Nociceptive system
... reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... types of neurons? Describe the structure and functions of the three parts of a neuron • Sensory Neurons: take info from sensory receptors to the CNS • Interneurons: Receive input from all sensory and other interneurons and communicate with motor neurons • Motor: Takes info from CNS to rest of body • ...
... types of neurons? Describe the structure and functions of the three parts of a neuron • Sensory Neurons: take info from sensory receptors to the CNS • Interneurons: Receive input from all sensory and other interneurons and communicate with motor neurons • Motor: Takes info from CNS to rest of body • ...
Research Methods
... Basically a combo of RF signals and a REALLY strong magnetic field Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function ...
... Basically a combo of RF signals and a REALLY strong magnetic field Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function ...
Stimulus space topology and geometry from neural activity
... generated in our brains. How do we do this? Many studies have investigated how the electrical activity of neurons (action potentials) is related to outside stimuli, and maps of these relationships – often called receptive fields – are routinely computed from data collected in neuroscience experiment ...
... generated in our brains. How do we do this? Many studies have investigated how the electrical activity of neurons (action potentials) is related to outside stimuli, and maps of these relationships – often called receptive fields – are routinely computed from data collected in neuroscience experiment ...
Text - Department of Physiology, UCLA
... Work in our lab spans many levels of analysis, from the molecular to the behavioral. We are studying how voltage controls the activity of K+ channels, how changes in channel function or expression affect the firing patterns of neurons and the emergent properties of neuronal circuits, and how alterin ...
... Work in our lab spans many levels of analysis, from the molecular to the behavioral. We are studying how voltage controls the activity of K+ channels, how changes in channel function or expression affect the firing patterns of neurons and the emergent properties of neuronal circuits, and how alterin ...
chapter 15 sensory, motor, and integrative systems
... 3. Which of the following is an example of rapid (phasic) adaptation? a. Loss of ability to smell the baking cake after a few minutes b. After too many stimuli, neurons start to fire uncontrollably c. Loss of ability to feel a toothache after 1 - 2 hours d. Hitting the “snooze” button when the alarm ...
... 3. Which of the following is an example of rapid (phasic) adaptation? a. Loss of ability to smell the baking cake after a few minutes b. After too many stimuli, neurons start to fire uncontrollably c. Loss of ability to feel a toothache after 1 - 2 hours d. Hitting the “snooze” button when the alarm ...
Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the
... identify when exactly and in which type of neurons Runx1t1is expressed in the developing dorsal root ganglion. My results show that the expression of Runx1t1 is very strong during embryonic development, at a time when different types of neurons are being specified. In the future, we are planning to ...
... identify when exactly and in which type of neurons Runx1t1is expressed in the developing dorsal root ganglion. My results show that the expression of Runx1t1 is very strong during embryonic development, at a time when different types of neurons are being specified. In the future, we are planning to ...
Parts and Functions of a Nervous System
... Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consists of a ______________ and spreading branches that send or receive impulses to and from other cells. The cell body varies in shape. ____ ...
... Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consists of a ______________ and spreading branches that send or receive impulses to and from other cells. The cell body varies in shape. ____ ...
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... *transmit information from the organs to the CNS and vice versa -All nerves are protected ->brain by the skull and sheathing ->spinal cord by vertebrae -> PNS by sheathing ...
... *transmit information from the organs to the CNS and vice versa -All nerves are protected ->brain by the skull and sheathing ->spinal cord by vertebrae -> PNS by sheathing ...
Chapter 4
... psychosocial experience; there will eventually be an alteration in cerebral function that accounts for disturbances in pt’s behavior and mental experience ...
... psychosocial experience; there will eventually be an alteration in cerebral function that accounts for disturbances in pt’s behavior and mental experience ...
What is CDNF?
... • CDNF was injected into Striatum of rats before 6-OHDA – CDNF prevented PD symptoms from occurring ...
... • CDNF was injected into Striatum of rats before 6-OHDA – CDNF prevented PD symptoms from occurring ...
The biological basis of behavior
... of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. • Synaptic vesicles: tiny sacs in a terminal button that release chemicals into the ...
... of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. • Synaptic vesicles: tiny sacs in a terminal button that release chemicals into the ...
Behavioral Neuroscience: The NeuroPsychological approach
... Bernard Katz (1911-2003, Nobel): neurotransmitter release in synapses is quantal (Ach in motor nerve -> muscles) ...
... Bernard Katz (1911-2003, Nobel): neurotransmitter release in synapses is quantal (Ach in motor nerve -> muscles) ...
Slide ()
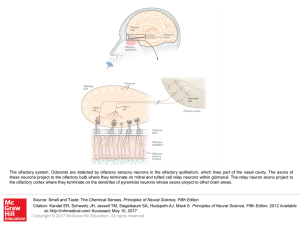
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Chapter 10 - Dr. Eric Schwartz
... by pathways that ascend to the cerebral cortex and by pathways that descend from some of the brainstem nuclei. • It is not known to what extent, if any, these structures are involved in initiating movements. • Their role is to establish the programs that determine the specific sequence of movements ...
... by pathways that ascend to the cerebral cortex and by pathways that descend from some of the brainstem nuclei. • It is not known to what extent, if any, these structures are involved in initiating movements. • Their role is to establish the programs that determine the specific sequence of movements ...
2015 Midterm Exam
... 53. Which of the following are consequences of the stress response? [increased heart rate / fragmented sleep / decreased exploration / “freezing-like” behavior] ...
... 53. Which of the following are consequences of the stress response? [increased heart rate / fragmented sleep / decreased exploration / “freezing-like” behavior] ...
Primary motor cortex
... Motor Cortex Cortical columns Motor patterns for synergistic muscle groups Stimulus amplification for contraction Dynamic and static neurons In motor cortex and Red nucleus (n. Ruber) ...
... Motor Cortex Cortical columns Motor patterns for synergistic muscle groups Stimulus amplification for contraction Dynamic and static neurons In motor cortex and Red nucleus (n. Ruber) ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... b. Brain reception region 8. Describe the following for the Anterolateral Spinothalamic Pathway. a. ...
... b. Brain reception region 8. Describe the following for the Anterolateral Spinothalamic Pathway. a. ...
What are Neurons
... neurons are specialized to transmit information throughout the body there are approximately 100 billion neurons in the human brain alone neurons, as highly specialized nerve cells, communicate information in both chemical and electrical forms (an electro-chemical process) There are thee basi ...
... neurons are specialized to transmit information throughout the body there are approximately 100 billion neurons in the human brain alone neurons, as highly specialized nerve cells, communicate information in both chemical and electrical forms (an electro-chemical process) There are thee basi ...