The Torah of Life - The Torah Science Foundation
... program that starts with a germinating seed and culminates in fruits and new seeds. The Tree of Life symbolizes the creation of life, and the evolution of life from the perspective of the Torah. “Knowledge” in Hebrew also means “consciousness.” The Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil symbolizes the “ ...
... program that starts with a germinating seed and culminates in fruits and new seeds. The Tree of Life symbolizes the creation of life, and the evolution of life from the perspective of the Torah. “Knowledge” in Hebrew also means “consciousness.” The Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil symbolizes the “ ...
Adaptation of Firing Rate and Spike
... was defined as the slope of the voltage– current relationship obtained by measuring membrane voltage during the last 10 ms of 100 ms depolarizing current injections from 0 to 200 pA. Cells that fired action potentials throughout the depolarizing steps in the presence of ␣-DTX were not used for measu ...
... was defined as the slope of the voltage– current relationship obtained by measuring membrane voltage during the last 10 ms of 100 ms depolarizing current injections from 0 to 200 pA. Cells that fired action potentials throughout the depolarizing steps in the presence of ␣-DTX were not used for measu ...
Odorant Category Profile Selectivity of Olfactory Cortex Neurons
... continuously monitored by measuring the individual foods show distinct odorant-category profiles. The names of the odorants in the boxes a–z, aa–az, ba– bz, and ca– cr chest movement with a strain gauge (TR-651T; are listed in the supplemental Figures 1 and 2 (available at www.jneurosci.org as suppl ...
... continuously monitored by measuring the individual foods show distinct odorant-category profiles. The names of the odorants in the boxes a–z, aa–az, ba– bz, and ca– cr chest movement with a strain gauge (TR-651T; are listed in the supplemental Figures 1 and 2 (available at www.jneurosci.org as suppl ...
Cerebrospinal fluid nerve growth factor levels in patients with
... AD exists in a genetically determined form, known as the familial form (with an autosomal dominant character), and a sporadic form. Postmortem studies of brains from AD patients show cortical atrophy with a loss of from 8% to 10% of brain weight every 10 years of disease progression and histopatholo ...
... AD exists in a genetically determined form, known as the familial form (with an autosomal dominant character), and a sporadic form. Postmortem studies of brains from AD patients show cortical atrophy with a loss of from 8% to 10% of brain weight every 10 years of disease progression and histopatholo ...
Developmental origin of shark electrosensory organs
... skin and transmit them somatotopically to the brain. In chondrichthyans, the electrosensory system is composed of a cephalic network of ampullary organs, known as the ampullae of Lorenzini, that can detect extremely weak electric fields during hunting and navigation. Each ampullary organ consists of ...
... skin and transmit them somatotopically to the brain. In chondrichthyans, the electrosensory system is composed of a cephalic network of ampullary organs, known as the ampullae of Lorenzini, that can detect extremely weak electric fields during hunting and navigation. Each ampullary organ consists of ...
TOPIC: progesterone exert neuroprotective and myelinating effects
... Progesterone (PROG) is synthesized in the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Its direct precursor pregnenolone is either derived from the circulation or from local de novo synthesis as cytochrome P450scc, which converts cholesterol to pregnenolone, is expressed in the nervous system. Pregneno ...
... Progesterone (PROG) is synthesized in the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Its direct precursor pregnenolone is either derived from the circulation or from local de novo synthesis as cytochrome P450scc, which converts cholesterol to pregnenolone, is expressed in the nervous system. Pregneno ...
Multiple dynamic representations in the motor cortex
... L2/3 neurons also participate in learning-related plasticity. Synapses from the somatosensory cortex to L2/3 neurons are critical for learning new motor skills13 and support long-term potentiation14. Learning causes plasticity in networks of L2/3 cells5,15. L2/3 neurons are thus poised to organize l ...
... L2/3 neurons also participate in learning-related plasticity. Synapses from the somatosensory cortex to L2/3 neurons are critical for learning new motor skills13 and support long-term potentiation14. Learning causes plasticity in networks of L2/3 cells5,15. L2/3 neurons are thus poised to organize l ...
microcircuits in the striatum striatal cell types and their
... Figure 2. Paired whole cell recordings of spiny neurons in organotypic cocultures. A. Spontaneous cortical activity in the culture (not shown) drives spiny neurons through up and down state transitions. Up states are characterized by a relatively fast transition from the down state at ~ -80 mV to th ...
... Figure 2. Paired whole cell recordings of spiny neurons in organotypic cocultures. A. Spontaneous cortical activity in the culture (not shown) drives spiny neurons through up and down state transitions. Up states are characterized by a relatively fast transition from the down state at ~ -80 mV to th ...
