Chapter 3
... dopamine neutotransmitter and dopamine neurons in several brain areas. Antipsychotic drugs inhibit the effects of dopamine in the brain, reducing the over- reaction to it. • Depression, probably the most common psychological disturbance, appears to be related to 2 neurotransmitters: norepinephrine a ...
... dopamine neutotransmitter and dopamine neurons in several brain areas. Antipsychotic drugs inhibit the effects of dopamine in the brain, reducing the over- reaction to it. • Depression, probably the most common psychological disturbance, appears to be related to 2 neurotransmitters: norepinephrine a ...
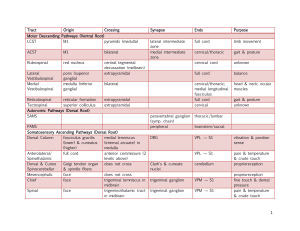
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... distinct pathways for: motor control, eye movements, cognitive & emotional functions direct pathway: excite thalamus via disinhibition cortex → striatum → inhibits GPi/SNr → reduces inhibition of thalamus indirect pathway: inhibit thalamus via STN cortex → striatum → inhibits GPe → reduces inhibitio ...
... distinct pathways for: motor control, eye movements, cognitive & emotional functions direct pathway: excite thalamus via disinhibition cortex → striatum → inhibits GPi/SNr → reduces inhibition of thalamus indirect pathway: inhibit thalamus via STN cortex → striatum → inhibits GPe → reduces inhibitio ...
Chicurel2001NatureNV..
... develop devices that turn thoughts into actions — a concept that could lead to the development of functional prostheses for paralysed patients. Out on a limb As early as 1970, researchers showed that by monitoring the activities of just five neurons in an area of a monkey’s brain controlling limb mo ...
... develop devices that turn thoughts into actions — a concept that could lead to the development of functional prostheses for paralysed patients. Out on a limb As early as 1970, researchers showed that by monitoring the activities of just five neurons in an area of a monkey’s brain controlling limb mo ...
Nerve
... proprioceptive nerve fibers stimulus. The external stimulus may be electrical, microelectrodes are inserted into cells, membrane (axons ...
... proprioceptive nerve fibers stimulus. The external stimulus may be electrical, microelectrodes are inserted into cells, membrane (axons ...
Synaptic receptors, neurotransmitters and brain modulators
... dorsal thalamus, which is comprised of roughly 15 nuclei with relay cells that project to the cerebral cortex. ventral thalamus (the major portion of which is the thalamic reticular nucleus) - reticular cells are GABAergic and project into the dorsal thalamus to inhibit relay cells. Function: to g ...
... dorsal thalamus, which is comprised of roughly 15 nuclei with relay cells that project to the cerebral cortex. ventral thalamus (the major portion of which is the thalamic reticular nucleus) - reticular cells are GABAergic and project into the dorsal thalamus to inhibit relay cells. Function: to g ...
The Nervous System
... cm rod enter his skull just under his left eye and exited through the top of his head. The rod destroyed a very large portion of his frontal lobe. He was able to recover, but his emotions changed. This left a connection with the frontal lobe and emotional responses. ...
... cm rod enter his skull just under his left eye and exited through the top of his head. The rod destroyed a very large portion of his frontal lobe. He was able to recover, but his emotions changed. This left a connection with the frontal lobe and emotional responses. ...
Neurons and how they communicate
... After passing through the empty synaptic cleft the neurotransmitters attach or bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron These neurotransmitters can then make the receiving neuron either more or less likely to fire It is in this infinitesimally small space that irregularities can have profound ef ...
... After passing through the empty synaptic cleft the neurotransmitters attach or bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron These neurotransmitters can then make the receiving neuron either more or less likely to fire It is in this infinitesimally small space that irregularities can have profound ef ...
The Brain The brain is responsible for everything we think, feel and
... information about muscle movement and position of limbs. The somatosensory cortex runs parallel to the primary motor cortex and like it has different parts the body associated with areas of the cortex. Some body parts have a larger area of cortex devoted to them, depending on the sensitivity of the ...
... information about muscle movement and position of limbs. The somatosensory cortex runs parallel to the primary motor cortex and like it has different parts the body associated with areas of the cortex. Some body parts have a larger area of cortex devoted to them, depending on the sensitivity of the ...
Chapter 11 - Central Nervous System
... brain portion 100,000,000,000 neurons Cerebral hemispheres connected by corpus callosum Divided into lobes named for bones that cover them Internal lobe – Insula Convolutions are made up of • sulci - shallow groove • central sulcus • lateral sulcus • fissure - deep groove • longitudinal fissur ...
... brain portion 100,000,000,000 neurons Cerebral hemispheres connected by corpus callosum Divided into lobes named for bones that cover them Internal lobe – Insula Convolutions are made up of • sulci - shallow groove • central sulcus • lateral sulcus • fissure - deep groove • longitudinal fissur ...
Nervous System
... Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
... Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
File
... ___________________ The branching filaments that conduct nerve impulses towards the cell. ___________________ The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from within and outside the body. ___________________ The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. ___________________ The part of the nerve ...
