Common and specific inhibitory motor neurons innervate
... careful, though, to interpret this as common inhibitory innervation since a DUM neuron that supplies both muscles was described previously (Bräunig, 1997). In six preparations this DUM neuron, termed DUM1B, with its soma located in the mesothoracic ganglion, stained exceptionally well such that its ...
... careful, though, to interpret this as common inhibitory innervation since a DUM neuron that supplies both muscles was described previously (Bräunig, 1997). In six preparations this DUM neuron, termed DUM1B, with its soma located in the mesothoracic ganglion, stained exceptionally well such that its ...
Cranial Nerves: Assessment of Functions
... Figure 1.4 Extrinsic eye muscles, cranial nerve innervation, and the eyeball movement First, observe how much of the subject's iris (colored part around pupil) is covered by the eyelid. Normally about one-third will be covered. Drooping of the eyelid (ptosis) occurs in paralysis of the oculomotor n ...
... Figure 1.4 Extrinsic eye muscles, cranial nerve innervation, and the eyeball movement First, observe how much of the subject's iris (colored part around pupil) is covered by the eyelid. Normally about one-third will be covered. Drooping of the eyelid (ptosis) occurs in paralysis of the oculomotor n ...
LINKING PROPOSITIONS*
... testing of physiological hypotheses. He noted that in visual science, in addition to purely physiological data, one has available data from what he called “sensory experiments; that is, experiments in which an essential part of the results is a subject’s report of his own sensations” (p. 144). Brind ...
... testing of physiological hypotheses. He noted that in visual science, in addition to purely physiological data, one has available data from what he called “sensory experiments; that is, experiments in which an essential part of the results is a subject’s report of his own sensations” (p. 144). Brind ...
Spinal Cord Motor Activity
... these conditions, the Golgi tendon system tends to maintain a steady level of muscle force, counteracting effects such as fatique, which diminishes muscle force. sIf the muscle spindle system is viewed as a feedback system that monitors and maintains muscle length, then the Golgi tendon system is a ...
... these conditions, the Golgi tendon system tends to maintain a steady level of muscle force, counteracting effects such as fatique, which diminishes muscle force. sIf the muscle spindle system is viewed as a feedback system that monitors and maintains muscle length, then the Golgi tendon system is a ...
Neural correlates of a decision in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of
... commit to an action the moment the stimulus is seen. In contrast, near psychophysical threshold, the monkey must base its direction judgments on weak sensory signals perceived over hundreds of milliseconds1. The extrastriate visual cortex (areas MT and MST) contains the neural representation of visu ...
... commit to an action the moment the stimulus is seen. In contrast, near psychophysical threshold, the monkey must base its direction judgments on weak sensory signals perceived over hundreds of milliseconds1. The extrastriate visual cortex (areas MT and MST) contains the neural representation of visu ...
text
... These controls are not reflexes, but are predicted scaled adjustments of axial and proximal muscles scheduled to occur before and during the movement. They are, therefore, learned postural components of learned motor programs. For example, abduction of flexion of the limbs is counterbalanced by a de ...
... These controls are not reflexes, but are predicted scaled adjustments of axial and proximal muscles scheduled to occur before and during the movement. They are, therefore, learned postural components of learned motor programs. For example, abduction of flexion of the limbs is counterbalanced by a de ...
Nuclear receptor coactivators: Regulators of steroid action in brain
... hormone action in brain. A number of studies indicate that hormones can regulate coactivator expression in rodent and bird brain. In rodents, SRC-1 is expressed in a sexually dimorphic manner in the pituitary gland, with males having higher mRNA (52) and protein (93) levels than females. In further ...
... hormone action in brain. A number of studies indicate that hormones can regulate coactivator expression in rodent and bird brain. In rodents, SRC-1 is expressed in a sexually dimorphic manner in the pituitary gland, with males having higher mRNA (52) and protein (93) levels than females. In further ...
The contribution of intrinsic membrane dynamics to fast network
... fast oscillations in the local field potential (40 –100 Hz gamma, 100 –200 Hz sharp-wave ripples) single cortical neurons typically fire irregularly at rates that are much lower than the oscillation frequency. Recent computational studies have provided a mathematical description of such fast oscilla ...
... fast oscillations in the local field potential (40 –100 Hz gamma, 100 –200 Hz sharp-wave ripples) single cortical neurons typically fire irregularly at rates that are much lower than the oscillation frequency. Recent computational studies have provided a mathematical description of such fast oscilla ...
