Textbook PowerPoint
... Network of neurons Alert and arouse higher brain Limbic system Ring of structures important to learning and emotional behavior ...
... Network of neurons Alert and arouse higher brain Limbic system Ring of structures important to learning and emotional behavior ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint Biological basis of behavior-
... Wrinkles on the brain are made by fissures and folds called gyri ...
... Wrinkles on the brain are made by fissures and folds called gyri ...
Lecture 5 Sensory and Motor Systems
... • Prefers motion of 5-100 deg/sec either across the field or towards/away from the eye. • Some nerves respond to particular speeds and others to disparities between near and far objects. ...
... • Prefers motion of 5-100 deg/sec either across the field or towards/away from the eye. • Some nerves respond to particular speeds and others to disparities between near and far objects. ...
Peripheral nervous system
... • outer zone (white matter) - consists of sensory axons (in dorsal column) and motor axons (in ventral column) ...
... • outer zone (white matter) - consists of sensory axons (in dorsal column) and motor axons (in ventral column) ...
Chapter 3
... Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses? ...
... Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses? ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-09
... -Pyramidal neurons (multipolar neurons that sends info down to body) in this gyrus that project via the internal capsule to synapse in the brainstem or spinal cord; they talk to the neurons that contact the muscles (they do NOT directly synapse on the muscles!!) Neurons in the primary motor cortex a ...
... -Pyramidal neurons (multipolar neurons that sends info down to body) in this gyrus that project via the internal capsule to synapse in the brainstem or spinal cord; they talk to the neurons that contact the muscles (they do NOT directly synapse on the muscles!!) Neurons in the primary motor cortex a ...
Lecture 7 Neurons
... Operate through electrical impulses Communicate with other neurons through chemical signals More about neurons and neuronal anatomy later ...
... Operate through electrical impulses Communicate with other neurons through chemical signals More about neurons and neuronal anatomy later ...
topic 6.5 Neurons
... Operate through electrical impulses Communicate with other neurons through chemical signals More about neurons and neuronal anatomy later ...
... Operate through electrical impulses Communicate with other neurons through chemical signals More about neurons and neuronal anatomy later ...
Biological foundations of psychology
... • Broca’s area – speach production • Wernicke’s area – speach understanding ...
... • Broca’s area – speach production • Wernicke’s area – speach understanding ...
The Somatic Motor System
... – Role: Generation of coordinated movements – Parts of motor control • Spinal cord coordinated muscle contraction • Brain motor programs in spinal cord ...
... – Role: Generation of coordinated movements – Parts of motor control • Spinal cord coordinated muscle contraction • Brain motor programs in spinal cord ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VI. Growth Factors
... that are secreted by the target nerve cells, bind to specific receptors, and signal to the nearby developing synapse. Within the nervous system, the most extensively studied of these factors is the family of neurotrophins. Almost 50 years ago, Rita Levi-Montalcini and Stanley Cohen isolated and iden ...
... that are secreted by the target nerve cells, bind to specific receptors, and signal to the nearby developing synapse. Within the nervous system, the most extensively studied of these factors is the family of neurotrophins. Almost 50 years ago, Rita Levi-Montalcini and Stanley Cohen isolated and iden ...
The Nervous System
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT
... – Sensory neuron from the extensor muscle synapses with the motor neuron for that extensor muscle – Only found in the stretch reflex ...
... – Sensory neuron from the extensor muscle synapses with the motor neuron for that extensor muscle – Only found in the stretch reflex ...
Neurons
... • 10x more glial cells • Glial cells – Support neurons (literally, provide physical support, as well as nutrients) – Cover neurons with myelin – Clean up debris – “Housewives” ...
... • 10x more glial cells • Glial cells – Support neurons (literally, provide physical support, as well as nutrients) – Cover neurons with myelin – Clean up debris – “Housewives” ...
Temporal Aspects of Visual Extinction
... Responsible for manipulating discrete and skilled voluntary movements through planning and innervation of muscles Refers to highly conscious planning and sequencing Site of reasoning, thinking, planning ...
