Neural Nets: introduction
... essential for understanding the main principles – Allows us to apply mathematics and to make analogies to other, familiar systems. – Once we understand the basic principles, its easy to add complexity to make the model more faithful • It is often worth understanding models that are known to be wrong ...
... essential for understanding the main principles – Allows us to apply mathematics and to make analogies to other, familiar systems. – Once we understand the basic principles, its easy to add complexity to make the model more faithful • It is often worth understanding models that are known to be wrong ...
The Nervous System and the Brain
... The somatic nervous system connects the CNS to sensory receptors and muscles. Neurons in the somatic nervous system transmit messages about sights, sounds, smell, temperature, and body position to the CNS. It also transmits information from the brain to produce purposeful motor movements. The autono ...
... The somatic nervous system connects the CNS to sensory receptors and muscles. Neurons in the somatic nervous system transmit messages about sights, sounds, smell, temperature, and body position to the CNS. It also transmits information from the brain to produce purposeful motor movements. The autono ...
Control of Movement
... HD is caused by degeneration of the caudate nucleus and putamen Cell loss involves GABA-secreting axons that innervate the external division of the globus pallidus (GPe) The GPe cells increase their activity, which inhibits the activity of the subthalamic nucleus, which reduces the activity level of ...
... HD is caused by degeneration of the caudate nucleus and putamen Cell loss involves GABA-secreting axons that innervate the external division of the globus pallidus (GPe) The GPe cells increase their activity, which inhibits the activity of the subthalamic nucleus, which reduces the activity level of ...
Lecture-24-2012-Bi
... In the middle stages of AD, individuals may forget how to do simple tasks, like brushing their teeth or combing their hair. They can no longer think clearly. They begin to have problems speaking, understanding, reading, or writing. Late stage: AD patients may become anxious or aggressive, or wander ...
... In the middle stages of AD, individuals may forget how to do simple tasks, like brushing their teeth or combing their hair. They can no longer think clearly. They begin to have problems speaking, understanding, reading, or writing. Late stage: AD patients may become anxious or aggressive, or wander ...
The Nervous System
... The Nervous System • Transmission of nerve impulse – Chemical changes across the membrane of neuron. – Membrane of a unstimulated neuron is polarized. • Difference in electrical charges between the outside and inside of the membrane. • Inside is negative; outside is positive. ...
... The Nervous System • Transmission of nerve impulse – Chemical changes across the membrane of neuron. – Membrane of a unstimulated neuron is polarized. • Difference in electrical charges between the outside and inside of the membrane. • Inside is negative; outside is positive. ...
The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... 9. Which portion of the cerebral cortex receives sensory input for touch and body position? ANSWER ...
... 9. Which portion of the cerebral cortex receives sensory input for touch and body position? ANSWER ...
VNS Worksheet - Rice CAAM Department
... 4. Why is the locus coeruleus (LC) called the "blue spot." 5. How many neurons are contained in the blue spot. 6. If the volume of a typical LC neuron is 50,000 cubic microns and there are 2.54 cm in one inch what is the volume of such a cell in cubic inches? 7. What important molecule is delivered ...
... 4. Why is the locus coeruleus (LC) called the "blue spot." 5. How many neurons are contained in the blue spot. 6. If the volume of a typical LC neuron is 50,000 cubic microns and there are 2.54 cm in one inch what is the volume of such a cell in cubic inches? 7. What important molecule is delivered ...
Exploiting the potential of Selective serotonin receptor antagonists
... Chandran 2012), interestingly in connection with the pathological changes in Broca’s area of the brain, known to be crucially important for language (Bak et al 2001). Such observations are of crucial importance for the intensely debated theory of embodied cognition (Bak 2013). Since MND is usually c ...
... Chandran 2012), interestingly in connection with the pathological changes in Broca’s area of the brain, known to be crucially important for language (Bak et al 2001). Such observations are of crucial importance for the intensely debated theory of embodied cognition (Bak 2013). Since MND is usually c ...
3 layers
... -damage to the basal ganglia: -results in uncontrollable, abnormal body movements -muscle rigidity may develop and tremors -Parkinson – neurons that extend from the substantia nigra to the caudate nucleus and putamen ...
... -damage to the basal ganglia: -results in uncontrollable, abnormal body movements -muscle rigidity may develop and tremors -Parkinson – neurons that extend from the substantia nigra to the caudate nucleus and putamen ...
Everson Nervous system I. Functional/ Anatomical Divisions A
... C. Nerve cell impulse transmission: the electricity! 1. Essentially the same as described in muscle impulse. 2. Neuron not carrying an impulse is said to be _______________, where the Na+ ions are more abundant on the outside and the K+ ions are most abundant on the inside. 3. A stimulus, like a ___ ...
... C. Nerve cell impulse transmission: the electricity! 1. Essentially the same as described in muscle impulse. 2. Neuron not carrying an impulse is said to be _______________, where the Na+ ions are more abundant on the outside and the K+ ions are most abundant on the inside. 3. A stimulus, like a ___ ...
Griggs Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... Conduit for incoming sensory data and outgoing movement commands Provides for spinal reflexes, which are simple automatic actions not involving the brain ◦ The brain is the control center for the entire nervous system ...
... Conduit for incoming sensory data and outgoing movement commands Provides for spinal reflexes, which are simple automatic actions not involving the brain ◦ The brain is the control center for the entire nervous system ...
A Journey Through the Central Nervous System
... – Precise timing and patterning skeletal muscle contractions – Smooth and coordinated movements – Agility ...