Spike-Timing Theory of Working Memory
... n1, n2, …, n7 have different axonal conduction delays arranged such that the network forms two functional subnetworks, red and black, corresponding to two distinct PNGs, consisting of the same neurons. Firing of neurons n1 and n2 can trigger the whole red or black PNG: (B) If neuron n1 fires followe ...
... n1, n2, …, n7 have different axonal conduction delays arranged such that the network forms two functional subnetworks, red and black, corresponding to two distinct PNGs, consisting of the same neurons. Firing of neurons n1 and n2 can trigger the whole red or black PNG: (B) If neuron n1 fires followe ...
Otxl and Otx2 Define Layers and Regions in Developing Cerebral
... of pattern in addition to lamination. Each of these structures is also divided along the plane tangential to the pial surface into functionally distinct areas or regions. The cerebral cortex is composed of areas that subserve functions ranging from the processing of incoming sensory information to t ...
... of pattern in addition to lamination. Each of these structures is also divided along the plane tangential to the pial surface into functionally distinct areas or regions. The cerebral cortex is composed of areas that subserve functions ranging from the processing of incoming sensory information to t ...
Cell Surface Molecules Containing IV
... yellow-stained neurons were made with a 63 x Plan Neofluor objective (N.A. 1.3) and a camera lucida, using a wide-band fluorescein filter set. Cells were selected for reconstruction based on extensive filling of axon collaterals, and cells with evident truncation of axons were not used. However, som ...
... yellow-stained neurons were made with a 63 x Plan Neofluor objective (N.A. 1.3) and a camera lucida, using a wide-band fluorescein filter set. Cells were selected for reconstruction based on extensive filling of axon collaterals, and cells with evident truncation of axons were not used. However, som ...
Stem cell factor induces outgrowth of c-kit-positive
... resulted from the survival of DRG neurons induced by rmSCF. Since quantitation of neuronal survival is difficult in organ cultures of DRGs, those from 15.5-day p.c. embryos were dissociated into single cells by trypsinization. These were cultured and the number of surviving neurons was counted. When ...
... resulted from the survival of DRG neurons induced by rmSCF. Since quantitation of neuronal survival is difficult in organ cultures of DRGs, those from 15.5-day p.c. embryos were dissociated into single cells by trypsinization. These were cultured and the number of surviving neurons was counted. When ...
Mouse Nerve Growth Factor Prevents Degeneration of Axotomized
... edge-detection program. Particular effort was made to eliminate ChATimmunoreactive swollen fiber fragments (present only in the caudal MSN in lesioned animals) from analysis. For statistical analysis, the numbers of neurons ipsilateral to the lesion were expressed as percentages of numbers of nerve ...
... edge-detection program. Particular effort was made to eliminate ChATimmunoreactive swollen fiber fragments (present only in the caudal MSN in lesioned animals) from analysis. For statistical analysis, the numbers of neurons ipsilateral to the lesion were expressed as percentages of numbers of nerve ...
LYRICA (pregabalin) eLearning System
... caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction in the nervous system itself. Neuropathic pain is sometimes perceived at a location remote from the actual site of injury, the pain is often out of proportion to the stimulus, and the duration of the pain may be prolonged. Two of the key types of neuropathic ...
... caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction in the nervous system itself. Neuropathic pain is sometimes perceived at a location remote from the actual site of injury, the pain is often out of proportion to the stimulus, and the duration of the pain may be prolonged. Two of the key types of neuropathic ...
Serotonin release from the neuronal cell body and its long
... assembles a complementary active actin–myosin transport system that propels the vesicles towards the plasma membrane at a lower energy cost [44]. ...
... assembles a complementary active actin–myosin transport system that propels the vesicles towards the plasma membrane at a lower energy cost [44]. ...
Dual single unit recording in Globus Pallidus (GP) and Subthalamic
... At the end of each experiment, the recording sites were marked by the microiontophoresis of Pontamine Skyblue (-20 µA, 15 min). Each rat was given an overdose of Urethane. The brain was immediately removed and fixed in 4% Para formaldehyde for 4 hrs and placed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with ...
... At the end of each experiment, the recording sites were marked by the microiontophoresis of Pontamine Skyblue (-20 µA, 15 min). Each rat was given an overdose of Urethane. The brain was immediately removed and fixed in 4% Para formaldehyde for 4 hrs and placed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with ...
cortical input to the basal forebrain
... asymmetric synaptic contacts with neurons that were immunonegative for choline acetyltransferase, including spines and small dendrites (87%) or dendritic shafts (13%). Unequivocal evidence for synaptic interactions between tracer labeled terminals and cholinergic profiles could not be obtained in th ...
