Slide ()
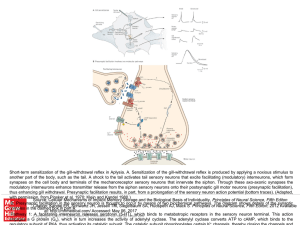
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Document
... • Cerebral cortex forms the outer layer of the forebrain • It appears wrinkled as it is folded • Folding allows more outer cortex to be fitted into a smaller space • A groove is called a sulcus • Between grooves is a gyrus ...
... • Cerebral cortex forms the outer layer of the forebrain • It appears wrinkled as it is folded • Folding allows more outer cortex to be fitted into a smaller space • A groove is called a sulcus • Between grooves is a gyrus ...
LECTURE14.SpinalReflexes
... specific motor cortex neurons with corticospinal projection are active Corticospinal axons branch and synapse on both alpha motor neurons and opposing Ia interneurons Therefore, cortical command promotes muscle contraction and reciprocal muscle inhibition using the spinal reflex circuitry ...
... specific motor cortex neurons with corticospinal projection are active Corticospinal axons branch and synapse on both alpha motor neurons and opposing Ia interneurons Therefore, cortical command promotes muscle contraction and reciprocal muscle inhibition using the spinal reflex circuitry ...
Researchers find that neurons in the primary visual cortex listen to
... neurons in the primary visual cortex of mice listen begs the question of why have so many to just a small subset of the huge number of connections if most of them are going to be mostly synaptic inputs vying for attention. In their paper ignored. The researchers do not know yet, but published in the ...
... neurons in the primary visual cortex of mice listen begs the question of why have so many to just a small subset of the huge number of connections if most of them are going to be mostly synaptic inputs vying for attention. In their paper ignored. The researchers do not know yet, but published in the ...
Slide ()
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function – responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. M ...
... sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function – responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. M ...
Chapter 13 and 16
... A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid ...
... A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid ...
Lewy Body Diseases
... sits in cytosol, transiently binds to cell memb and other synaptic proteins role in synaptic transport, synaptic change, learning aggregation may cause neuronal dysfunction potential disease marker lewy body distribution can occur in - substantia nigra, nucleus basalis, locus ceruleus, ser ...
... sits in cytosol, transiently binds to cell memb and other synaptic proteins role in synaptic transport, synaptic change, learning aggregation may cause neuronal dysfunction potential disease marker lewy body distribution can occur in - substantia nigra, nucleus basalis, locus ceruleus, ser ...
Cell Structure: From an Information Processing View
... – Firing is not perfect, Noise: can fire for no reason, or not fire when it “should” ...
... – Firing is not perfect, Noise: can fire for no reason, or not fire when it “should” ...
PNS and CNS Nervous System Organization Peripheral Nervous
... • Interpretation of textures and shapes ...
... • Interpretation of textures and shapes ...
Chapter 11- 14 Integration of Nervous System Functions
... • Broca's area: motor speech area - sending messages to the appropriate muscles to actually make the sounds • Aphasia: absent or defective speech or language comprehension. Caused by lesion in the language area of the cortex ...
... • Broca's area: motor speech area - sending messages to the appropriate muscles to actually make the sounds • Aphasia: absent or defective speech or language comprehension. Caused by lesion in the language area of the cortex ...
Document
... Primary motor cortex in the precentral gyrus. Gets input from basal ganglia, cerebellum and other cortical areas. Has 6 layers, layer V is the output layer (pyramidal cells or Betz cells). Primary pathway- the pyramidal system. ...
... Primary motor cortex in the precentral gyrus. Gets input from basal ganglia, cerebellum and other cortical areas. Has 6 layers, layer V is the output layer (pyramidal cells or Betz cells). Primary pathway- the pyramidal system. ...
Structure of the Brain PowerPoint Notes
... – the nerve impulse refers to the series of ________________________________________ that take place segment by segment as they move down the length of the axon • ____________________ – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed s ...
... – the nerve impulse refers to the series of ________________________________________ that take place segment by segment as they move down the length of the axon • ____________________ – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed s ...
Neurology-Extrapyramidal Disorders
... anterior (ventral) horn cells. Extrapyramidal tracts-chiefly found in reticular formation of the pons and medulla, and target neurons in SC involved in reflexes, locomotion, complex movements, and postural control. These tracts are in turn modulated by various parts of the CNS, including the nigrost ...
... anterior (ventral) horn cells. Extrapyramidal tracts-chiefly found in reticular formation of the pons and medulla, and target neurons in SC involved in reflexes, locomotion, complex movements, and postural control. These tracts are in turn modulated by various parts of the CNS, including the nigrost ...
Motor Systems I Cortex
... • current position of body parts; and • location of external objects of interest The PPAC receives input from the dorsal streams of the somatosensory, auditory and visual systems and thus plays an important role in integrating these two types of information. ...
... • current position of body parts; and • location of external objects of interest The PPAC receives input from the dorsal streams of the somatosensory, auditory and visual systems and thus plays an important role in integrating these two types of information. ...
Histology of Nerve the Nervous System
... Usually show numerous long processes, and several types of glial cells which have short processes,support and protect neurons, and participate in neural activity,neural lnutrition, and the defense processe softh ecentral nervous system. amodification of electrical potential that may be restricted to ...
... Usually show numerous long processes, and several types of glial cells which have short processes,support and protect neurons, and participate in neural activity,neural lnutrition, and the defense processe softh ecentral nervous system. amodification of electrical potential that may be restricted to ...
Basal Ganglia
... cerebral cortex. They receive information from the frontal cortex about behavior that is being planned for a particular situation. In turn, the basal ganglia affect activity in the frontal cortex through a series of neural projections that ultimately go back up to the same cortical areas from which ...
... cerebral cortex. They receive information from the frontal cortex about behavior that is being planned for a particular situation. In turn, the basal ganglia affect activity in the frontal cortex through a series of neural projections that ultimately go back up to the same cortical areas from which ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and between sensory inputs and motor outputs ...
... neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and between sensory inputs and motor outputs ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... The Human Nervous System •CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: comprised of the brain and spinal chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundl ...
... The Human Nervous System •CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: comprised of the brain and spinal chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundl ...
Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
... Carry incoming information from sensory receptors to the brain/spinal cord E.g. Perceiving something as “hot” Carry outgoing information from the brain/spinal cord to the ...
... Carry incoming information from sensory receptors to the brain/spinal cord E.g. Perceiving something as “hot” Carry outgoing information from the brain/spinal cord to the ...























