abstract - ELSC at
... potential generators can even lead to a temporally irregular circuit dynamics that is not chaotic but stable. This phenomenon can be understood from the bandwidth of population encoding in an ensemble of uncoupled noise-driven neurons. At fixed rate of AP firing, spike trains generated by model neur ...
... potential generators can even lead to a temporally irregular circuit dynamics that is not chaotic but stable. This phenomenon can be understood from the bandwidth of population encoding in an ensemble of uncoupled noise-driven neurons. At fixed rate of AP firing, spike trains generated by model neur ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... a. Sensory input – sense receptors to monitor change in and out of body b. Integration – processes and interprets data to see what to do c. Motor output – causes response of effector organs ...
... a. Sensory input – sense receptors to monitor change in and out of body b. Integration – processes and interprets data to see what to do c. Motor output – causes response of effector organs ...
The Nervous System
... Interesting Facts about the Neuron • Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime • Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose ...
... Interesting Facts about the Neuron • Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime • Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose ...
Ch. 2 the LGN and Striate Cortex
... • Neurons that fire to specific features of a stimulus • Pathway away from retina shows neurons that fire to more complex stimuli • Cells that are feature detectors: – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
... • Neurons that fire to specific features of a stimulus • Pathway away from retina shows neurons that fire to more complex stimuli • Cells that are feature detectors: – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
PR_161115_Inaktive_Gehirnzellen_E
... in live organisms. This allows recording action potentials from these neurons while they work, and while simultaneously identifying the cells that the recordings are taken from for later analysis. During this analysis, morphological traits of the analysed cells are identified, most importantly their ...
... in live organisms. This allows recording action potentials from these neurons while they work, and while simultaneously identifying the cells that the recordings are taken from for later analysis. During this analysis, morphological traits of the analysed cells are identified, most importantly their ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... – Single process arises from body – Branches into an axon and dendrite – e.g., Present in spinal and cranial ganglia (sensory neuron) Bipolar: – Single axon and single dendrite on opposite ends of the soma. e.g., interneuron Multipolar; – Single axon & multiple dendrites – Most common type in men – ...
... – Single process arises from body – Branches into an axon and dendrite – e.g., Present in spinal and cranial ganglia (sensory neuron) Bipolar: – Single axon and single dendrite on opposite ends of the soma. e.g., interneuron Multipolar; – Single axon & multiple dendrites – Most common type in men – ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam2_180117_final
... This can occur in the presynaptic neuron or in neighboring glial cells. Itself serves as metabolic precursor for the major inhibitory neurotransmitter ____________________________, via the action of the enzyme ____ ______________________________________. It binds to four families of cell surface rec ...
... This can occur in the presynaptic neuron or in neighboring glial cells. Itself serves as metabolic precursor for the major inhibitory neurotransmitter ____________________________, via the action of the enzyme ____ ______________________________________. It binds to four families of cell surface rec ...
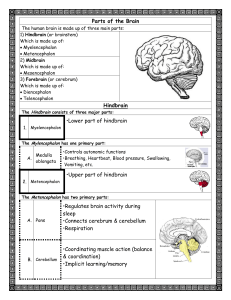
Parts of the Brain Hindbrain •Lower part of hindbrain •Upper part of
... •Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. ...
... •Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. ...
Chapter 17
... bv to kidneys and GI constrict blood flow there & urine output bv to skeletal, cardiac muscle dilate glycogenolysis & lipolysis by liver; blood glucose Processes not essential to stress response slow or stop ...
... bv to kidneys and GI constrict blood flow there & urine output bv to skeletal, cardiac muscle dilate glycogenolysis & lipolysis by liver; blood glucose Processes not essential to stress response slow or stop ...
Nature Medicine Interview
... escape the draft but also since it was the place to go for research training. It was five of the best years of my life and an unprecedented opportunity to just do research without any clinical responsibilities. I began to figure out how to record single-cell activity in subcortical structures in beh ...
... escape the draft but also since it was the place to go for research training. It was five of the best years of my life and an unprecedented opportunity to just do research without any clinical responsibilities. I began to figure out how to record single-cell activity in subcortical structures in beh ...
Slide 1
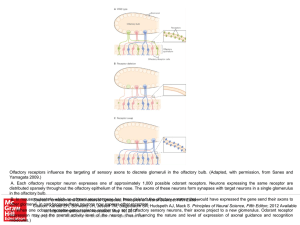
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
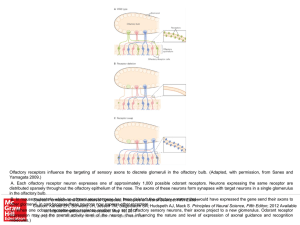
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Human Cortex: Reflections of Mirror Neurons
... signature of mirror neurons since visual adaptation may also be generated by movement-selective visual neurons (Figure 1, brown) and motor adaptation may be generated by movementselective motor neurons (Figure 1, red). Three studies [12–14] have recently used adaptation protocols to localize neural ...
