6. Peripheral Nervous System
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS) One Motor Neuron to Single Effector Tissue ...
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS) One Motor Neuron to Single Effector Tissue ...
Nervous System PPT - Effingham County Schools
... – Nodes of Ranvier (short region of exposed axon between Schwann cells on neurons) – The more myelin the faster the impulse ...
... – Nodes of Ranvier (short region of exposed axon between Schwann cells on neurons) – The more myelin the faster the impulse ...
Chapter 15 - Austin Community College
... Three important areas of cortex: • Motor areas control voluntary movement. • Sensory areas provide consciousness and awareness of sensations. • Association areas act mainly to integrate diverse information into decisive and meaningful actions. This is done via interneurons or association neurons. ...
... Three important areas of cortex: • Motor areas control voluntary movement. • Sensory areas provide consciousness and awareness of sensations. • Association areas act mainly to integrate diverse information into decisive and meaningful actions. This is done via interneurons or association neurons. ...
Dr. Carlos Paladini
... The dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, located within the ventral mesencephalon, encode perhaps one of the most important signals for reinforcement learning in the brain: reward prediction error. This signal is encoded by the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons, which con ...
... The dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, located within the ventral mesencephalon, encode perhaps one of the most important signals for reinforcement learning in the brain: reward prediction error. This signal is encoded by the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons, which con ...
E.4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses
... The drug traps the chemical dopamine in the spaces between nerve cells. Dopamine creates the feelings of pleasure we get from enjoyable activities such as eating and having sex. But in cocaine users, dopamine keeps stimulating those cells, creating a "high" -- a euphoric feeling that lasts anywhere ...
... The drug traps the chemical dopamine in the spaces between nerve cells. Dopamine creates the feelings of pleasure we get from enjoyable activities such as eating and having sex. But in cocaine users, dopamine keeps stimulating those cells, creating a "high" -- a euphoric feeling that lasts anywhere ...
neuron
... – 1. sensory neurons: respond to input from sensory organs (skin, eyes, etc.) – 2. motor neurons: send signals to muscles to control movement – 3. interneurons: connect the sensory neurons and motor neurons • most of the neurons in the brain = interneurons ...
... – 1. sensory neurons: respond to input from sensory organs (skin, eyes, etc.) – 2. motor neurons: send signals to muscles to control movement – 3. interneurons: connect the sensory neurons and motor neurons • most of the neurons in the brain = interneurons ...
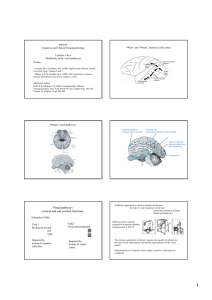
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... Electrophysiological studies in monkeys 1970s Mountcastle & Hyvarinen electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
... Electrophysiological studies in monkeys 1970s Mountcastle & Hyvarinen electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
Summary - Publikationsserver UB Marburg
... Summary Dopaminergic midbrain Neurons are located mainly in two regions, the substantia nigra (SN) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA). These neurons play an important role in the pathophysiology of drug abuse. The dopaminergic projections from the VTA to the Nucleus accumbens, amygdala and prefron ...
... Summary Dopaminergic midbrain Neurons are located mainly in two regions, the substantia nigra (SN) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA). These neurons play an important role in the pathophysiology of drug abuse. The dopaminergic projections from the VTA to the Nucleus accumbens, amygdala and prefron ...
Nervous System Introduction
... – 6. Over 3 million people are afflicted with Alzheimer’s disease – 7. At least 700,000 have cerebral palsy – 8. More than 250,000 have multiple sclerosis – 9. In addition, there are over 500,000 accidental head and spine injuries annually; fortunately only a minority of which actually injure the br ...
... – 6. Over 3 million people are afflicted with Alzheimer’s disease – 7. At least 700,000 have cerebral palsy – 8. More than 250,000 have multiple sclerosis – 9. In addition, there are over 500,000 accidental head and spine injuries annually; fortunately only a minority of which actually injure the br ...
8Neurotrophins PCD
... Anatomy and physiology are especially sensitive to modulation by experience. Critical Period An extreme form of Sensitive Period. Appropriate expression is essential for the normal development of a pathway or set of connections (and after this period, it cannot be repaired). e.g., There was a critic ...
... Anatomy and physiology are especially sensitive to modulation by experience. Critical Period An extreme form of Sensitive Period. Appropriate expression is essential for the normal development of a pathway or set of connections (and after this period, it cannot be repaired). e.g., There was a critic ...
Hourly2_2012 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... 2. Dr. Otis P. Kribblekoblitz discovers that a rare subterranean rodent, the shrew-faced schmoo, has a specialized sensory system for detecting microwave radiation. He identifies a thalamic nucleus that serves as the specific relay nucleus for the microwave sense, which he modestly names "the nucleu ...
