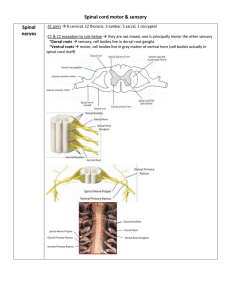
Changes in spinal cord
... *tectum is associated with visual movements also- coordination of muscle with visual input? ...
... *tectum is associated with visual movements also- coordination of muscle with visual input? ...
Fill in the blanks on LB page 67-68.
... A. The nervous system is organized into two major divisions: 1. The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord. 2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes all the nerves that carry signals to and from the brain and spinal cord. B. General Paths of Information Flow 1. ...
... A. The nervous system is organized into two major divisions: 1. The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord. 2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes all the nerves that carry signals to and from the brain and spinal cord. B. General Paths of Information Flow 1. ...
Central Nervous System
... Transverse gyri (pleated) called folia. Pattern of white matter inside resembles a ...
... Transverse gyri (pleated) called folia. Pattern of white matter inside resembles a ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... • All parts of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
... • All parts of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
Nolte Chapter 22: Cerebral Cortex
... telencephalon. Most of the hippocampus is archicortex. Puramidal cells are the most numerous neurons of the neocortex and have a conical cell body from which dendrites emerge but a long apical dendrite ascends vertically and a series of basal dendrites spread out horizontally. Pyramidals can go all ...
... telencephalon. Most of the hippocampus is archicortex. Puramidal cells are the most numerous neurons of the neocortex and have a conical cell body from which dendrites emerge but a long apical dendrite ascends vertically and a series of basal dendrites spread out horizontally. Pyramidals can go all ...
Calcium-activated chloride channels: a new target to
... characteristic of the ANO2 channels. This phenotype was also observed in the knockdown of ANO2 in CA1 hippocampal neurons, providing further evidence that Ca2+-activated Cl− conductance via ANO2 channels hyperpolarizes the membrane potential in these CNS neurons. The thalamus-specific ANO2 knockdown ...
... characteristic of the ANO2 channels. This phenotype was also observed in the knockdown of ANO2 in CA1 hippocampal neurons, providing further evidence that Ca2+-activated Cl− conductance via ANO2 channels hyperpolarizes the membrane potential in these CNS neurons. The thalamus-specific ANO2 knockdown ...
high. 1, treated virgin
... ipsilateral uropod blades produced impulses in the fiber and simultaneously excited flexor motoneurons. Thus sensory inputs to the command fiber can be identified, and they have an action identical with that produced by electrical stimulation of the central neuron itself. A command fiber producing e ...
... ipsilateral uropod blades produced impulses in the fiber and simultaneously excited flexor motoneurons. Thus sensory inputs to the command fiber can be identified, and they have an action identical with that produced by electrical stimulation of the central neuron itself. A command fiber producing e ...
peripheral nervous system
... Cocaine affects neurons in the brain’s “pleasure pathways” (limbic system) -Binds dopamine transporters and prevents the reuptake of dopamine -Dopamine survives longer in the synapse and fires pleasure pathways more and more -Prolonged exposure triggers the limbic system neurons to reduce receptor n ...
... Cocaine affects neurons in the brain’s “pleasure pathways” (limbic system) -Binds dopamine transporters and prevents the reuptake of dopamine -Dopamine survives longer in the synapse and fires pleasure pathways more and more -Prolonged exposure triggers the limbic system neurons to reduce receptor n ...
neurons
... A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
... A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
The Human Nervous System
... stimulant that causes actual physical changes to the brain. It effects the level of dopamine in the brain and is highly addictive. Stimulants will increase the activity of the Central ...
... stimulant that causes actual physical changes to the brain. It effects the level of dopamine in the brain and is highly addictive. Stimulants will increase the activity of the Central ...
BIOL241NSintro12aJUL2012
... • Masses of neuron cell bodies – Called ganglia in the PNS and are surrounded by satellite cells – Called nuclei in the CNS ...
... • Masses of neuron cell bodies – Called ganglia in the PNS and are surrounded by satellite cells – Called nuclei in the CNS ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Many different stimuli excite neurons to become active and generate an impulse. Light excites the eye receptors, sound excites some of the ear receptors, and pressure excites some cutaneous receptors of the skin. Most neurons in the body are excited by neurotransmitters released by other neuro ...
... Many different stimuli excite neurons to become active and generate an impulse. Light excites the eye receptors, sound excites some of the ear receptors, and pressure excites some cutaneous receptors of the skin. Most neurons in the body are excited by neurotransmitters released by other neuro ...
CranialN11
... B. Cortical areas involved in eye movement control. Rapid and slow eye movements: Rapid: saccades: quick movements of eyes in tandem to bring the fovea to an image. Slow: smooth pursuit: eyes in tandem to track a moving object Slow: convergence: disconjugate eye movement for viewing an object at a ...
