The Nervous System
... cord and the brain – Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands – Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them ...
... cord and the brain – Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands – Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them ...
Cognitive Psychology
... and uncontrolled. No two people ever have the exact same lesion. With animals, we can control the characteristics of the lesions. (Area MT) • Single-cell recording - Also with animals, we can attach electrodes to neurons and measure the firing pattern of individual neurons. (Feature detectors in are ...
... and uncontrolled. No two people ever have the exact same lesion. With animals, we can control the characteristics of the lesions. (Area MT) • Single-cell recording - Also with animals, we can attach electrodes to neurons and measure the firing pattern of individual neurons. (Feature detectors in are ...
Autonomic Nervous System Period 5 Jacquelene Hanein, Karina
... o Cranial Nerves: connect the upper body and head o Spinal Nerves: connect the rest of the body ...
... o Cranial Nerves: connect the upper body and head o Spinal Nerves: connect the rest of the body ...
C! **D!**E!**F! - Amherst College
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
LAB 10 NEURON and SPINAL CORD
... It is all the nervous system except the brain and spinal cord. It consists of nerves and ganglia. It deliveries sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands to peripheral tissues and system. ...
... It is all the nervous system except the brain and spinal cord. It consists of nerves and ganglia. It deliveries sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands to peripheral tissues and system. ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... Drugs can act by - modifying amount of NT, or - binding to receptor (nicotine) The net effect on neuron could be: - activation (action potential) - inhibition ...
... Drugs can act by - modifying amount of NT, or - binding to receptor (nicotine) The net effect on neuron could be: - activation (action potential) - inhibition ...
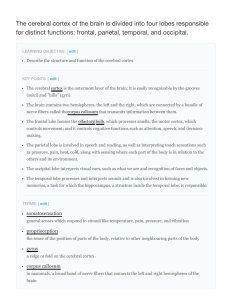
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... Each hemisphere of the mammalian cerebral cortex can be broken down into four functionally- and spatially-defined lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital . The frontal lobe is located at the front of the brain, over the eyes. This lobe contains the olfactory bulb, which processes smells. T ...
... Each hemisphere of the mammalian cerebral cortex can be broken down into four functionally- and spatially-defined lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital . The frontal lobe is located at the front of the brain, over the eyes. This lobe contains the olfactory bulb, which processes smells. T ...
Name: Date: Grade / Section: _____ Neurons Questions Notes 1
... Ferries are boats that carry cars and people across a river. If the river represents the synapse… 1. What could the ferry represent? 2. What could the cars / people represent? 3. What could the road leading the ferry represent? ...
... Ferries are boats that carry cars and people across a river. If the river represents the synapse… 1. What could the ferry represent? 2. What could the cars / people represent? 3. What could the road leading the ferry represent? ...
AP Psychology
... 7. What are the two examples of poison that affect Ach transmission and what does each do? 8. What are the opiate receptors that we naturally produce and what is their purpose? 9. Give two examples of how drugs and other chemicals alter neurotransmission. 10. What are agonists and antagonists? 11. W ...
... 7. What are the two examples of poison that affect Ach transmission and what does each do? 8. What are the opiate receptors that we naturally produce and what is their purpose? 9. Give two examples of how drugs and other chemicals alter neurotransmission. 10. What are agonists and antagonists? 11. W ...
Neurology - wsscience
... Saltatory conduction conducts impulses along an axon: 2-3 times more slowly than continuous conduction 5-7 times faster than continuous conduction At a rate determined by the strength of the stimulus At a velocity determined by the rate at which the stimulus is applied ...
... Saltatory conduction conducts impulses along an axon: 2-3 times more slowly than continuous conduction 5-7 times faster than continuous conduction At a rate determined by the strength of the stimulus At a velocity determined by the rate at which the stimulus is applied ...
Interference to Neurotransmitter function
... • Levodopa (L-Dopa) can cross the blood-brain barrier and be converted into dopamine by the brain. • Dopamine agonists stimulate the dopamine receptors in the brain, mimicking the effect of dopamine in the brain. • Both drugs can alleviate symptoms of Parkinson’s, but are not a cure. The disease con ...
... • Levodopa (L-Dopa) can cross the blood-brain barrier and be converted into dopamine by the brain. • Dopamine agonists stimulate the dopamine receptors in the brain, mimicking the effect of dopamine in the brain. • Both drugs can alleviate symptoms of Parkinson’s, but are not a cure. The disease con ...
chapt10_lecture09
... Motor activity must be informed about the body’s center of gravity in order to make adjustments in the level of stimulation to muscles whose contraction prevents unstable conditions (falling). ...