... Responsible for manipulating discrete and skilled voluntary movements through planning and innervation of muscles Refers to highly conscious planning and sequencing Site of reasoning, thinking, planning ...
Harnessing Plasticity to Reset Dysfunctional Neurons
... (from milliseconds to months), and are incompletely understood. They include changes in synaptic strength, the pruning and growth of neuronal connections, and even the introduction of new neurons within certain existing circuits. The brain can thus develop attributes and abilities far beyond those t ...
... (from milliseconds to months), and are incompletely understood. They include changes in synaptic strength, the pruning and growth of neuronal connections, and even the introduction of new neurons within certain existing circuits. The brain can thus develop attributes and abilities far beyond those t ...
study notes quiz 1
... (a) responsible for audiovisual reactions (contains inferior and superior colliculi) 2) Tegmentum: “covering” (a) red nucleus: sends motor info from cortex to cerebellum and spinal cord (b) substantia nigra: “black substance”: communicates with caudate and basil ganglia; involved in control of volun ...
... (a) responsible for audiovisual reactions (contains inferior and superior colliculi) 2) Tegmentum: “covering” (a) red nucleus: sends motor info from cortex to cerebellum and spinal cord (b) substantia nigra: “black substance”: communicates with caudate and basil ganglia; involved in control of volun ...
107B exam 1 test yourself
... Response field – defined by area that, when exposed to stimulus, causes neuron to respond (either by depolarization, in other words e________________ or hyperpolarization_________________). Somatosensory response fields can be direction sensitive. (example: surround inhibition gives information abou ...
... Response field – defined by area that, when exposed to stimulus, causes neuron to respond (either by depolarization, in other words e________________ or hyperpolarization_________________). Somatosensory response fields can be direction sensitive. (example: surround inhibition gives information abou ...
receptor
... Neurological Disorders Lesson 2.1 How are neuronal structures specialized for function? ...
... Neurological Disorders Lesson 2.1 How are neuronal structures specialized for function? ...
Page 1
... Make a prediction about the answer to each question. Put a star next to the answer that you think is correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line before the number as you watch the video. The Nervous System _________1. What are ...
... Make a prediction about the answer to each question. Put a star next to the answer that you think is correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line before the number as you watch the video. The Nervous System _________1. What are ...
Neurons, Synapses and Long-term Potentiation
... changes in behaviour and are therefore linked to changes in the cellular level • So what are the cellular changes? ...
... changes in behaviour and are therefore linked to changes in the cellular level • So what are the cellular changes? ...
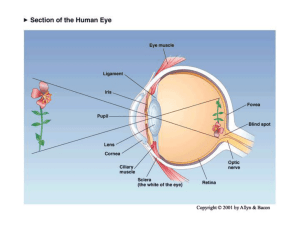
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... – the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then the primary visual cortex (V1, area 17): more to come… ...
... – the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then the primary visual cortex (V1, area 17): more to come… ...
Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Lectures 1 and 10 White
... 23. Which of the following controls movements guided by external stimuli? a. Premotor cortex b. Primary motor cortex c. Postmotor cortex d. Supplementary motor area 24. Which of the following is more responsible for planning and learning complex for movements? a. Premotor cortex b. Primary motor cor ...
... 23. Which of the following controls movements guided by external stimuli? a. Premotor cortex b. Primary motor cortex c. Postmotor cortex d. Supplementary motor area 24. Which of the following is more responsible for planning and learning complex for movements? a. Premotor cortex b. Primary motor cor ...
motor systems
... is called a motor unit. Muscles used for delicate movements, like the hand muscles, have small motor units in the sense that one motor neuron may supply less than 100 muscle fibers; the eye muscles have even smaller motor units. The junction between the terminal branches of the axon and the muscle f ...
... is called a motor unit. Muscles used for delicate movements, like the hand muscles, have small motor units in the sense that one motor neuron may supply less than 100 muscle fibers; the eye muscles have even smaller motor units. The junction between the terminal branches of the axon and the muscle f ...