Slide ()
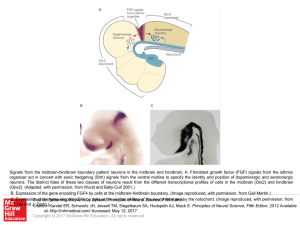
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
pharm chapter 8 [3-16
... Cellular Organization of the Nervous System Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic ...
... Cellular Organization of the Nervous System Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic ...
Mirror neurons – the missing link for consciousness?
... this ability evolve? We may have to turn away from our fellow humans and towards the even more mysterious minds of animals to find the answers to these questions. While some would say that consciousness is a unique property of human brains, others would argue that some animals possess this fascinati ...
... this ability evolve? We may have to turn away from our fellow humans and towards the even more mysterious minds of animals to find the answers to these questions. While some would say that consciousness is a unique property of human brains, others would argue that some animals possess this fascinati ...
Nervous System
... • Intention to contract a muscle begins in motor association (premotor) area of frontal lobes • Precentral gyrus (primary motor area) processes that order by sending signals to the spinal cord • Motor homunculus is proportional to number of muscle motor units in a region (fine control) ...
... • Intention to contract a muscle begins in motor association (premotor) area of frontal lobes • Precentral gyrus (primary motor area) processes that order by sending signals to the spinal cord • Motor homunculus is proportional to number of muscle motor units in a region (fine control) ...
File
... Reverberating pathway neurons later synapse with earlier ones, sending the in the pathway impulse back through the circuit Plasticity of response is ...
... Reverberating pathway neurons later synapse with earlier ones, sending the in the pathway impulse back through the circuit Plasticity of response is ...
Brain Anatomy
... Works on the voluntary muscles Also abundant in the brain. Nicotine reacts with the receptors that respond to acetylcholine. Alzheimer’s patients lose neurons that release Acetylcholine. ...
... Works on the voluntary muscles Also abundant in the brain. Nicotine reacts with the receptors that respond to acetylcholine. Alzheimer’s patients lose neurons that release Acetylcholine. ...
Target in Field Search: Distractor in Field - Smith
... • Location on SC map determined by recording and stimulation • Injected Lidocaine (2%; 0.25 - 1.25 ul) or muscimol (0.5 ug/ul; 0.25 - 1 ul) • Test target selection and motor execution pre-injection, post-injection, and after recovery ...
... • Location on SC map determined by recording and stimulation • Injected Lidocaine (2%; 0.25 - 1.25 ul) or muscimol (0.5 ug/ul; 0.25 - 1 ul) • Test target selection and motor execution pre-injection, post-injection, and after recovery ...
The Peripheral and Autonomic Nervous Systems
... 2. Activation of a sensory neuron 3. Information processing 4. Activation of a motor neuron 5. Response by an effector ...
... 2. Activation of a sensory neuron 3. Information processing 4. Activation of a motor neuron 5. Response by an effector ...
Bio_246_files/Motor Control
... • Detect deep touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception. • Carry signals from arm and leg • Cross in the medulla • Synapses in the thalamus carries signal to cerebral cortex ...
... • Detect deep touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception. • Carry signals from arm and leg • Cross in the medulla • Synapses in the thalamus carries signal to cerebral cortex ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
Neurotransmitters
... with musical and artistic abilities). The brain is also divided into four lobes: Frontal – (motor cortex) motor behavior, expressive language, higher level cognitive processes, and orientation to person, place, time, and situation (social behavior, conscience) Parietal – (somatosensory Cortex) invol ...
... with musical and artistic abilities). The brain is also divided into four lobes: Frontal – (motor cortex) motor behavior, expressive language, higher level cognitive processes, and orientation to person, place, time, and situation (social behavior, conscience) Parietal – (somatosensory Cortex) invol ...
cogsci200
... Each region encompasses a cortical surface area of roughly 2 mm2 and possesses a total of about 200,000 neurons. ...
... Each region encompasses a cortical surface area of roughly 2 mm2 and possesses a total of about 200,000 neurons. ...
Physiological Nature
... * 78% water/fat/proteinslippery * connected to the entire human physiology * in order to understand how the brain works, it is important to understand each of the components, functions, regions, structures, etc. In a review of 37 imaging studies related to intelligence, including their own, Haier a ...
... * 78% water/fat/proteinslippery * connected to the entire human physiology * in order to understand how the brain works, it is important to understand each of the components, functions, regions, structures, etc. In a review of 37 imaging studies related to intelligence, including their own, Haier a ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... Neural Tissue • Master controlling /communicating system of the body. • 3 overlapping functions: (1) Sensory input; (2) Integration; (3) Motor output. • Neuron ...
... Neural Tissue • Master controlling /communicating system of the body. • 3 overlapping functions: (1) Sensory input; (2) Integration; (3) Motor output. • Neuron ...
7-6_TheGenOfSpecResp_MajorosMyrtill
... in a continuous loop. Conscious movement comes from impulses in the brain travelling down the spinal cord, over this loop, and then back to the brain for processing. However, the stretch reflex skips the brain portion of the trip and follows the simple loop from muscle to spinal cord and back, makin ...
... in a continuous loop. Conscious movement comes from impulses in the brain travelling down the spinal cord, over this loop, and then back to the brain for processing. However, the stretch reflex skips the brain portion of the trip and follows the simple loop from muscle to spinal cord and back, makin ...
Neural coding in the primary olfactory cortex
... respond in characteristic ways to ’naturalistic’ trains of afferent stimulation, modelled on in vivo recordings. Together, SP and SL cells had the effect of dispersing the firing rate and latency of output action potentials to an extent that depended on the strength of the input. In a second series ...
... respond in characteristic ways to ’naturalistic’ trains of afferent stimulation, modelled on in vivo recordings. Together, SP and SL cells had the effect of dispersing the firing rate and latency of output action potentials to an extent that depended on the strength of the input. In a second series ...
Distinction of a left or right hand keypress
... The principal component analysis is computed for each channel, then the second principal mode is used (I have not used the first because it contains the normal activity of the brain instead the features to discriminate between left or rigth hand). This mode is correlated with the signals (only the s ...
... The principal component analysis is computed for each channel, then the second principal mode is used (I have not used the first because it contains the normal activity of the brain instead the features to discriminate between left or rigth hand). This mode is correlated with the signals (only the s ...
Guided Notes for the Nervous System-
... 5.There are two subdivisions of the PNS. The sensory, or afferent, division consists of nerve fibers that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. The motor, or efferent, division carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the ...
... 5.There are two subdivisions of the PNS. The sensory, or afferent, division consists of nerve fibers that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. The motor, or efferent, division carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the ...
Nervous System
... Function: To sense changes in their surroundings and respond by transmitting nerve impulses along cellular processes to other neurons or to muscles and glands. ◦ The complex patterns in which the neurons connect with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integ ...
... Function: To sense changes in their surroundings and respond by transmitting nerve impulses along cellular processes to other neurons or to muscles and glands. ◦ The complex patterns in which the neurons connect with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integ ...