CHAPTER OUTLINE
... The four major parts of the brain are the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellum, and the brain stem. The Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest portion of the brain. It is the last center to receive sensory input and carry out integration before commanding voluntary motor responses. It communicat ...
... The four major parts of the brain are the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellum, and the brain stem. The Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest portion of the brain. It is the last center to receive sensory input and carry out integration before commanding voluntary motor responses. It communicat ...
Neurology for Psychiatrists - the Peninsula MRCPsych Course
... IC (white matter) runs between the CN and the LN = Corpus Striatum Artery of Stroke Pure damage to Basal Ganglia = No corticospinal symptoms, No neuropsychological dysfunction, No cognitive Dysfunction, contra lateral Result of biochemical not usually structural, B/L, slow progress ...
... IC (white matter) runs between the CN and the LN = Corpus Striatum Artery of Stroke Pure damage to Basal Ganglia = No corticospinal symptoms, No neuropsychological dysfunction, No cognitive Dysfunction, contra lateral Result of biochemical not usually structural, B/L, slow progress ...
Exam - McLoon Lab
... D. the membrane potential for most neurons reaches approximately -65mV. E. More than one of the above is true. 27. The refractory period for a neuron … A. is the time when threshold has been reached and an action potential is about to be generated. B. is the time during which the soma of a neuron is ...
... D. the membrane potential for most neurons reaches approximately -65mV. E. More than one of the above is true. 27. The refractory period for a neuron … A. is the time when threshold has been reached and an action potential is about to be generated. B. is the time during which the soma of a neuron is ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVE 5: Explain how an injured nerve fiber may
... LEARNING OBJECTIVE 4: Name four types of neuroglial cells and describe the functions of each. Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines 1. Introduce neuroglial cells as accessory cells which fill spaces, support neurons, hold nervous tissue together, metabolize glucose, regulate potassium ions, produce mye ...
... LEARNING OBJECTIVE 4: Name four types of neuroglial cells and describe the functions of each. Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines 1. Introduce neuroglial cells as accessory cells which fill spaces, support neurons, hold nervous tissue together, metabolize glucose, regulate potassium ions, produce mye ...
01Integrated Normal Cells of CNS
... At the end of this lecture, you should describe the microscopic structure and the function of: 1- Neurons: - Cell body (perikaryon). - Processes: An axon and dendrites. ...
... At the end of this lecture, you should describe the microscopic structure and the function of: 1- Neurons: - Cell body (perikaryon). - Processes: An axon and dendrites. ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? a Class Objectives a What
... and control the precision of the signal being carried from one neuron to the next. - It is associated with _________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ...
... and control the precision of the signal being carried from one neuron to the next. - It is associated with _________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ...
Lecture3
... – Parkinson’s Disease is a condition in which the individual has trouble executing voluntary movements, and has tremors, rigidity and a depressed mood. – This condition has been linked to a gradual decay in a system of axons that release the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
... – Parkinson’s Disease is a condition in which the individual has trouble executing voluntary movements, and has tremors, rigidity and a depressed mood. – This condition has been linked to a gradual decay in a system of axons that release the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... Incorrect theory that claimed bumps on the skull could reveal mental abilities as well as character traits c. Correctly focused attention on the fact that various parts of the brain have different functions C. Biological psychology ...
... Incorrect theory that claimed bumps on the skull could reveal mental abilities as well as character traits c. Correctly focused attention on the fact that various parts of the brain have different functions C. Biological psychology ...
The Nervous System
... uses chemical signals (hormones) that produce slower ( but long lasting) responses. 3. Nervous system has 3 major functions: Sensory input – sensory or afferent neutron detect internal or external changes ( stimuli ) and send the message to the brain or spinal cord. Integration – interneurons in the ...
... uses chemical signals (hormones) that produce slower ( but long lasting) responses. 3. Nervous system has 3 major functions: Sensory input – sensory or afferent neutron detect internal or external changes ( stimuli ) and send the message to the brain or spinal cord. Integration – interneurons in the ...
On the Brain of a Scientist: Albert Einstein
... "higher" neural functions. These regions do not directly receive primary sensory information, but rather, as their name implies, ,.associate,, or. analyze inputs from other brain regions. The associaiion-cortices are the last domains of the cortex to myerinate, indicating their comparatruety rate de ...
... "higher" neural functions. These regions do not directly receive primary sensory information, but rather, as their name implies, ,.associate,, or. analyze inputs from other brain regions. The associaiion-cortices are the last domains of the cortex to myerinate, indicating their comparatruety rate de ...
