Human Anatomy and Physiology, Nervous System and Special
... _______________: branched and attached along tendon to sense changes in length Physiology Nerve Impulses 10. How is the resting membrane potential established? __________________ __________________________________ 11. What stimuli can cause the generation of a neuronal action potential? ___________ ...
... _______________: branched and attached along tendon to sense changes in length Physiology Nerve Impulses 10. How is the resting membrane potential established? __________________ __________________________________ 11. What stimuli can cause the generation of a neuronal action potential? ___________ ...
The Brainstem
... • Reticular activating system (RAS) - critical for maintaining consciousness • Substantia nigra - dopamine containing neurons that are part of the basal ganglia (motor), die in Parkinson’s disease • Red nucleus – arm flexion, damage results in a decerebrate posture which is a poor clinical sign • Ce ...
... • Reticular activating system (RAS) - critical for maintaining consciousness • Substantia nigra - dopamine containing neurons that are part of the basal ganglia (motor), die in Parkinson’s disease • Red nucleus – arm flexion, damage results in a decerebrate posture which is a poor clinical sign • Ce ...
File
... depending on the range that it covers (longer axons are myelinated). - it is possible for more than one interneuron to be involved in ‘connecting’ a sensory neuron to a motor neuron ...
... depending on the range that it covers (longer axons are myelinated). - it is possible for more than one interneuron to be involved in ‘connecting’ a sensory neuron to a motor neuron ...
The language of the brain
... for increasing the strengths of synapses—an important process in forming long-term memories. A synapse is said to be strengthened when the firing of a neuron on one side of a synapse leads the neuron on the other side of the synapse to register a stronger response. In 1997 Henry Markram and Bert Sak ...
... for increasing the strengths of synapses—an important process in forming long-term memories. A synapse is said to be strengthened when the firing of a neuron on one side of a synapse leads the neuron on the other side of the synapse to register a stronger response. In 1997 Henry Markram and Bert Sak ...
The Nervous System - Appoquinimink High School
... 1. Use the book and your notes to create a foldable about the different types of neurons. 2. You may fold it anyway you like as long as on the outside you have three flaps (1 for each of the types of neurons) 3. The outside you will need to draw what each neuron looks like and label it. 4. The insi ...
... 1. Use the book and your notes to create a foldable about the different types of neurons. 2. You may fold it anyway you like as long as on the outside you have three flaps (1 for each of the types of neurons) 3. The outside you will need to draw what each neuron looks like and label it. 4. The insi ...
Chapter 10
... premotor cortex of monkeys (Gallese, Fadiga, et al. 1996; Rizzolatti and Arbib 1998; Gallese 2000). Using microelectrodes that recorded from individual neurons, they observed that the same neuron fired both when the monkey grasped an object, such as a raisin, and when a human or another monkey perfo ...
... premotor cortex of monkeys (Gallese, Fadiga, et al. 1996; Rizzolatti and Arbib 1998; Gallese 2000). Using microelectrodes that recorded from individual neurons, they observed that the same neuron fired both when the monkey grasped an object, such as a raisin, and when a human or another monkey perfo ...
Classes #9-11: Differentiation of the brain vesicles
... class sessions 9-11. The first 46 questions are for review, and can be answered from earlier lectures. Many of these questions are answered in the readings as well. 1. The forebrain probably expanded in evolution initially because of the importance of _________________________________. 2. Give an ex ...
... class sessions 9-11. The first 46 questions are for review, and can be answered from earlier lectures. Many of these questions are answered in the readings as well. 1. The forebrain probably expanded in evolution initially because of the importance of _________________________________. 2. Give an ex ...
WHY STUDY THE BRAIN IN PSYCHOLOGY?
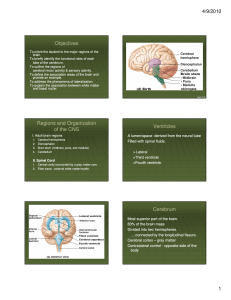
... • Brain is divided into two hemispheres or parts. • The line that divides the is called a Fissure. • Right and Left: each side of brain controls the opposite side of the body. • Corpus Callosum: bundle of fibers that help each side of the brain communicate with the other. ...
... • Brain is divided into two hemispheres or parts. • The line that divides the is called a Fissure. • Right and Left: each side of brain controls the opposite side of the body. • Corpus Callosum: bundle of fibers that help each side of the brain communicate with the other. ...