... signature of mirror neurons since visual adaptation may also be generated by movement-selective visual neurons (Figure 1, brown) and motor adaptation may be generated by movementselective motor neurons (Figure 1, red). Three studies [12–14] have recently used adaptation protocols to localize neural ...
Chapter 9: Nervous System guide—Please complete these notes on
... 28. What are they? The paths a nerve impulse follows as it travels through the nervous system 29. A reflex arc makes up the simplest nerve pathway (only a few neurons). ...
... 28. What are they? The paths a nerve impulse follows as it travels through the nervous system 29. A reflex arc makes up the simplest nerve pathway (only a few neurons). ...
Biological Psychology A branch of psychology concerned with links
... Areas of the cerebral cortex not involved in primary motor or sensory functions, but involved in higher mental functions (eg. Learning, remembering, thinking, speaking) ...
... Areas of the cerebral cortex not involved in primary motor or sensory functions, but involved in higher mental functions (eg. Learning, remembering, thinking, speaking) ...
C48 Nervous System
... (carried out by central nervous system (CNS), brain and spinal cord in vertebrates) via interneurons Motor input – conduction of signal from CNS to effector cells, ex. muscle or gland cells that carry out responses via motor neurons Reflex – automatic response uses only sensory and motor neurons. ...
... (carried out by central nervous system (CNS), brain and spinal cord in vertebrates) via interneurons Motor input – conduction of signal from CNS to effector cells, ex. muscle or gland cells that carry out responses via motor neurons Reflex – automatic response uses only sensory and motor neurons. ...
Bio 17 – Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
... low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
neurophilosophical foundations 2 levels of organization cell theory
... Observations are generally taken as the foundations on which science is built • Hypotheses (of laws or mechanisms) advanced to explain them • But observation (perception) is influenced top-down by our previous experience as well as bottom-up by what is in front of our eyes • Some philosophers (e.g., ...
... Observations are generally taken as the foundations on which science is built • Hypotheses (of laws or mechanisms) advanced to explain them • But observation (perception) is influenced top-down by our previous experience as well as bottom-up by what is in front of our eyes • Some philosophers (e.g., ...
Lecture 14 - School of Computing
... Question: Given the partial data, is there sufficient information to classify images as trees or non-trees? Answer: A 2-node Kohonen net trained on the Table of neuronal responses was able to classify new images with an 84% success rate. ...
... Question: Given the partial data, is there sufficient information to classify images as trees or non-trees? Answer: A 2-node Kohonen net trained on the Table of neuronal responses was able to classify new images with an 84% success rate. ...
28.1_Responses
... following in response to a stimuli: interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, muscle Review What are two general ways in which nervous systems differ among animal groups Review Give an example of an animal with a very simple sensory system and an example of one with a complex sensory system ...
... following in response to a stimuli: interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, muscle Review What are two general ways in which nervous systems differ among animal groups Review Give an example of an animal with a very simple sensory system and an example of one with a complex sensory system ...
CNS_notes
... bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of both pathways 1st order neuron cell body in DRG 1st order neuron’s axon enters spinal cord via dorsal root 2nd order neuron’s axon crosses midline, terminates in thalamus (synapse onto target neur ...
... bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of both pathways 1st order neuron cell body in DRG 1st order neuron’s axon enters spinal cord via dorsal root 2nd order neuron’s axon crosses midline, terminates in thalamus (synapse onto target neur ...
extra pyramidal system
... • It controls the activity of both alpha and gamma motor neurons. • In the control of muscle tone it plays an important role. ...
... • It controls the activity of both alpha and gamma motor neurons. • In the control of muscle tone it plays an important role. ...
Slide ()
... The spinal cord varies slightly in diameter along its length but in cross section always shows bilateral symmetry around the small, CSF-filled central canal (C). Unlike the cerebrum and cerebellum, in the spinal cord the gray matter is internal, forming a roughly H-shaped structure that consists of ...
... The spinal cord varies slightly in diameter along its length but in cross section always shows bilateral symmetry around the small, CSF-filled central canal (C). Unlike the cerebrum and cerebellum, in the spinal cord the gray matter is internal, forming a roughly H-shaped structure that consists of ...
Nerves Ganglia Spinal nerves Cranial nerves Afferent neurons
... The system that transmits action potentials from the CNS to the smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands ...
... The system that transmits action potentials from the CNS to the smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... E. Long term memory seems to be unaffected. F. More time to fall asleep, more walking periods during the night, and longer amount of time being awake at night. G. Many older people shoe no change and some show a 10% increase in thinking ability due to education, health, motivation. ...
... E. Long term memory seems to be unaffected. F. More time to fall asleep, more walking periods during the night, and longer amount of time being awake at night. G. Many older people shoe no change and some show a 10% increase in thinking ability due to education, health, motivation. ...