... – Precise timing and patterning skeletal muscle contractions – Smooth and coordinated movements – Agility ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Diverging -- single cell stimulates many others • Converging -- one cell stimulated by many others • Reverberating -- impulses from later cells repeatedly stimulate early cells in the circuit (short-term memory) • Parallel-after-discharge -- single cell stimulates a group of cells that all stimula ...
... • Diverging -- single cell stimulates many others • Converging -- one cell stimulated by many others • Reverberating -- impulses from later cells repeatedly stimulate early cells in the circuit (short-term memory) • Parallel-after-discharge -- single cell stimulates a group of cells that all stimula ...
SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COMPLETION 1. A function
... 18. Transmitter release initiated by an action potential in the synaptic terminal would be decreased in the presence of (A) curare (B) TEA (C) AChE (D) low concentrations of extracellular Ca2+ (E) low concentrations of extracellular Mg2+ 19. A ten-fold decrease in the concentration of e in the extr ...
... 18. Transmitter release initiated by an action potential in the synaptic terminal would be decreased in the presence of (A) curare (B) TEA (C) AChE (D) low concentrations of extracellular Ca2+ (E) low concentrations of extracellular Mg2+ 19. A ten-fold decrease in the concentration of e in the extr ...
Project Report - Anatomical Society
... Brief Resume of your Project’s outcomes: (no more than 200-250 words). The title of your project and a brief 200-250 word description of the proposed/completed project. The description should include sufficient detail to be of general interest to a broad readership including scientists and non-speci ...
... Brief Resume of your Project’s outcomes: (no more than 200-250 words). The title of your project and a brief 200-250 word description of the proposed/completed project. The description should include sufficient detail to be of general interest to a broad readership including scientists and non-speci ...
Exam 4
... -Describe the components and functions of somatic motor pathways - Identify the locations and functions of the different types of neurons in the somatic motor pathways (Describe the characteristics of first, second and third order neurons in somatic sensory pathways). -Understand wakefulness and sle ...
... -Describe the components and functions of somatic motor pathways - Identify the locations and functions of the different types of neurons in the somatic motor pathways (Describe the characteristics of first, second and third order neurons in somatic sensory pathways). -Understand wakefulness and sle ...
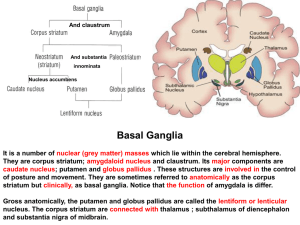
21. Basal ganglion
... Originates from the pars compacta of the ipsilateral substantia nigra of the midbrain tegmentum to caudate nucleus and putamen. The neurons of pars compacta contain the dark pigment neuromelanin. Their transmitter is the monoamine dopamine which has both excitatory and inhibitory effects upon striat ...
... Originates from the pars compacta of the ipsilateral substantia nigra of the midbrain tegmentum to caudate nucleus and putamen. The neurons of pars compacta contain the dark pigment neuromelanin. Their transmitter is the monoamine dopamine which has both excitatory and inhibitory effects upon striat ...
Context Dependency in the Globus Pallidus Internal Segment
... exhibiting statistically significant changes in discharge rate at any time between the presentation of visual cues and end of movement. Representative responses from three well-modulated GPi neurons during the execution of the task are shown in Fig. 1. Neuron B181 (Fig. 1A) paused phasically in asso ...
... exhibiting statistically significant changes in discharge rate at any time between the presentation of visual cues and end of movement. Representative responses from three well-modulated GPi neurons during the execution of the task are shown in Fig. 1. Neuron B181 (Fig. 1A) paused phasically in asso ...
Parkinson`s disease - Computation & Neural Systems
... Constipation. Detailed surveys show that most PD patients have constipation long before the clinical symptoms. Constipation does not predict PD. Intestinal biopsies show Lewy bodies in the neurons of the intestinal wall. ...
... Constipation. Detailed surveys show that most PD patients have constipation long before the clinical symptoms. Constipation does not predict PD. Intestinal biopsies show Lewy bodies in the neurons of the intestinal wall. ...
The Nervous System
... • Fastest responses go only to the spinal cord, not all the way to the brain ...
... • Fastest responses go only to the spinal cord, not all the way to the brain ...
14-1 SENSATION 1. The general senses provide information about
... A. The motivation and the foresight to plan and initiate movements occur here. B. Movements can be initiated in the prefrontal area, organized in the premotor area, and implemented in the primary motor area. Simplistic summary: Prefrontal area = I want to do this; Premotor area = Here’s how to do it ...
... A. The motivation and the foresight to plan and initiate movements occur here. B. Movements can be initiated in the prefrontal area, organized in the premotor area, and implemented in the primary motor area. Simplistic summary: Prefrontal area = I want to do this; Premotor area = Here’s how to do it ...
Nerve Tissue Slides Lab Handout
... (Lab Reference: Page 3) a. This slide shows many motor neurons. Begin on low power and find an area of the slide with many neurons. It will look like many dark purple spots – these are the cell bodies. Even at low power, you should be able to see the nucleus in each one. Move up to 100x power, and d ...
... (Lab Reference: Page 3) a. This slide shows many motor neurons. Begin on low power and find an area of the slide with many neurons. It will look like many dark purple spots – these are the cell bodies. Even at low power, you should be able to see the nucleus in each one. Move up to 100x power, and d ...
Symptoms: visual disturbances, ______, loss of
... 1. Central sulcus- separates the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe and the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe 2. Longitudinal fissure- separates the two hemispheres 3. Transverse cerebral fissure- separates the cerebrum and the cerebellum ii. Lobes 1. Frontal ...
... 1. Central sulcus- separates the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe and the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe 2. Longitudinal fissure- separates the two hemispheres 3. Transverse cerebral fissure- separates the cerebrum and the cerebellum ii. Lobes 1. Frontal ...