Slide ()
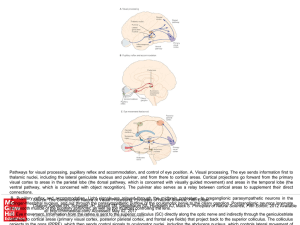
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
Role of Basal Ganglia in the Regulation of Motor Activities by the
... The onset of voluntary motor activity takes place under the influence of cerebral cortex. The basal ganglia is capable of controlling these motor activities due to the presence of neuronal circuits between the basal ganglia and the motor cortex and supplementary motor area. This neuronal circuit inc ...
... The onset of voluntary motor activity takes place under the influence of cerebral cortex. The basal ganglia is capable of controlling these motor activities due to the presence of neuronal circuits between the basal ganglia and the motor cortex and supplementary motor area. This neuronal circuit inc ...
Chapter 16: Basal Ganglia
... such things as the positions of the body and the target in space. It thereby produces internal models of the movement to be made, prior to the involvement of the premotor and motor cortices. Within the posterior parietal cortex, two particular areas are distinguished. Area 5 receives information fro ...
... such things as the positions of the body and the target in space. It thereby produces internal models of the movement to be made, prior to the involvement of the premotor and motor cortices. Within the posterior parietal cortex, two particular areas are distinguished. Area 5 receives information fro ...
Neuron Unit 3A
... second cell. Depending on the site they will either excite an action potential or inhibit the action potential molds the connections that are made in our brains by outside events ...
... second cell. Depending on the site they will either excite an action potential or inhibit the action potential molds the connections that are made in our brains by outside events ...
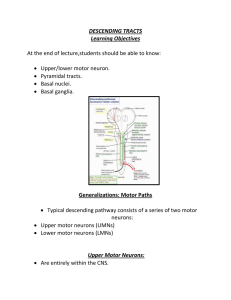
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Thought to mediate larger movements of trunk and limbs that do not require balance or fine movements of upper limbs. ...
... Thought to mediate larger movements of trunk and limbs that do not require balance or fine movements of upper limbs. ...
The relationship between the activity of neurons recorded
... Accurate decoding of the neural activity in the primary motor cortex (M1) could be very useful for brain machine interface applications such as computer displays or prosthetic limbs. In this study we examined information coding in M1 neurons to elucidate the relationship between the activity of M1 n ...
... Accurate decoding of the neural activity in the primary motor cortex (M1) could be very useful for brain machine interface applications such as computer displays or prosthetic limbs. In this study we examined information coding in M1 neurons to elucidate the relationship between the activity of M1 n ...
Neurotransmisson Practice
... 6. Neurotransmitters influence neurons either by _______________ or ______________ their readiness to fire. 7. Excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed to the sending neuron in a process called _______________________. 8. Among the neurotransmitters that researchers have pinpointed is ________, which ...
... 6. Neurotransmitters influence neurons either by _______________ or ______________ their readiness to fire. 7. Excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed to the sending neuron in a process called _______________________. 8. Among the neurotransmitters that researchers have pinpointed is ________, which ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... to carry charges During an action potential, there’s a sudden reversal of charge, carrying a message down the axis ...
... to carry charges During an action potential, there’s a sudden reversal of charge, carrying a message down the axis ...
Division of Brain Sciences Department of Medicine PhD studentship
... buffering, has been extensively implicated in neurodegenerative disorders including Parkinson’s disease. In recent years there has been growing evidence that such dysfunctions are the causes for the gradual loss of specific population of neurons, due to the failure in ATP production to match cellula ...
... buffering, has been extensively implicated in neurodegenerative disorders including Parkinson’s disease. In recent years there has been growing evidence that such dysfunctions are the causes for the gradual loss of specific population of neurons, due to the failure in ATP production to match cellula ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... (stimuli) from the external and internal environments to CNS Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
... (stimuli) from the external and internal environments to CNS Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
THE BASAL GANGLIA
... along with their connected cortical and thalamic areas, are viewed as components of parallel circuits whose functional and morphological segregation is rather strictly maintained. Each circuit is thought to engage separate regions of the basal ganglia and thalamus, and the output of each appears to ...
