56 Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia
... -- Provide the circuitry for coordinating mainly the movements of the distal portions of the limbs, especially the hands and fingers -- Compared the “intentions ” from the motor cortex and red nucleus, with the “performance” from the peripheral parts of the ...
... -- Provide the circuitry for coordinating mainly the movements of the distal portions of the limbs, especially the hands and fingers -- Compared the “intentions ” from the motor cortex and red nucleus, with the “performance” from the peripheral parts of the ...
chapter 8 movement
... – The Initiation and Awareness of Movement • Increased activity in frontal (preSMA and SMA) and parietal lobes • Activation of primary motor cortex ...
... – The Initiation and Awareness of Movement • Increased activity in frontal (preSMA and SMA) and parietal lobes • Activation of primary motor cortex ...
Nervous System Chapter 14 – 18
... enclose) capillaries so that any substance that can diffuse through the capillary wall must also diffuse through the astrocyte to get the brain. ...
... enclose) capillaries so that any substance that can diffuse through the capillary wall must also diffuse through the astrocyte to get the brain. ...
Synapses and neuronal signalling
... • Membrane capacitance prolongs the timecourse of signals • Membrane and cytoplasmic resistance affect the efficiency of the spread of depolarising pulses • Speed and efficiency of action potential propagation determined by passive membrane properties and axon ...
... • Membrane capacitance prolongs the timecourse of signals • Membrane and cytoplasmic resistance affect the efficiency of the spread of depolarising pulses • Speed and efficiency of action potential propagation determined by passive membrane properties and axon ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... responses to changes. 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolar ...
... responses to changes. 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolar ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... - includes all sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic fibers - all parasympathetic postganglionic fibers - a few sympathetic postganglionic fibers - all somatic motor neurons 2. Adrenergic - release norepinephrine - most sympathetic postganglionic fibers Activities of the ANS - most effectors ...
... - includes all sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic fibers - all parasympathetic postganglionic fibers - a few sympathetic postganglionic fibers - all somatic motor neurons 2. Adrenergic - release norepinephrine - most sympathetic postganglionic fibers Activities of the ANS - most effectors ...
The Neural Optimal Control Hierarchy
... learned motor components (i.e., synergies), are used as basis functions, and combined through weighted summation to compose the desired movement. This process is described in detail in [?]. The PM/SMA areas act as the highest levels in the motor hierarchy, generating signals that proceed through M1, ...
... learned motor components (i.e., synergies), are used as basis functions, and combined through weighted summation to compose the desired movement. This process is described in detail in [?]. The PM/SMA areas act as the highest levels in the motor hierarchy, generating signals that proceed through M1, ...
Supporting Information S1.
... MEA recording system with an inter-node spacing of 200 m. Consequently, here we show that neurites can extend significantly from the soma over multiple nodes, up to 800 m (4 nodes). (Right) The same culture was counterstained with an antibody against βTubIII to show the whole network development. ...
... MEA recording system with an inter-node spacing of 200 m. Consequently, here we show that neurites can extend significantly from the soma over multiple nodes, up to 800 m (4 nodes). (Right) The same culture was counterstained with an antibody against βTubIII to show the whole network development. ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... There are hundreds of dendrites but usually just one axon. Axons can be very long (> 1 m) while dendrites are < 2 mm. Axons have the same diameter the entire length – dendrites taper. Axons have terminals (synapses) and no ribosomes. Dendrites have spines (punching bags). Don’t be fooled by the bran ...
... There are hundreds of dendrites but usually just one axon. Axons can be very long (> 1 m) while dendrites are < 2 mm. Axons have the same diameter the entire length – dendrites taper. Axons have terminals (synapses) and no ribosomes. Dendrites have spines (punching bags). Don’t be fooled by the bran ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
cerebral cortex - krigolson teaching
... or extension in a joint, mostly in experiments on monkeys. If a monkey is trained to make a simple movement in response to a sensory stimulus, the first changes in the muscle activity (EMG) occur at a delay (latency) of about 150 ms. Changes in the activity of pyramidal neurons can be seen up to 100 ...
... or extension in a joint, mostly in experiments on monkeys. If a monkey is trained to make a simple movement in response to a sensory stimulus, the first changes in the muscle activity (EMG) occur at a delay (latency) of about 150 ms. Changes in the activity of pyramidal neurons can be seen up to 100 ...
THE BASAL GANGLIA - Selam Higher Clinic
... The Vestibulospinal tract Originates in the vestibular nuclei. ...
... The Vestibulospinal tract Originates in the vestibular nuclei. ...
Functions of the Nervous System
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
activities unit 5 - Junta de Andalucía
... a) The passage of a nerve impulse from a dendrite to an axon is produced because neurotransmitters are released. b) The cerebrum coordinates muscle movements. c) The cerebrum has grey matter on the outside and white matter on the inside. d) The grey matter in the spinal cord is shaped like a butterf ...
... a) The passage of a nerve impulse from a dendrite to an axon is produced because neurotransmitters are released. b) The cerebrum coordinates muscle movements. c) The cerebrum has grey matter on the outside and white matter on the inside. d) The grey matter in the spinal cord is shaped like a butterf ...
APPLICATION FOR MRC STUDENTSHIPS TO COMMENCE 2009
... This studentship will investigate how dopamine neurons are specified during development and how its dysfunction is associated with neurodevelopmental disorders including ADHD and Schizophrenia. The study will focus on the function of a transcription factor in the specification and function of a grou ...
... This studentship will investigate how dopamine neurons are specified during development and how its dysfunction is associated with neurodevelopmental disorders including ADHD and Schizophrenia. The study will focus on the function of a transcription factor in the specification and function of a grou ...
Ling411-02-Neurons - OWL-Space
... A person’s linguistic system is largely represented in his/her cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system does what it does by virtue of its connections to other components • ...
... A person’s linguistic system is largely represented in his/her cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system does what it does by virtue of its connections to other components • ...
Objectives 35 - U
... Globus Pallidus (pallidum) – external segment (GPe) and internal segment (GPi) - Putamen and globus pallidus make up lenticular nucleus Substantia Nigra Subthalamic nucleus Nucleus Accumbens –related to caudate and putamen - caudate nucleus, putamen, and nucleus accumbens have similar but parallel c ...
... Globus Pallidus (pallidum) – external segment (GPe) and internal segment (GPi) - Putamen and globus pallidus make up lenticular nucleus Substantia Nigra Subthalamic nucleus Nucleus Accumbens –related to caudate and putamen - caudate nucleus, putamen, and nucleus accumbens have similar but parallel c ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • All parts of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • All parts of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
DESCENDING TRACTS - University of Kansas
... Thought to mediate larger movements of trunk and limbs that do not require balance or fine movements of upper limbs. ...
... Thought to mediate larger movements of trunk and limbs that do not require balance or fine movements of upper limbs. ...
Slide ()
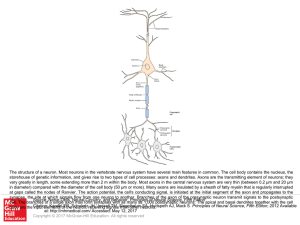
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
Andrea Sookchan Jasmine Hodge Billy Chang
... Interneurons – Analyze and interpret information Motor neurons – Convey signal to muscles Neurons follow an “all or none” principle. This means they either fire the impulse, or they do not. There is no in between. ...
... Interneurons – Analyze and interpret information Motor neurons – Convey signal to muscles Neurons follow an “all or none” principle. This means they either fire the impulse, or they do not. There is no in between. ...