... Motor activity must be informed about the body’s center of gravity in order to make adjustments in the level of stimulation to muscles whose contraction prevents unstable conditions (falling). ...
10-21-09
... Macaque. It is more challenging to select options when their rewards are more similar than when they’re more difference. It’s even more difficult when there are multiple options. mOFC damage influences how much the third option influences the choice in options. Four monkeys were lesioned in the mOFC ...
... Macaque. It is more challenging to select options when their rewards are more similar than when they’re more difference. It’s even more difficult when there are multiple options. mOFC damage influences how much the third option influences the choice in options. Four monkeys were lesioned in the mOFC ...
BCH 450 Nervous Tissues
... occupies only a small region in humans (it is relatively much larger in "lower" vertebrates ...
... occupies only a small region in humans (it is relatively much larger in "lower" vertebrates ...
White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections
... 1. Background of research ...
... 1. Background of research ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Preganglionic fibers arise from the nuclei of cranial nerves and spinal cord segments S2 through S4 • For this reason this division is called the Craniosacral Division (or Craniosacral outflow) ...
... • Preganglionic fibers arise from the nuclei of cranial nerves and spinal cord segments S2 through S4 • For this reason this division is called the Craniosacral Division (or Craniosacral outflow) ...
Anatomy of the Nervous System
... involves your nervous system. • Coordinated motions (which do not seems to be coordinated) are controlled mostly by the nervous system. • nervous system + endocrine system control the actions of the body. ...
... involves your nervous system. • Coordinated motions (which do not seems to be coordinated) are controlled mostly by the nervous system. • nervous system + endocrine system control the actions of the body. ...
Neural Oscillators on the Edge: Harnessing Noise to Promote Stability
... Abnormal neural oscillations are implicated in certain disease states, for example repetitive firing of injured axons evoking painful paresthesia, and rhythmic discharges of cortical neurons in patients with epilepsy. In other clinical conditions, the pathological state manifests as a vulnerability ...
... Abnormal neural oscillations are implicated in certain disease states, for example repetitive firing of injured axons evoking painful paresthesia, and rhythmic discharges of cortical neurons in patients with epilepsy. In other clinical conditions, the pathological state manifests as a vulnerability ...
mspn1a
... The ventral horn contains the bodies of motor neurons that control the skeletal muscles of the body. The larger neurons are known as alpha motor neurons and they innervate striated muscles. The other, smaller neurons are known as gamma motor neurons and they innervate the muscle spindle (See Muscle ...
... The ventral horn contains the bodies of motor neurons that control the skeletal muscles of the body. The larger neurons are known as alpha motor neurons and they innervate striated muscles. The other, smaller neurons are known as gamma motor neurons and they innervate the muscle spindle (See Muscle ...
MCB 163: Mammalian Neuroanatomy
... topographic map of the body or the muscles, and many cells discharge after rather than before movement; severely damaged in Parkinsonism. 9. CINGULATE CORTEX A critical part of Papez’ circuit involved in the analysis of sensory events in the limbic system, this structure is now known to play a key r ...
... topographic map of the body or the muscles, and many cells discharge after rather than before movement; severely damaged in Parkinsonism. 9. CINGULATE CORTEX A critical part of Papez’ circuit involved in the analysis of sensory events in the limbic system, this structure is now known to play a key r ...
Chapter 28- Nervous System
... – Synaptic cleft- gap between neurons, prevents action potential from sending info, action potentials can be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitters) • The action potential triggers vesicles to fuse with plasma membrane • Neurotransmitters bind to receptors and open ion channels to ions tha ...
... – Synaptic cleft- gap between neurons, prevents action potential from sending info, action potentials can be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitters) • The action potential triggers vesicles to fuse with plasma membrane • Neurotransmitters bind to receptors and open ion channels to ions tha ...
Chapter 8 - Nervous Pre-Test
... A. occurs because the cell membrane is more permeable to potassium ions than sodium ions. B. partly results from the sodium-potassium exchange pump. C. occurs because the cell membrane remains polarized at rest. D. occurs because there are negatively charged proteins and ions inside the cell. E. has ...
... A. occurs because the cell membrane is more permeable to potassium ions than sodium ions. B. partly results from the sodium-potassium exchange pump. C. occurs because the cell membrane remains polarized at rest. D. occurs because there are negatively charged proteins and ions inside the cell. E. has ...