... along with their connected cortical and thalamic areas, are viewed as components of parallel circuits whose functional and morphological segregation is rather strictly maintained. Each circuit is thought to engage separate regions of the basal ganglia and thalamus, and the output of each appears to ...
THE BASAL GANGLIA
... along with their connected cortical and thalamic areas, are viewed as components of parallel circuits whose functional and morphological segregation is rather strictly maintained. Each circuit is thought to engage separate regions of the basal ganglia and thalamus, and the output of each appears to ...
... along with their connected cortical and thalamic areas, are viewed as components of parallel circuits whose functional and morphological segregation is rather strictly maintained. Each circuit is thought to engage separate regions of the basal ganglia and thalamus, and the output of each appears to ...
Neuro 16 Neurotransmitters Student
... May contribute to presence of uncontrolled involuntary movements. ...
... May contribute to presence of uncontrolled involuntary movements. ...
Document
... indirect projections from cortex to brainstem and brainstem itself can sustain motor behaviour involving proximal muscles. Direct projections for the motor cortex to the spinal cord provide the speed and agility of movements, these enable precision of finger movement. Eg. After motor cortex da ...
... indirect projections from cortex to brainstem and brainstem itself can sustain motor behaviour involving proximal muscles. Direct projections for the motor cortex to the spinal cord provide the speed and agility of movements, these enable precision of finger movement. Eg. After motor cortex da ...
04 Physiology of large hemispheres, cerebellum
... In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largely unchanged with age. Meissner’s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles, however, decrease in number. The capsules of those that remain become thicker and structurally distorted and, therefore, exhibit reduced function. As a result ...
... In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largely unchanged with age. Meissner’s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles, however, decrease in number. The capsules of those that remain become thicker and structurally distorted and, therefore, exhibit reduced function. As a result ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... Parkinson’s is caused by a destruction of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter Dopamine 1.Biochemistry. a catecholamine neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, retina, and sympathetic ganglia, acting within the brain to help regulate movement and emotion: its depletion may cause Par ...
... Parkinson’s is caused by a destruction of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter Dopamine 1.Biochemistry. a catecholamine neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, retina, and sympathetic ganglia, acting within the brain to help regulate movement and emotion: its depletion may cause Par ...
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual
... Motor system includes • Tracts Corticospinal tract (Pyramidal tract ) Extra-pyramidal system ...
... Motor system includes • Tracts Corticospinal tract (Pyramidal tract ) Extra-pyramidal system ...
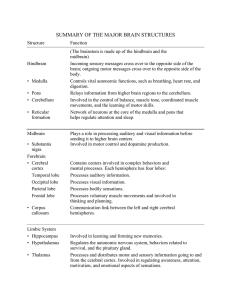
SUMMARY OF THE MAJOR BRAIN STRUCTURES
... Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays information from higher brain regions to the cerebellum. Involved in t ...
... Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays information from higher brain regions to the cerebellum. Involved in t ...
psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... undergraduate level. The materials are from different sources including the internet and the contributors do not in any way claim authorship or ownership of them. The materials are also not to be used for any commercial purpose. ...
... undergraduate level. The materials are from different sources including the internet and the contributors do not in any way claim authorship or ownership of them. The materials are also not to be used for any commercial purpose. ...
Avello_1.4_The_Believer_s_Brain
... The Paradox of Nietzschean Atheism Jason Wakefield, University of Cambridge, England. Review: The Believer's Brain (2014) R.S Donda & K.M Heilman. Psychology Press. Heilman was raised in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in 1963 before studying neuro ...
... The Paradox of Nietzschean Atheism Jason Wakefield, University of Cambridge, England. Review: The Believer's Brain (2014) R.S Donda & K.M Heilman. Psychology Press. Heilman was raised in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in 1963 before studying neuro ...
Brain and Neuron Quiz Key
... Parts and functions of the brain and Neurons quiz Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
... Parts and functions of the brain and Neurons quiz Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...