Figure 7.13a - Scranton Public School
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
Nervous System
... “excitatory” Epinephrine, dopamine, serotonin – inhibitory Neurotransmitters bind and allow Ca+2 to flow sending the message Caffeine lowers thresholds – neurons more easily excited Antidepressants – keep serotonin in synapses longer Prozac, Paxil, Zoloft Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education ...
... “excitatory” Epinephrine, dopamine, serotonin – inhibitory Neurotransmitters bind and allow Ca+2 to flow sending the message Caffeine lowers thresholds – neurons more easily excited Antidepressants – keep serotonin in synapses longer Prozac, Paxil, Zoloft Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education ...
chapter_9_powerpoint_le - AandP2010-2011
... The region of positive charge causes nearby voltage gated sodium channels to close. Just after the sodium channels close, the potassium channels open wide, and potassium exits the axon, so the charge across the membrane is brought back to its resting potential. This is called repolarization. ...
... The region of positive charge causes nearby voltage gated sodium channels to close. Just after the sodium channels close, the potassium channels open wide, and potassium exits the axon, so the charge across the membrane is brought back to its resting potential. This is called repolarization. ...
Repetition suppression - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal
... primary visual cortex suggest that both the BOLD signal and fMRI repetition suppression effects more closely reflect LFPs as opposed to spiking activity per se [66,67]. The BOLD signal may therefore be best understood to reflect integrative synaptic and dendro-somatic processes within the local netw ...
... primary visual cortex suggest that both the BOLD signal and fMRI repetition suppression effects more closely reflect LFPs as opposed to spiking activity per se [66,67]. The BOLD signal may therefore be best understood to reflect integrative synaptic and dendro-somatic processes within the local netw ...
directional asymmetries of optokinetic nystagmus: developmental
... inputs are involved and are called optokinetic eye movements when only visual inputs are involved. Between these extremes there is a broad range within the spectrum of normal head movements where both visual and vestibular signals are used. For the brain to have an unambiguous head velocity signal i ...
... inputs are involved and are called optokinetic eye movements when only visual inputs are involved. Between these extremes there is a broad range within the spectrum of normal head movements where both visual and vestibular signals are used. For the brain to have an unambiguous head velocity signal i ...
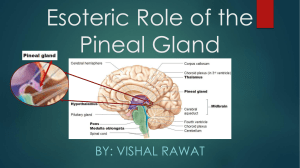
Esoteric Role of the Pineal Gland
... - His work has made significant contribution in identifying the effects of the endocrine glands on physiology and psychology - In his perspective the corporeal and intellectual health of an individual and his integral propensities could be assessed in terms of the level and pattern of hormonal secre ...
... - His work has made significant contribution in identifying the effects of the endocrine glands on physiology and psychology - In his perspective the corporeal and intellectual health of an individual and his integral propensities could be assessed in terms of the level and pattern of hormonal secre ...
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 12, 2016
... Hormonal release mechanisms from the anterior and posterior pituitary are completely different. Hormones released from the anterior pituitary are produced by endocrine cells located in this glandular tissue. However, the synthesis and release of these hormones is tightly controlled by the hypothalam ...
... Hormonal release mechanisms from the anterior and posterior pituitary are completely different. Hormones released from the anterior pituitary are produced by endocrine cells located in this glandular tissue. However, the synthesis and release of these hormones is tightly controlled by the hypothalam ...
melanogaster
... the ocelli. The ocelli are a set of three simple eyes positioned on the top (dorsal most part) of the head, and are believed to aid in gaze stabilization (Goodman, 1970; Schuppe and Hengstenberg, 1993). Ocellar interneurons, called L-neurons, sum information from photoreceptor outputs in each of the ...
... the ocelli. The ocelli are a set of three simple eyes positioned on the top (dorsal most part) of the head, and are believed to aid in gaze stabilization (Goodman, 1970; Schuppe and Hengstenberg, 1993). Ocellar interneurons, called L-neurons, sum information from photoreceptor outputs in each of the ...
color vision - UCSD Psychology
... processing, which is performed by horizontal cells and ganglion cells in the retina. Note that we only dealt with the cone receptors in our discussion of photoreceptors. Rods contribute to vision only at low light levels. Although they are known to have an effect on color perception in the mesopic r ...
... processing, which is performed by horizontal cells and ganglion cells in the retina. Note that we only dealt with the cone receptors in our discussion of photoreceptors. Rods contribute to vision only at low light levels. Although they are known to have an effect on color perception in the mesopic r ...
Image-based Screening Identifies Novel Roles for I B Kinase and
... The axon is a uniquely neuronal structure whose specialized architecture facilitates the rapid transmission of information across long distances. Just as compromised cells undergo programmed cell death, damaged axons undergo an active selfdestruct process that involves cytoskeletal disassembly, swel ...
... The axon is a uniquely neuronal structure whose specialized architecture facilitates the rapid transmission of information across long distances. Just as compromised cells undergo programmed cell death, damaged axons undergo an active selfdestruct process that involves cytoskeletal disassembly, swel ...
the mirror-neuron system - Psychology and Neuroscience
... which respond to the presentation of an object, and mirror neurons, which respond when the monkey sees object-directed action (Rizzolatti & Luppino 2001). In order to be triggered by visual stimuli, mirror neurons require an interaction between a biological effector (hand or mouth) and an object. Th ...
