Maximum entropy modeling of multi-neuron firing patterns in V1
... Understanding the activity of a network of neurons is challenging due to the exponential growth in potential interactions as the network size increases. In the visual cortex, the firing activity of pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of the ...
... Understanding the activity of a network of neurons is challenging due to the exponential growth in potential interactions as the network size increases. In the visual cortex, the firing activity of pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of the ...
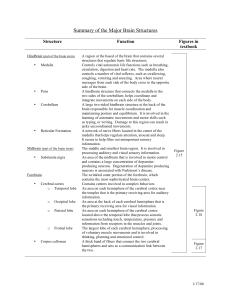
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... A region at the based of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life structures. Controls vital autonomic life functions such as breathing, circulation, digestion and heart rate. The medulla also controls a number of vital reflexes, such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting and ...
... A region at the based of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life structures. Controls vital autonomic life functions such as breathing, circulation, digestion and heart rate. The medulla also controls a number of vital reflexes, such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting and ...
1-nervous_system
... Major functions of the nervous system-the 3 C’s Control Communicate Coordinate Receive stimuli Process information and decide output Direct response ...
... Major functions of the nervous system-the 3 C’s Control Communicate Coordinate Receive stimuli Process information and decide output Direct response ...
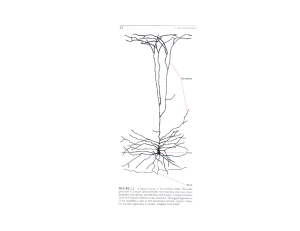
The Brain and the Neuron (1)
... • Railroad worker who had a spike fly through his skull due to an explosion. (Frontal Lobe) • Most famous case in neuroscience. • Personality changed after the accident. ...
... • Railroad worker who had a spike fly through his skull due to an explosion. (Frontal Lobe) • Most famous case in neuroscience. • Personality changed after the accident. ...
Modeling and Imagery
... • The γ activation of the intrafusal fibers serves as a reflexive check on the α activated extrafusal fibers • If there’s a match, all is well • If there’s a mismatch, the α–motor neuron fires some ...
... • The γ activation of the intrafusal fibers serves as a reflexive check on the α activated extrafusal fibers • If there’s a match, all is well • If there’s a mismatch, the α–motor neuron fires some ...
Motor pathways
... Cerebral cortex contains numerous circuits for motor control Cerebellum and basal ganglia also participate in important feedback loops in which they project back to cerebral cortex via thalamus Sensory inputs also plays an essential role in motor circuits and feedback loops ...
... Cerebral cortex contains numerous circuits for motor control Cerebellum and basal ganglia also participate in important feedback loops in which they project back to cerebral cortex via thalamus Sensory inputs also plays an essential role in motor circuits and feedback loops ...
Motor System: Reflexes, Pyramidal Tract and Basal Ganglia
... trigeminal, and RF C. control over external eye muscles: input comes from frontal and parietal eye fields, rather than from MI; projection to midbrain and paramedian pontine RF D. control over tongue: hypoglossal and RF E. control over swallowing reflexes: nucleus ambiguus and RF ...
... trigeminal, and RF C. control over external eye muscles: input comes from frontal and parietal eye fields, rather than from MI; projection to midbrain and paramedian pontine RF D. control over tongue: hypoglossal and RF E. control over swallowing reflexes: nucleus ambiguus and RF ...
The (un)coupling between action execution and
... agent [1]. The exact features of this resonant motor response, however, are unclear. Do we mirror the goal of others’ actions or rather the low-kinematic features of their movements? D’Ausilio et al. suggest that this is an ill-defined problem: the mirror system plausibly replicates the same computa ...
... agent [1]. The exact features of this resonant motor response, however, are unclear. Do we mirror the goal of others’ actions or rather the low-kinematic features of their movements? D’Ausilio et al. suggest that this is an ill-defined problem: the mirror system plausibly replicates the same computa ...
Neurons Firing of a neuron
... inhibitory signals the exceed membrane positive minimum intensitybecomes (threshold) permeable the combined & signals trigger action potential. ions rush intoancell ...
