Spinal Cord
... Decussate in medulla into medial lemniscal tract Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st order neurons synapse with interneruons at level of spine entry creating reflex arcs ...
... Decussate in medulla into medial lemniscal tract Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st order neurons synapse with interneruons at level of spine entry creating reflex arcs ...
Physiology 1B
... The Axon Terminals at Synapse contain tiny vesicles, or sacs. These are known as Neurotansmitters. ...
... The Axon Terminals at Synapse contain tiny vesicles, or sacs. These are known as Neurotansmitters. ...
The dorsal anterior cingulate cortex ( BA32) in autism: an
... and 11 controls (28.1 ± 3.9 years) matched for age, gender and hemisphere, were obtained via the Autism Tissue Program (USA) with LREC approval. A 1-in-4 series of sections were immunolabelled to detect MAP2+ neurons (clone HM2, Sigma), and analysed using customised software (Image Pro Plus, Version ...
... and 11 controls (28.1 ± 3.9 years) matched for age, gender and hemisphere, were obtained via the Autism Tissue Program (USA) with LREC approval. A 1-in-4 series of sections were immunolabelled to detect MAP2+ neurons (clone HM2, Sigma), and analysed using customised software (Image Pro Plus, Version ...
Part 1: Multiple choice
... A. Red muscle fibers contract slowly and produce the smallest amount of force B. Large motor neurons are recruited only at higher levels of stimulus intensity C. The fastest, strongest muscle fibers can produce the most sustained force output <––– D. Successive stimulation of muscles can produce for ...
... A. Red muscle fibers contract slowly and produce the smallest amount of force B. Large motor neurons are recruited only at higher levels of stimulus intensity C. The fastest, strongest muscle fibers can produce the most sustained force output <––– D. Successive stimulation of muscles can produce for ...
Diseases of the Basal Ganglia
... along with their connected cortical and thalamic areas, are viewed as components of parallel circuits whose functional and morphological segregation is rather strictly maintained. Each circuit is thought to engage separate regions of the basal ganglia and thalamus, and the output of each appears to ...
... along with their connected cortical and thalamic areas, are viewed as components of parallel circuits whose functional and morphological segregation is rather strictly maintained. Each circuit is thought to engage separate regions of the basal ganglia and thalamus, and the output of each appears to ...
Slide 1
... – more than just a conduit for signals from periphery of body to brain and vice versa. – cord contains: • walking circuits. • reflexes circuits. ...
... – more than just a conduit for signals from periphery of body to brain and vice versa. – cord contains: • walking circuits. • reflexes circuits. ...
NMSI - 1 Intro to the Nervous System
... • The nervous system interacts with sensory and internal body systems to coordinate responses and behaviors. ...
... • The nervous system interacts with sensory and internal body systems to coordinate responses and behaviors. ...
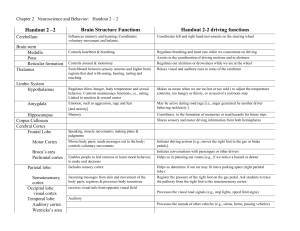
Handout 2 –2 Brain Structure Functions Handout 2-2 driving
... Linked to emotion & reward center ...
... Linked to emotion & reward center ...
Exam 3 Review KEY
... 6) The smaller / bigger the size of the nerve fiber, the slower / faster the speed of nerve impulse. And the less / more myelin, which means larger diameter of the nerve fiber, the greater the speed. 7) Bundles of afferent and efferent neurons outside the CNS but inside the PNS are referred to as ne ...
... 6) The smaller / bigger the size of the nerve fiber, the slower / faster the speed of nerve impulse. And the less / more myelin, which means larger diameter of the nerve fiber, the greater the speed. 7) Bundles of afferent and efferent neurons outside the CNS but inside the PNS are referred to as ne ...
Print this Page Presentation Abstract Program#/Poster#: 532.07/GG10
... Surround suppression in the cortex can be explained by normalization models in which the output is modulated by the summed local activity. In these models, the region of the sensory space that is pooled to produce suppression to a neuron is larger than that for summation. The neural implementation o ...
... Surround suppression in the cortex can be explained by normalization models in which the output is modulated by the summed local activity. In these models, the region of the sensory space that is pooled to produce suppression to a neuron is larger than that for summation. The neural implementation o ...
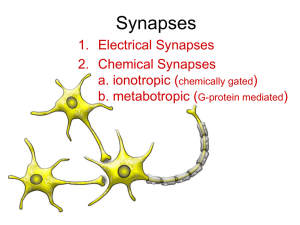
Synapses - Franklin College
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Reflex Arc - Point Loma High School
... Reflex Arc • Monosynaptic- When a reflex arc consists of only two ...