... asymmetric synaptic contacts with neurons that were immunonegative for choline acetyltransferase, including spines and small dendrites (87%) or dendritic shafts (13%). Unequivocal evidence for synaptic interactions between tracer labeled terminals and cholinergic profiles could not be obtained in th ...
Reward-Dependent Spatial Selectivity of Anticipatory Activity in
... of the previous studies were not designed to differentiate between these possibilities, since the task-related events were, typically, behaviorally significant in that they were followed by reward. Although some recent studies have provided an experimental condition in which different events (stimul ...
... of the previous studies were not designed to differentiate between these possibilities, since the task-related events were, typically, behaviorally significant in that they were followed by reward. Although some recent studies have provided an experimental condition in which different events (stimul ...
Brainstem
... project to the nucleus cuneatus - primary afferents below T6 ascend in the fasciculus gracilis and project to the nucleus gracilis - axons of 2nd neurons in the posterior column nuclei course ventromedially (as the internal arcuate fibers) and cross to the opposite side (sensory decussation) above t ...
... project to the nucleus cuneatus - primary afferents below T6 ascend in the fasciculus gracilis and project to the nucleus gracilis - axons of 2nd neurons in the posterior column nuclei course ventromedially (as the internal arcuate fibers) and cross to the opposite side (sensory decussation) above t ...
C-fos Expression in the Pons and Medulla of the Cat during
... clean and topical antibiotics were administered on a daily basis. Following a 5-7 d period, the cats were adapted to the recording apparatus; thereafter, they exhibited spontaneous periods of wakefulness, quiet sleep, and active sleep. Experimental paradigm. Following the adaptation period, the dura ...
... clean and topical antibiotics were administered on a daily basis. Following a 5-7 d period, the cats were adapted to the recording apparatus; thereafter, they exhibited spontaneous periods of wakefulness, quiet sleep, and active sleep. Experimental paradigm. Following the adaptation period, the dura ...
Neurokinin B Signaling in the Female Rat: a Novel
... The underlying mechanism involves stress-induced suppression of the GnRH pulse generator, the functional unit of which is considered to be the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin A neurons. Agonists of the neurokinin B (NKB) receptor (NK3R) have been shown to suppress the ...
... The underlying mechanism involves stress-induced suppression of the GnRH pulse generator, the functional unit of which is considered to be the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin A neurons. Agonists of the neurokinin B (NKB) receptor (NK3R) have been shown to suppress the ...
Guided outgrowth of leech neurons in culture
... bent lanes. Foot-like sites of adhesion are revealed at intervals of about l0 pro. The neurites are connected to these sites by filaments. ...
... bent lanes. Foot-like sites of adhesion are revealed at intervals of about l0 pro. The neurites are connected to these sites by filaments. ...
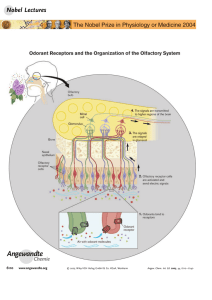
Scents and Sensibility: A Molecular Logic of Olfactory Perception
... same time, a research fellow, Dan Littman, now a Professor at NYU, joined the lab and was interested in two molecules that characterize the major classes of T cells. Dan, along with a student, Paul Maddon, succeeded in exploiting the gene transfer to isolate these two molecules. As often in science, ...
... same time, a research fellow, Dan Littman, now a Professor at NYU, joined the lab and was interested in two molecules that characterize the major classes of T cells. Dan, along with a student, Paul Maddon, succeeded in exploiting the gene transfer to isolate these two molecules. As often in science, ...
Nissl substance and cellular structures involved in the intraneuronal
... The neuronal and glial membranes are separated by a 10-15 nm gap [8]. Small molecules and ions easily diffuse through this space. Macromolecules like proteins and mRNA cannot cross cellular membranes. After vesicular transport from the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane, proteins are released from ...
... The neuronal and glial membranes are separated by a 10-15 nm gap [8]. Small molecules and ions easily diffuse through this space. Macromolecules like proteins and mRNA cannot cross cellular membranes. After vesicular transport from the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane, proteins are released from ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) The ANS consists of motor
... When the main fibers reach the esophagus, they intermingle then “ride” the esophagus down to the abdominal cavity and innervate the liver, gall bladder, stomach, small intestine, kidneys, pancreas, and proximal half of the large intestine ...
... When the main fibers reach the esophagus, they intermingle then “ride” the esophagus down to the abdominal cavity and innervate the liver, gall bladder, stomach, small intestine, kidneys, pancreas, and proximal half of the large intestine ...