Article PDF
... tissue sections. AP expression in cell bodies and processes usually allowed identification of most labeled cells as neurons or glia. Cortical cell types were frequently discernible in AP-stained sections according to standard morphological criteria (for review, see Peters and Jones, 1984). The pyram ...
... tissue sections. AP expression in cell bodies and processes usually allowed identification of most labeled cells as neurons or glia. Cortical cell types were frequently discernible in AP-stained sections according to standard morphological criteria (for review, see Peters and Jones, 1984). The pyram ...
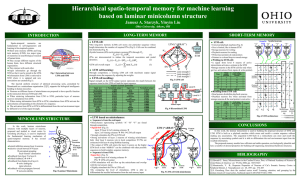
From/To LTM - Ohio University
... Short term memory (STM) and long term memory (LTM): two major types of memories in neurobiological research of human brain. They occupy different regions of the human brain, have different structural organization. They interact with each other. Input information go through the STM so that it ...
... Short term memory (STM) and long term memory (LTM): two major types of memories in neurobiological research of human brain. They occupy different regions of the human brain, have different structural organization. They interact with each other. Input information go through the STM so that it ...
Self-referential forces are sufficient to explain different dendritic
... Dendrites are beautiful arbors sprouting from the cell bodies of neurons. The shape of dendrites is of great importance to the nervous system for two interrelated reasons. First, a neuron’s dendrites receive inputs from other neurons. Since dendritic morphologies define which spatial domain can be r ...
... Dendrites are beautiful arbors sprouting from the cell bodies of neurons. The shape of dendrites is of great importance to the nervous system for two interrelated reasons. First, a neuron’s dendrites receive inputs from other neurons. Since dendritic morphologies define which spatial domain can be r ...
Classification of Diuretics
... Hypovolemia is perceived by “pressure receptors” -carotid and aortic baroreceptors, and stretch receptors in left atrium and pulmonary veins. Normally, pressure receptors tonically inhibit ADH release. Decrease in blood pressure induces ADH secretion by reducing input from pressure receptors. The re ...
... Hypovolemia is perceived by “pressure receptors” -carotid and aortic baroreceptors, and stretch receptors in left atrium and pulmonary veins. Normally, pressure receptors tonically inhibit ADH release. Decrease in blood pressure induces ADH secretion by reducing input from pressure receptors. The re ...
Mechanisms of cell migration in the nervous system
... multiple growth cones (Fig. 2 A, i). Indeed, the leading process does not turn when the source of attractant changes (Ward et al., 2005; Martini et al., 2009). Rather, branches are selectively stabilized based on proximity to the source of attractant: the branch whose growth cone is nearer the attra ...
... multiple growth cones (Fig. 2 A, i). Indeed, the leading process does not turn when the source of attractant changes (Ward et al., 2005; Martini et al., 2009). Rather, branches are selectively stabilized based on proximity to the source of attractant: the branch whose growth cone is nearer the attra ...
Binding Mechanisms in Visual Perception
... responses with frequency range of 40-60 Hz were observed across separated recording areas. When two neurons were activated individually by two light bars moving in opposite directions, the activities of these two neurons didn’t show correlated relation. If the two light bars were moving in the same ...
... responses with frequency range of 40-60 Hz were observed across separated recording areas. When two neurons were activated individually by two light bars moving in opposite directions, the activities of these two neurons didn’t show correlated relation. If the two light bars were moving in the same ...
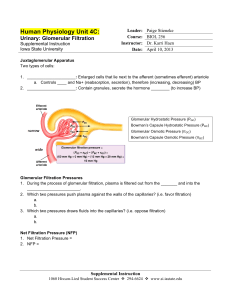
Bio 256 Unit 4C - Iowa State University
... Intrinsic System i. ___________________: Affects afferent arteriole constriction or dilation ii. ___________________: Affects afferent arteriole constriction or dilation b. c. Renin-Angiotensin System 1. Juxtaglomerular ______________________ release _________ 2. Renin stimulates ___________________ ...
... Intrinsic System i. ___________________: Affects afferent arteriole constriction or dilation ii. ___________________: Affects afferent arteriole constriction or dilation b. c. Renin-Angiotensin System 1. Juxtaglomerular ______________________ release _________ 2. Renin stimulates ___________________ ...