... inhibitory signals the exceed membrane positive minimum intensitybecomes (threshold) permeable the combined & signals trigger action potential. ions rush intoancell ...
Principles of neural ensemble physiology underlying the operation
... BMI studies also revealed that a single motor output is often associated with distinct spatiotemporal patterns of neural ensemble firing on the millisecond scale Following the nomenclature introduced by Reeke and Edelman, this principle, which states that identical behavioural outputs can be produce ...
... BMI studies also revealed that a single motor output is often associated with distinct spatiotemporal patterns of neural ensemble firing on the millisecond scale Following the nomenclature introduced by Reeke and Edelman, this principle, which states that identical behavioural outputs can be produce ...
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
... No cure has yet been found for ALS Riluzole (Rilutek) is believed to reduce damage ...
... No cure has yet been found for ALS Riluzole (Rilutek) is believed to reduce damage ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior
... The brain utilizes several components in order to communicate with the rest of the body, specifically the neuron Neurons are highly specialized cells that receive and transmit information from one part of the body to another They communicate information in electrical and chemical form Your entire br ...
... The brain utilizes several components in order to communicate with the rest of the body, specifically the neuron Neurons are highly specialized cells that receive and transmit information from one part of the body to another They communicate information in electrical and chemical form Your entire br ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ...
... ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal. • Positive Potassium (K) is pumped out AS THE PROCESS OCCURS DOWN THE AXON and now the neuron is in a state of ...
... • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal. • Positive Potassium (K) is pumped out AS THE PROCESS OCCURS DOWN THE AXON and now the neuron is in a state of ...
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body - Nicole
... animals to detect a stimulus and coordinate a response. ...
... animals to detect a stimulus and coordinate a response. ...
NervousSystem3
... basis ponti. Axons of the cells of the pontine nuclei as pontocerebellar fibers collectively form the middle cerebellar peduncles and end in the cerebellar cortex. Descending motor fibers of the red nucleus of the midbrain give off collaterals to the inferior olivary nucleus of the medulla, which pr ...
... basis ponti. Axons of the cells of the pontine nuclei as pontocerebellar fibers collectively form the middle cerebellar peduncles and end in the cerebellar cortex. Descending motor fibers of the red nucleus of the midbrain give off collaterals to the inferior olivary nucleus of the medulla, which pr ...
6.1 Overview of the Nervous System
... microscopic gap known as the synaptic cleft - The intersection of an axon terminal of one neuron, the cleft, and the dendrite of another neuron or muscle is known as a synapse ...
... microscopic gap known as the synaptic cleft - The intersection of an axon terminal of one neuron, the cleft, and the dendrite of another neuron or muscle is known as a synapse ...
vocab - sociallyconsciousbird.com
... the visual areas, which receive visual information from the opposite visual field temporal lobes – the portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each of which receives auditory information primarily from the opposite ear motor cortex – an area at the r ...
... the visual areas, which receive visual information from the opposite visual field temporal lobes – the portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each of which receives auditory information primarily from the opposite ear motor cortex – an area at the r ...
Associated Reactions
... Schematic drawing of the neuronal mechanisms involved in human gait. a | Physiological condition. Leg muscles become activated by a programmed pattern that is generated in spinal neuronal circuits (turquoise pathway). This pattern is modulated by multisensory afferent input, which adapts the patter ...
... Schematic drawing of the neuronal mechanisms involved in human gait. a | Physiological condition. Leg muscles become activated by a programmed pattern that is generated in spinal neuronal circuits (turquoise pathway). This pattern is modulated by multisensory afferent input, which adapts the patter ...
Slide ()
... The activity of functionally distinct parietal motor neurons varies with the purpose of a grasping action. (Modified, with permission, from Fogassi et al. ...
... The activity of functionally distinct parietal motor neurons varies with the purpose of a grasping action. (Modified, with permission, from Fogassi et al. ...
10 Control of Movement
... • Adjusting motor unit activity to local conditions (obstacles to movement, pain) ...
... • Adjusting motor unit activity to local conditions (obstacles to movement, pain) ...