... Reflex Arc • Monosynaptic- When a reflex arc consists of only two ...
Chapter 8
... Control of Movement by the Brain Imitating and Comprehending Movements: Role of the Mirror Neuron System • Investigators found that neurons in an area of the rostral part of the ventral premotor cortex in the monkey brain (area F5) became active when monkeys saw people or other monkeys perform vari ...
... Control of Movement by the Brain Imitating and Comprehending Movements: Role of the Mirror Neuron System • Investigators found that neurons in an area of the rostral part of the ventral premotor cortex in the monkey brain (area F5) became active when monkeys saw people or other monkeys perform vari ...
Handouts - motor units
... Each muscle is innervated by a pool of motor neurons, which typically contains a mixture of motor unit types, although in different proportions depending on the typical use of that muscle. An orderly sequence of motor neuron activation within a pool leads to activation of units producing the smalles ...
... Each muscle is innervated by a pool of motor neurons, which typically contains a mixture of motor unit types, although in different proportions depending on the typical use of that muscle. An orderly sequence of motor neuron activation within a pool leads to activation of units producing the smalles ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... The junction or region between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites or cell body of another Sensory Neurons Neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the brain via the spinal cord. Motor Neurons Neurons that carry signals from the spinal cord and pro ...
... The junction or region between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites or cell body of another Sensory Neurons Neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the brain via the spinal cord. Motor Neurons Neurons that carry signals from the spinal cord and pro ...
Laminar and Columnar organization of the cerebral cortex
... The cortex is organized horizontally into six laminae, and vertically into groups of cells linked synaptically across the horizontal laminae. ...
... The cortex is organized horizontally into six laminae, and vertically into groups of cells linked synaptically across the horizontal laminae. ...
The Neural Control of Movement
... Repeated activation results in a change in the ability of the information to cross the synapse from sensory neuron to motor neuron ...
... Repeated activation results in a change in the ability of the information to cross the synapse from sensory neuron to motor neuron ...
(A): The Neuron
... Carry incoming information from sensory receptors to the brain/spinal cord E.g. Perceiving something as “hot” Carry outgoing information from the brain/spinal cord to the ...
... Carry incoming information from sensory receptors to the brain/spinal cord E.g. Perceiving something as “hot” Carry outgoing information from the brain/spinal cord to the ...
brainbeebootcamp 2017
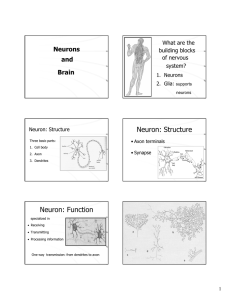
... Soma (cell body) – cell organelles Axon – conducts electrical impulse (action potential) Myelin: “insulation” for axon Node of Ranvier = gap in myelin Nerve terminal – contains neurotransmitter vesicles Synapse – communication with next neuron ...
... Soma (cell body) – cell organelles Axon – conducts electrical impulse (action potential) Myelin: “insulation” for axon Node of Ranvier = gap in myelin Nerve terminal – contains neurotransmitter vesicles Synapse – communication with next neuron ...
Movement
... Lowest level: The spinal cord which provides a point of contact between the nervous system and the muscles, and also controls reflexive movements. Middle level: The motor cortex and brainstem structures (plus the the cerebellum and basal ganglia) translate a specific set of action goals into mov ...
... Lowest level: The spinal cord which provides a point of contact between the nervous system and the muscles, and also controls reflexive movements. Middle level: The motor cortex and brainstem structures (plus the the cerebellum and basal ganglia) translate a specific set of action goals into mov ...
Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions
... • It is facilitatory to & motor neurons of the antigravity ms to maintain body posture & equilibrium in response to impulses from the vestibular apparatus which evoked by charges in head position or exposure to acceleration. • b. Medial V.S.T. • It is facilitatory to & motor neurons of the n ...
... • It is facilitatory to & motor neurons of the antigravity ms to maintain body posture & equilibrium in response to impulses from the vestibular apparatus which evoked by charges in head position or exposure to acceleration. • b. Medial V.S.T. • It is facilitatory to & motor neurons of the n ...
The Nervous System
... function • b. Primary motor area is on the precentral gyrus -governs conscious motor control which can be mapped ...
... function • b. Primary motor area is on the precentral gyrus -governs conscious motor control which can be mapped ...
Neurotransmission
... Neurons – a nerve cell that transmit information throughout the body via the nervous system. Synapse - is a small gap or junction between two neurons. ...
... Neurons – a nerve cell that transmit information throughout the body via the nervous system. Synapse - is a small gap or junction between two neurons. ...