Building silicon nervous systems with dendritic tree neuromorphs
... tree, so prominent and elaborate in neurons like the pyramidal cells of cerebral cortex and the Purkinje cells of the cerebellum. The classical conception of the neuron held that dendrites are inexcitable, extensions of the neuronal cell body [Eccles, 1957], expanding the neuron’s surface area for m ...
... tree, so prominent and elaborate in neurons like the pyramidal cells of cerebral cortex and the Purkinje cells of the cerebellum. The classical conception of the neuron held that dendrites are inexcitable, extensions of the neuronal cell body [Eccles, 1957], expanding the neuron’s surface area for m ...
Small Networks
... – To prove this, one must show that changing the levels of “noise” intrinsic to the system affects its performance. ...
... – To prove this, one must show that changing the levels of “noise” intrinsic to the system affects its performance. ...
Chapter 10 - MBFys Home Page
... The Formation of Images on the Retina Normal vision requires that the optical media of the eye be transparent, and both the cornea and the lens are remarkable examples of tissue specializations that achieve a level of transparency that rivals that found in inorganic materials such as glass. Not surp ...
... The Formation of Images on the Retina Normal vision requires that the optical media of the eye be transparent, and both the cornea and the lens are remarkable examples of tissue specializations that achieve a level of transparency that rivals that found in inorganic materials such as glass. Not surp ...
Neural Coding and Auditory Perception
... We have previously shown that the spatio-temporal pattern of auditory nerve (AN) fibers contains robust cues to the pitch of complex tones [2]. To investigate whether these cues are extracted centrally, we are evaluating whether cochlear nucleus (CN) neurons are sensitive to manipulations of the spa ...
... We have previously shown that the spatio-temporal pattern of auditory nerve (AN) fibers contains robust cues to the pitch of complex tones [2]. To investigate whether these cues are extracted centrally, we are evaluating whether cochlear nucleus (CN) neurons are sensitive to manipulations of the spa ...
Prevalent Presence of Periodic Actin-spectrin-based
... neuronal subtypes exhibited a periodic distribution of βII spectrin in their axons, with a spacing of ~190 nm. Autocorrelation analyses showed that the degree of periodicity (i.e. autocorrelation amplitude) was similar among most of these excitatory and inhibitory neurons (Fig. 2J, K). Two exception ...
... neuronal subtypes exhibited a periodic distribution of βII spectrin in their axons, with a spacing of ~190 nm. Autocorrelation analyses showed that the degree of periodicity (i.e. autocorrelation amplitude) was similar among most of these excitatory and inhibitory neurons (Fig. 2J, K). Two exception ...
Memory, Learning, and Synaptic Plasticity
... corresponding output patterns, Y1, Y2, and Y3. In these input and Left, a highly simplified model is used to illustrate how a synaptic output patterns 1 and 0 represent an action potential or no action matrix can store memory. In this synaptic matrix, axons of five potential, respectively. The integ ...
... corresponding output patterns, Y1, Y2, and Y3. In these input and Left, a highly simplified model is used to illustrate how a synaptic output patterns 1 and 0 represent an action potential or no action matrix can store memory. In this synaptic matrix, axons of five potential, respectively. The integ ...
DESCENDING TRACTS
... Regulate muscle tone and muscle force. May be involved in selecting and inhibiting specific motor synergies. ...
... Regulate muscle tone and muscle force. May be involved in selecting and inhibiting specific motor synergies. ...
Artificial Intelligence (AI). Neural Networks
... the neuron is said to fire. The impulse is sent from the cell body (soma), through the axon, which influences the dendrites of the next neuron over narrow gaps called synapses. They translate the pulse in some degree into excitatory or inhibitory impulse of the next neuron (fig.9). ...
... the neuron is said to fire. The impulse is sent from the cell body (soma), through the axon, which influences the dendrites of the next neuron over narrow gaps called synapses. They translate the pulse in some degree into excitatory or inhibitory impulse of the next neuron (fig.9). ...
Learning Through Imitation: a Biological Approach to Robotics
... precisely, if we consider for example a “grasping to place” sequence, the first motor pool that is activated is the one in the parietal cortex encoding a reaching movement. This activity is immediately propagated to the premotor cortex, which computes finer details about the movement, integrating in ...
... precisely, if we consider for example a “grasping to place” sequence, the first motor pool that is activated is the one in the parietal cortex encoding a reaching movement. This activity is immediately propagated to the premotor cortex, which computes finer details about the movement, integrating in ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.