Loss of orexin/NARP neurons in human narcolepsy
... of the paraventricular nucleus and reached a high density in the dorsal hypothalamic area, dorsomedial nucleus, and perifornical region. Caudally, cells were abundant in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Across the entire ORX field, nearly all ORX-ir neurons contained NARP-immunoreactivity. In ...
... of the paraventricular nucleus and reached a high density in the dorsal hypothalamic area, dorsomedial nucleus, and perifornical region. Caudally, cells were abundant in the lateral and posterior hypothalamus. Across the entire ORX field, nearly all ORX-ir neurons contained NARP-immunoreactivity. In ...
File chapter 2 vocab pp
... above the kidneys. They secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (nonadrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress. ...
... above the kidneys. They secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (nonadrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress. ...
Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines
... 2. Describe four major types of neuroglial cells, including characteristics and functions of each. Discussion should include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. Application Question(s) 1. Ask students to develop a table which summarizes four major types of neuroglial cells, ...
... 2. Describe four major types of neuroglial cells, including characteristics and functions of each. Discussion should include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. Application Question(s) 1. Ask students to develop a table which summarizes four major types of neuroglial cells, ...
Griggs_Chapter_02_Neuroscience
... Split-brain people can only identify information orally when it is presented briefly in the right visual field (and thus processing in the left hemisphere) If a spoon was flashed in the left visual field, split-brained people could not say it was a spoon If the person was blind-folded and told t ...
... Split-brain people can only identify information orally when it is presented briefly in the right visual field (and thus processing in the left hemisphere) If a spoon was flashed in the left visual field, split-brained people could not say it was a spoon If the person was blind-folded and told t ...
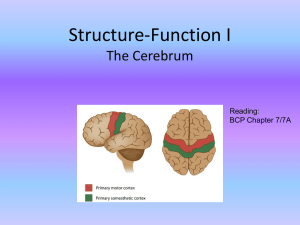
Structure-Function I
... reward learning, and in addiction. The nucleus basalis plays a role in the sleep-wake cycle and learning and memory (this nucleus undergoes damage in Alzheimer’s disease). ...
... reward learning, and in addiction. The nucleus basalis plays a role in the sleep-wake cycle and learning and memory (this nucleus undergoes damage in Alzheimer’s disease). ...
02Biology of the brain
... to his frontal lobe. She is perplexed by his behavior. Which of the following would you tell her is “normal behavior” for a person with frontal lobe damage? A. B. C. D. ...
... to his frontal lobe. She is perplexed by his behavior. Which of the following would you tell her is “normal behavior” for a person with frontal lobe damage? A. B. C. D. ...
Griggs Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... Split-brain people can only identify information orally when it is presented briefly in the right visual field (and thus processing in the left hemisphere) If a spoon was flashed in the left visual field, split-brained people could not say it was a spoon If the person was blind-folded and told t ...
... Split-brain people can only identify information orally when it is presented briefly in the right visual field (and thus processing in the left hemisphere) If a spoon was flashed in the left visual field, split-brained people could not say it was a spoon If the person was blind-folded and told t ...
Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... Excitation- the process of making a neuron more likely to generate an action potential (excitatory neurotransmitters binding to receptors) must be greater than – Inhibition – the process of making the neuron less likely to generate an action potential (inhibitory neurotransmitters binding to recepto ...
... Excitation- the process of making a neuron more likely to generate an action potential (excitatory neurotransmitters binding to receptors) must be greater than – Inhibition – the process of making the neuron less likely to generate an action potential (inhibitory neurotransmitters binding to recepto ...
Answers
... CELLS COMPARED TO THAT ON NERVE CELLS 10. State five ways that glia differ from neurons. Neurons have TWO "processes" called axons and dendrites....glial cells only have ONE; Neurons CAN generate action potentials...glial cells CANNOT. However, glial cells do have a resting potential; neurons HAVE s ...
... CELLS COMPARED TO THAT ON NERVE CELLS 10. State five ways that glia differ from neurons. Neurons have TWO "processes" called axons and dendrites....glial cells only have ONE; Neurons CAN generate action potentials...glial cells CANNOT. However, glial cells do have a resting potential; neurons HAVE s ...
Single Neurons
... memory by recording the activity of a population of single neurons. More specifically this study chose to isolate brain oscillations in the theta frequency range (3 – 8 Hz) as synaptic plasticity is induced, and analyse the synchronisation in terms of phase between the local theta oscillation and th ...
... memory by recording the activity of a population of single neurons. More specifically this study chose to isolate brain oscillations in the theta frequency range (3 – 8 Hz) as synaptic plasticity is induced, and analyse the synchronisation in terms of phase between the local theta oscillation and th ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...