... which respond to the presentation of an object, and mirror neurons, which respond when the monkey sees object-directed action (Rizzolatti & Luppino 2001). In order to be triggered by visual stimuli, mirror neurons require an interaction between a biological effector (hand or mouth) and an object. Th ...
the mirror-neuron system - UCSF Center for Integrative Neuroscience
... which respond to the presentation of an object, and mirror neurons, which respond when the monkey sees object-directed action (Rizzolatti & Luppino 2001). In order to be triggered by visual stimuli, mirror neurons require an interaction between a biological effector (hand or mouth) and an object. Th ...
... which respond to the presentation of an object, and mirror neurons, which respond when the monkey sees object-directed action (Rizzolatti & Luppino 2001). In order to be triggered by visual stimuli, mirror neurons require an interaction between a biological effector (hand or mouth) and an object. Th ...
Basal Ganglia: Internal Organization
... GPe (see the next section) and provide an inhibitory input to the MSNs. The striatum also contains a population of large cholinergic interneurons that receive input from the cortex, thalamus and MSNs, and in turn innervate MSNs. The interneurons are also targets of the dopaminergic input from the SN ...
... GPe (see the next section) and provide an inhibitory input to the MSNs. The striatum also contains a population of large cholinergic interneurons that receive input from the cortex, thalamus and MSNs, and in turn innervate MSNs. The interneurons are also targets of the dopaminergic input from the SN ...
Andrea Kádár
... A dense network of both AGRP- and α-MSH-IR axons was observed in the PVN surrounding the TRH neurons. The density of the α-MSH-containing axons was slightly higher in the most anterior part of PVN, while the network of the AGRP-IR axons seemed to be denser in the posterior level of the PVN. In the s ...
... A dense network of both AGRP- and α-MSH-IR axons was observed in the PVN surrounding the TRH neurons. The density of the α-MSH-containing axons was slightly higher in the most anterior part of PVN, while the network of the AGRP-IR axons seemed to be denser in the posterior level of the PVN. In the s ...
download file
... exhibit facilitation to rapidly repeated sounds. Neurons in PAF do not exhibit strong selectivity for rate or direction of narrowband one octave FM sweeps. These results indicate that PAF, like nonprimary visual fields, processes sensory information on larger spectral and longer temporal scales than ...
... exhibit facilitation to rapidly repeated sounds. Neurons in PAF do not exhibit strong selectivity for rate or direction of narrowband one octave FM sweeps. These results indicate that PAF, like nonprimary visual fields, processes sensory information on larger spectral and longer temporal scales than ...
Definition of Neuronal Circuitry Controlling the Activity of Phrenic
... viruses. Dual-infected neurons were predominantly located in the magnocellular part of the MRF, but were absent from both the dorsal and ventral respiratory cell groups. These data suggest that coactivation of inspiratory and expiratory muscles during behaviors such as emesis and some postural adjus ...
... viruses. Dual-infected neurons were predominantly located in the magnocellular part of the MRF, but were absent from both the dorsal and ventral respiratory cell groups. These data suggest that coactivation of inspiratory and expiratory muscles during behaviors such as emesis and some postural adjus ...
ch_16_lecture_presentation
... 1. Most often, these two divisions have opposing effects • If the sympathetic division causes excitation, the ...
... 1. Most often, these two divisions have opposing effects • If the sympathetic division causes excitation, the ...
Seana Coulson, Jonathan W. King and Marta Kutas
... obtain ERPs by recording subjects' EEG and averaging the brain response to stimulus events; for example, the onset of the critical word in a large number of ungrammatical sentences. The logic behind averaging is to extract from the EEG only that information which is time-locked to the processing of ...
... obtain ERPs by recording subjects' EEG and averaging the brain response to stimulus events; for example, the onset of the critical word in a large number of ungrammatical sentences. The logic behind averaging is to extract from the EEG only that information which is time-locked to the processing of ...
Local network regulation of orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus
... by NMDA and non-NMDA receptors (122), whereas postsynaptic group I mGluRs provide another excitatory pathway to MCH neurons that induces a slow depolarization mediated by Na⫹/Ca2⫹ exchanger and potentiation of NMDA currents (57). Thus, somewhat akin to orexin neurons, MCH neurons are regulated by a ...
... by NMDA and non-NMDA receptors (122), whereas postsynaptic group I mGluRs provide another excitatory pathway to MCH neurons that induces a slow depolarization mediated by Na⫹/Ca2⫹ exchanger and potentiation of NMDA currents (57). Thus, somewhat akin to orexin neurons, MCH neurons are regulated by a ...
Chapter 18
... and roles of sensory tracts, motor tracts, and reflexes are explained. The 31 pairs of spinal nerves are identified and their protective coverings and their attachments to the spinal cord are described. The distribution of spinal nerves (i.e., branches, plexuses, and intercostal nerves) is portrayed ...
... and roles of sensory tracts, motor tracts, and reflexes are explained. The 31 pairs of spinal nerves are identified and their protective coverings and their attachments to the spinal cord are described. The distribution of spinal nerves (i.e., branches, plexuses, and intercostal nerves) is portrayed ...
Schwartz
... blocks was separated by a 95 s inter-block interval, during which images were digitized at 12-bit resolution and stored on the hard drive. Electrophysiology and Iontophoresis Epidural electrocorticography (ECoG) was monitored with two AgCl electrodes on either side of the craniotomy, ∼5 mm from the ...
... blocks was separated by a 95 s inter-block interval, during which images were digitized at 12-bit resolution and stored on the hard drive. Electrophysiology and Iontophoresis Epidural electrocorticography (ECoG) was monitored with two AgCl electrodes on either side of the craniotomy, ∼5 mm from the ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.