Neurons` Short-Term Plasticity Amplifies Signals
... focusing on cells from two particular regions, called CA1 and CA3, known for their role in encoding information about the animal’s position. The researchers recorded long series of this firing activity, which they then used to stimulate two classes of hippocampal neurons: excitatory neurons, whose fu ...
... focusing on cells from two particular regions, called CA1 and CA3, known for their role in encoding information about the animal’s position. The researchers recorded long series of this firing activity, which they then used to stimulate two classes of hippocampal neurons: excitatory neurons, whose fu ...
Chapter 13: The Nervous System
... The cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in clusters called ______________________ that are located outside of the spinal cord. ...
... The cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in clusters called ______________________ that are located outside of the spinal cord. ...
Anti-SPRR1a antibody ab125374 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 2 Images
... results were obtained when blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in 0.05% PBS-T. ...
... results were obtained when blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in 0.05% PBS-T. ...
primary cortex - u.arizona.edu
... speed and force of contralateral movements, and they make it difficult to move one body part independently of others (They do not produce paralysis) ...
... speed and force of contralateral movements, and they make it difficult to move one body part independently of others (They do not produce paralysis) ...
semicircular canals
... physical or chemical change. 2. The physical or chemical change causes action potentials in sensory neurons. 3. Sensory neurons carry action potentials through cranial nerves or spinal nerves to the CNS. 4. Typically the sensory information is carried to the thalamus where synapses occur. 5. Neurons ...
... physical or chemical change. 2. The physical or chemical change causes action potentials in sensory neurons. 3. Sensory neurons carry action potentials through cranial nerves or spinal nerves to the CNS. 4. Typically the sensory information is carried to the thalamus where synapses occur. 5. Neurons ...
1 - Kvalley Computers and Internet
... List the three different major types of neurons. What does each do? ...
... List the three different major types of neurons. What does each do? ...
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding glial
... a) The cell body is positively charged while the terminal buttons are negatively charged b) The neuron is negatively charged while the extra-cellular medium is positively charged c) The neuron predominantly contains negatively charged ions while the extra-cellular medium contains positively charged ...
... a) The cell body is positively charged while the terminal buttons are negatively charged b) The neuron is negatively charged while the extra-cellular medium is positively charged c) The neuron predominantly contains negatively charged ions while the extra-cellular medium contains positively charged ...
Modeling working memory and decision making using generic
... Neurons – leaky integrate-and-fire neurons, 20% of them inhibitory, neuron a is connected to neuron b with probability C.exp(-D2(a,b)/λ2) Synapses – dynamic synapses with fixed parameters w, U, D, F chosen from distributions based on empirical data from Henry Markram’s lab ...
... Neurons – leaky integrate-and-fire neurons, 20% of them inhibitory, neuron a is connected to neuron b with probability C.exp(-D2(a,b)/λ2) Synapses – dynamic synapses with fixed parameters w, U, D, F chosen from distributions based on empirical data from Henry Markram’s lab ...
Lecture 5 - Brain I - Linn
... To orient the student to the major regions of the brain. To briefly identify the functional roles of each lobe of the cerebrum. To outline the regions of cerebral motor activity & sensory activity. To define the association areas of the brain and ...
... To orient the student to the major regions of the brain. To briefly identify the functional roles of each lobe of the cerebrum. To outline the regions of cerebral motor activity & sensory activity. To define the association areas of the brain and ...
The Synaptic Cleft or Synapse
... A neuron’s axon ends in many small swellings called axon terminals. At the axon terminal the neuron may meet dendrites of another axon or an effector, like a muscle or gland. The space where neurons meet other neurons or effectors is called the synapse. There are presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic ...
... A neuron’s axon ends in many small swellings called axon terminals. At the axon terminal the neuron may meet dendrites of another axon or an effector, like a muscle or gland. The space where neurons meet other neurons or effectors is called the synapse. There are presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... come down the axon – no matter how strong it is. 9. The __________________ __________________ __________________ is the time immediately after the Na gates close and repolarization is still occurring that a exceptionally strong stimulus may cause depolarization. F. Impulses 1. Impulses travel at dif ...
... come down the axon – no matter how strong it is. 9. The __________________ __________________ __________________ is the time immediately after the Na gates close and repolarization is still occurring that a exceptionally strong stimulus may cause depolarization. F. Impulses 1. Impulses travel at dif ...