... ___________________ The branching filaments that conduct nerve impulses towards the cell. ___________________ The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from within and outside the body. ___________________ The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. ___________________ The part of the nerve ...
Answer Key
... 12. With regard to the process of neural transmission, a refractory period refers to a time interval in which A) a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. B) an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. C) positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membrane. D) a ...
... 12. With regard to the process of neural transmission, a refractory period refers to a time interval in which A) a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. B) an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. C) positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membrane. D) a ...
bioii ch10 ppt
... •Gamma Aminobutyric Acid is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA1 gene. GABA acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre and postsynaptic neuronal processes. The primary role of this neurotransmitter is to slo ...
... •Gamma Aminobutyric Acid is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA1 gene. GABA acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre and postsynaptic neuronal processes. The primary role of this neurotransmitter is to slo ...
The Nervous System
... around the larger nerve fibers in the PNS. Vital to neuronal regeneration ...
... around the larger nerve fibers in the PNS. Vital to neuronal regeneration ...
Descending Tracts
... It receives projection fibers from the globus pallidus of the basal ganglia, and gives origin to two descending extrapyramidal tracts: •The lateral tectospinal tract: Originates from the superior colliculus (the center of visual reflexes), crosses to the opposite side and terminates in the cervical ...
... It receives projection fibers from the globus pallidus of the basal ganglia, and gives origin to two descending extrapyramidal tracts: •The lateral tectospinal tract: Originates from the superior colliculus (the center of visual reflexes), crosses to the opposite side and terminates in the cervical ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • 5. Binding of neurotransmitter opens ion channels, resulting in graded potentials. • 6.Neurotransmitter effects are terminated. ...
... and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • 5. Binding of neurotransmitter opens ion channels, resulting in graded potentials. • 6.Neurotransmitter effects are terminated. ...
Nervous System
... Propagation of the Action Potential • Generated at the axon hillock • What is the “all or none” concept associated with an action potential? • How is it that you can feel different degrees of stimulus when action potentials are generated in an all or none fashion? • How is it that an action potent ...
... Propagation of the Action Potential • Generated at the axon hillock • What is the “all or none” concept associated with an action potential? • How is it that you can feel different degrees of stimulus when action potentials are generated in an all or none fashion? • How is it that an action potent ...
BrainMechanismsofUnconsciousInference2011
... On the skin In the visual world In non-spatial dimensions such as auditory frequency ...
... On the skin In the visual world In non-spatial dimensions such as auditory frequency ...
Chp 7 (part 1)
... proximal and distal processes. 2. only small branches at the end of the distal process are dendrites 3. The remainder of the process acts as an axon. 4. The axon then sends impulses toward and away from the cell body 5. Found in sensory neurons in PNS ganglia 7. Physiology a. Neurons have 2 major fu ...
... proximal and distal processes. 2. only small branches at the end of the distal process are dendrites 3. The remainder of the process acts as an axon. 4. The axon then sends impulses toward and away from the cell body 5. Found in sensory neurons in PNS ganglia 7. Physiology a. Neurons have 2 major fu ...
Chapter 11 The Nervous System
... Section 10-4 The Brain The cerebral hemispheres function in integration, sensory reception, and motor action. – The cerebrum with its two cerebral hemispheres is the largest part of the brain. – The outer layer of each hemisphere is the cortex. – The cerebral cortex consists of many discrete functi ...
... Section 10-4 The Brain The cerebral hemispheres function in integration, sensory reception, and motor action. – The cerebrum with its two cerebral hemispheres is the largest part of the brain. – The outer layer of each hemisphere is the cortex. – The cerebral cortex consists of many discrete functi ...
Medial Temporal Lobe Switches Memory Encoding in Neocortex
... artificial visuo-auditory memory traces can be established in the rat auditory cortex and that their encoding depends on the entorhinal cortex of the medial temporal lobe in the rat. We trained rats to associate a visual stimulus with electrical stimulation of the auditory cortex using a classical c ...
... artificial visuo-auditory memory traces can be established in the rat auditory cortex and that their encoding depends on the entorhinal cortex of the medial temporal lobe in the rat. We trained rats to associate a visual stimulus with electrical stimulation of the auditory cortex using a classical c ...
How the Brain Pays Attention
... to pinpoint the areas of the brain involved in visual attention and, likewise, where the control occurs. However, although MRI and fMRI scanners show the location of brain activity quite well, they don’t shed light on how the brain is working, at a fine temporal time scale. So we used a technique ca ...
... to pinpoint the areas of the brain involved in visual attention and, likewise, where the control occurs. However, although MRI and fMRI scanners show the location of brain activity quite well, they don’t shed light on how the brain is working, at a fine temporal time scale. So we used a technique ca ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CH 48 AND 49
... send info to interneurons which send info to motor neurons which send info to muscles or glands ...
... send info to interneurons which send info to motor neurons which send info to muscles or glands ...
Self-Guided Study for Chapter 12 and Review
... Here we make final sense of what we are sensing and this information may be stored. This sensory information is relayed onto the motor cortex area Area Anterior Association Area ...
... Here we make final sense of what we are sensing and this information may be stored. This sensory information is relayed onto the motor cortex area Area Anterior Association Area ...