... 2. Dr. Otis P. Kribblekoblitz discovers that a rare subterranean rodent, the shrew-faced schmoo, has a specialized sensory system for detecting microwave radiation. He identifies a thalamic nucleus that serves as the specific relay nucleus for the microwave sense, which he modestly names "the nucleu ...
Myers Module Four
... Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions to enter the recieving neuron and exci ...
... Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions to enter the recieving neuron and exci ...
4-CPG1
... removal of varying sensory afference. • The movement must not be extinguished by the removal of somatic feedback. • Experiments beginning in 1960s produced evidence for CPGs. Russian studies of decorticated cats showed they could maintain walking motion without a cortex. ...
... removal of varying sensory afference. • The movement must not be extinguished by the removal of somatic feedback. • Experiments beginning in 1960s produced evidence for CPGs. Russian studies of decorticated cats showed they could maintain walking motion without a cortex. ...
Neurons: A fish-eye view of the brain
... cells perform such magic? Surprisingly, we’re finding some answers to that question by studying the tiny, 10,000-neuron brains of the developing Danio rerio, known affectionately as the zebrafish. The stuff of brains What makes a brain powerful isn’t just its size or the number of neurons, but the w ...
... cells perform such magic? Surprisingly, we’re finding some answers to that question by studying the tiny, 10,000-neuron brains of the developing Danio rerio, known affectionately as the zebrafish. The stuff of brains What makes a brain powerful isn’t just its size or the number of neurons, but the w ...
Airgas template - Morgan Community College
... The parasympathetic nervous system functions in maintaining vital functions and responding when there is a critical threat to the integrity of the individual—the “fight-or-flight” response. ...
... The parasympathetic nervous system functions in maintaining vital functions and responding when there is a critical threat to the integrity of the individual—the “fight-or-flight” response. ...
Major Brain Structures and Functions
... cells that cover the hemispheres; contains more than 300 trillion synapses • The more complex the animal, the larger the cerebral cortex • What’s underneath? Filled with the axons that connect the cortex to the brain’s other regions • Divided into lobes based upon fissures or folds • Brain’s two hal ...
... cells that cover the hemispheres; contains more than 300 trillion synapses • The more complex the animal, the larger the cerebral cortex • What’s underneath? Filled with the axons that connect the cortex to the brain’s other regions • Divided into lobes based upon fissures or folds • Brain’s two hal ...
Disorders of the Nervous System
... 1. frontal lobe – voluntary muscle movement and speech 2. parietal lobe – touch, pain, temperature 3. temporal lobe (or auditory) – interpreting sounds 4. occipital lobe (or visual) – interpreting sights The brain contains areas of tissue; the internal tissue is called white matter, and the outer la ...
... 1. frontal lobe – voluntary muscle movement and speech 2. parietal lobe – touch, pain, temperature 3. temporal lobe (or auditory) – interpreting sounds 4. occipital lobe (or visual) – interpreting sights The brain contains areas of tissue; the internal tissue is called white matter, and the outer la ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • Proceeds without conscious intention but can be influenced by volition. ...
... • Proceeds without conscious intention but can be influenced by volition. ...
Learning in a neural network model in real time using real world
... using chunked sampling (23 ms), keeping stimulation of the input neurons constant during that time. This limits the phase information available, and hence does not allow usual approaches to localization of sound sources. This problem may be addressed by shortening the length of data samples, or usin ...
... using chunked sampling (23 ms), keeping stimulation of the input neurons constant during that time. This limits the phase information available, and hence does not allow usual approaches to localization of sound sources. This problem may be addressed by shortening the length of data samples, or usin ...
Information Theoretic Approach to the Study of Auditory Coding
... than MGB and AI neurons. Since AI neurons convey half the information that IC neurons do about stimulus identity we conclude that cortical neurons code the identity of the stimuli well without characterizing their ”physical” aspects. This observation hints that the cortex is sensitive to complex str ...
... than MGB and AI neurons. Since AI neurons convey half the information that IC neurons do about stimulus identity we conclude that cortical neurons code the identity of the stimuli well without characterizing their ”physical” aspects. This observation hints that the cortex is sensitive to complex str ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... maintaining the normal homeostasis of the body. Both systems detect changes in the physiologic set point of the body (temp., BP) they integrate the information they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to gene ...
... maintaining the normal homeostasis of the body. Both systems detect changes in the physiologic set point of the body (temp., BP) they integrate the information they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to gene ...
The Nervous System - Canton Local Schools
... neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Two parts: 1. Autonomatic (ANS): controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs. AUTOMATIC 2. Somatic (SNS): controls the body skeletal muscles ...
... neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Two parts: 1. Autonomatic (ANS): controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs. AUTOMATIC 2. Somatic (SNS): controls the body skeletal muscles ...
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... • Cell body: functional portion • Dendrites: short extensions that receive signals • Axon: long extension that transmits impulses away ...
... • Cell body: functional portion • Dendrites: short extensions that receive signals • Axon: long extension that transmits impulses away ...