... B. Cortical areas involved in eye movement control. Rapid and slow eye movements: Rapid: saccades: quick movements of eyes in tandem to bring the fovea to an image. Slow: smooth pursuit: eyes in tandem to track a moving object Slow: convergence: disconjugate eye movement for viewing an object at a ...
Eagleman Ch 3. Neurons and Synapses
... In the brain, there are approximately 100 billion neurons, each sending up to a few hundred action potentials per second. The number of spikes per second is used to describe the neuron’s response to a stimulus. ...
... In the brain, there are approximately 100 billion neurons, each sending up to a few hundred action potentials per second. The number of spikes per second is used to describe the neuron’s response to a stimulus. ...
The Nervous System
... replaced when they die. In fact, you have fewer neurons when you are old compared to when you are young. On the other hand, data published in November 1998 show that in one area of the brain (the hippocampus), new neurons CAN grow in adult humans. Neurons can be quite large - in some neurons, such a ...
... replaced when they die. In fact, you have fewer neurons when you are old compared to when you are young. On the other hand, data published in November 1998 show that in one area of the brain (the hippocampus), new neurons CAN grow in adult humans. Neurons can be quite large - in some neurons, such a ...
whisker outline.doc
... This mainly columnar relay is largely due to the axonal organization. Most of the axons from excitatory neurons relate to the main column, as is illustrated here in this camera lucida drawing. You see in red the dendritic arbor confined to layer 4 of this excitatory cell and then most of the axons d ...
... This mainly columnar relay is largely due to the axonal organization. Most of the axons from excitatory neurons relate to the main column, as is illustrated here in this camera lucida drawing. You see in red the dendritic arbor confined to layer 4 of this excitatory cell and then most of the axons d ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... A holding signal is generated by neurons in the INC. On receiving the pulsed excitation from RiMLF axons, INC neurons transduce this signal into a very long-lasting chain of action potentials. Since INC neurons project their axons into the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei, they transmit the long-last ...
... A holding signal is generated by neurons in the INC. On receiving the pulsed excitation from RiMLF axons, INC neurons transduce this signal into a very long-lasting chain of action potentials. Since INC neurons project their axons into the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei, they transmit the long-last ...
The Zombie Diaries
... that carries signals between neurons as well as other cells in the body. These chemicals are released from the end of one neuron and cross the synapse to receptor sites in the next neuron. ...
... that carries signals between neurons as well as other cells in the body. These chemicals are released from the end of one neuron and cross the synapse to receptor sites in the next neuron. ...
22_LectureSlides
... • Feed-forward control-predictive – Response anticipates stimulus – More timely, but depends on practice ...
... • Feed-forward control-predictive – Response anticipates stimulus – More timely, but depends on practice ...
BIOL241NSintro12aJUL2012
... • Masses of neuron cell bodies – Called ganglia in the PNS and are surrounded by satellite cells – Called nuclei in the CNS ...
... • Masses of neuron cell bodies – Called ganglia in the PNS and are surrounded by satellite cells – Called nuclei in the CNS ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can
... FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can elicit different perceptions (faces or vase) even though stimulus and sensation remain constant. The mind can “see” purple figures against a blue background or a blue figure against a purple background. FIGURE 22.2 Receptor morphology and relationship to g ...
... FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can elicit different perceptions (faces or vase) even though stimulus and sensation remain constant. The mind can “see” purple figures against a blue background or a blue figure against a purple background. FIGURE 22.2 Receptor morphology and relationship to g ...
Visualizing the Brain
... First: - lower brain regions and the spinal cord control involuntary skeletal muscle activity, such as the maintenance of posture. Second: - Although the motor cortex can activate motor neurons to bring about muscle contraction, the motor cortex itself does not initiate voluntary movements. The moto ...
... First: - lower brain regions and the spinal cord control involuntary skeletal muscle activity, such as the maintenance of posture. Second: - Although the motor cortex can activate motor neurons to bring about muscle contraction, the motor cortex itself does not initiate voluntary movements. The moto ...
Chapter 17
... a. astrocytes are star-shaped cells (with many processes) that perform several functions in support of neurons b. oligodendrocytes have few processes and produce a myelin sheath; each oligodendrocyte can myelinate parts of several axons c. microglia are small, phagocytic neuroglia that protect the n ...
... a. astrocytes are star-shaped cells (with many processes) that perform several functions in support of neurons b. oligodendrocytes have few processes and produce a myelin sheath; each oligodendrocyte can myelinate parts of several axons c. microglia are small, phagocytic neuroglia that protect the n ...
Biological Processes Neurons
... Your experiences and behaviors are a consequence of complex patterns of activity in groups of neurons in your brain ...
... Your experiences and behaviors are a consequence of complex patterns of activity in groups of neurons in your brain ...























