) Avoid a serious, dangerous game of “telephone” – misinterpretations that happen when multiple people pass on messages ...
... between the two countries during the Cold War led to serious situations that could escalate to nuclear war (Cuban Missile Crisis) Avoid a serious, dangerous game of “telephone” – misinterpretations that happen when multiple people pass on messages ...
The Cold War
... because they left the winning side; now they wanted to gain land because they had won. – They wanted to economically raid Eastern Europe to recoup their expenses during the war. – They saw the U.S. as a threat to their way of life; especially after the U.S. development of atomic weapons. ...
... because they left the winning side; now they wanted to gain land because they had won. – They wanted to economically raid Eastern Europe to recoup their expenses during the war. – They saw the U.S. as a threat to their way of life; especially after the U.S. development of atomic weapons. ...
The Cold War and the Collapse of the USSR
... independent state. The authority of the Soviet Union was discarded, and communism came to an abrupt end in Eastern Europe. Yeltsin was elected president of the newly formed Commonwealth of Independent States, which included Russia and many of the former republics of the Soviet Union. Boris Yeltsin ...
... independent state. The authority of the Soviet Union was discarded, and communism came to an abrupt end in Eastern Europe. Yeltsin was elected president of the newly formed Commonwealth of Independent States, which included Russia and many of the former republics of the Soviet Union. Boris Yeltsin ...
Ancient Rome
... about 500 actors, writers, producers, and directors who were not allowed to work on Hollywood films because of their alleged Communist connections. Subversives: people who work secretly inside a country to overthrow the government. ...
... about 500 actors, writers, producers, and directors who were not allowed to work on Hollywood films because of their alleged Communist connections. Subversives: people who work secretly inside a country to overthrow the government. ...
The Cold War - World History
... • The main fear is that the standard of living is so low in Europe, it’s citizens will turn to communism, and fall under Soviet Dominance • Turn to a Partner - How should president Truman react to this problem? ...
... • The main fear is that the standard of living is so low in Europe, it’s citizens will turn to communism, and fall under Soviet Dominance • Turn to a Partner - How should president Truman react to this problem? ...
Cold War

The Cold War was a state of political and military tension after World War II between powers in the Western Bloc (the United States, its NATO allies and others) and powers in the Eastern Bloc (the Soviet Union and its allies in the Warsaw Pact).Historians have not fully agreed on the dates, but 1947–1991 is common. It was termed as ""cold"" because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two sides, although there were major regional wars, known as proxy wars, in Korea, Vietnam and Afghanistan that the two sides supported. The Cold War split the temporary wartime alliance against Nazi Germany, leaving the USSR and the US as two superpowers with profound economic and political differences: the former being a single-party Marxist–Leninist state operating planned economy and controlled press while professing state atheism and owning exclusively the right to establish and govern communities, and the latter being a capitalist state with generally free elections and press, which also granted freedom of religion and freedom of association to its citizens. A self-proclaimed neutral bloc arose with the Non-Aligned Movement founded by Egypt, India, Indonesia and Yugoslavia; this faction rejected association with either the US-led West or the Soviet-led East. The two superpowers never engaged directly in full-scale armed combat but they each armed heavily in preparation for a possible all-out nuclear world war. Each side had a nuclear deterrent that deterred an attack by the other side, on the basis that such an attack would lead to total destruction of the attacker: the doctrine of mutually assured destruction (MAD). Aside from the development of the two sides' nuclear arsenals, and deployment of conventional military forces, the struggle for dominance was expressed via proxy wars around the globe, psychological warfare, massive propaganda campaigns and espionage, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race.The first phase of the Cold War began in the first two years after the end of the Second World War in 1945. The USSR consolidated its control over the states of the Eastern Bloc while the United States began a strategy of global containment to challenge Soviet power, extending military and financial aid to the countries of Western Europe (for example, supporting the anti-Communist side in the Greek Civil War) and creating the NATO alliance. The Berlin Blockade (1948–49) was the first major crisis of the Cold War.With victory of the Communist side in the Chinese Civil War and the outbreak of the Korean War (1950–53), the conflict expanded. The USSR and USA competed for influence in Latin America and decolonizing states of Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. Meanwhile, the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 was stopped by the Soviets. The expansion and escalation sparked more crises, such as the Suez Crisis (1956), the Berlin Crisis of 1961, and the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962. Following this last crisis a new phase began that saw the Sino-Soviet split complicate relations within the Communist sphere while US allies, particularly France, demonstrated greater independence of action. The USSR crushed the 1968 Prague Spring liberalization program in Czechoslovakia, and the Vietnam War (1955–1975) ended with a defeat of the US-backed Republic of South Vietnam, prompting further adjustments.By the 1970s, both sides had become interested in accommodations to create a more stable and predictable international system, inaugurating a period of détente that saw Strategic Arms Limitation Talks and the US opening relations with the People's Republic of China as a strategic counterweight to the Soviet Union. Détente collapsed at the end of the decade with the Soviet war in Afghanistan beginning in 1979.The early 1980s were another period of elevated tension, with the Soviet downing of Korean Air Lines Flight 007 (1983), and the ""Able Archer"" NATO military exercises (1983). The United States increased diplomatic, military, and economic pressures on the Soviet Union, at a time when the communist state was already suffering from economic stagnation. In the mid-1980s, the new Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced the liberalizing reforms of perestroika (""reorganization"", 1987) and glasnost (""openness"", c. 1985) and ended Soviet involvement in Afghanistan. Pressures for national independence grew stronger in Eastern Europe, especially Poland. Gorbachev meanwhile refused to use Soviet troops to bolster the faltering Warsaw Pact regimes as had occurred in the past. The result in 1989 was a wave of revolutions that peacefully (with the exception of the Romanian Revolution) overthrew all of the Communist regimes of Central and Eastern Europe. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union itself lost control and was banned following an abortive coup attempt in August 1991. This in turn led to the formal dissolution of the USSR in December 1991 and the collapse of Communist regimes in other countries such as Mongolia, Cambodia and South Yemen. The United States remained as the world's only superpower.The Cold War and its events have left a significant legacy, and it is often referred to in popular culture, especially in media featuring themes of espionage (such as the internationally successful James Bond film series) and the threat of nuclear warfare.