Receptor Tyrosine Kinases: Molecular Switches Regulating CNS
... manipulation of a single factor of intrinsic or extrinsic cues of a particular neuronal population may be sufficient to activate the Rho family GTPase intracellular signalling pathway, leading to actin depolymerisation in axon growth cones and preventing axon regeneration. Despite the fact that injure ...
... manipulation of a single factor of intrinsic or extrinsic cues of a particular neuronal population may be sufficient to activate the Rho family GTPase intracellular signalling pathway, leading to actin depolymerisation in axon growth cones and preventing axon regeneration. Despite the fact that injure ...
Project Report - Anatomical Society
... cones emerge at the appropriate time and place they will not be in a position to respond to guidance cues that orchestrate a correctly connected nervous system. Neuritogenesis depends on the co-ordinated dynamic behaviour of actin filaments (F-actin) and microtubules. An early event in growth cone f ...
... cones emerge at the appropriate time and place they will not be in a position to respond to guidance cues that orchestrate a correctly connected nervous system. Neuritogenesis depends on the co-ordinated dynamic behaviour of actin filaments (F-actin) and microtubules. An early event in growth cone f ...
stretch reflex 2
... represent 30% of AHCs. The axons (about 4 u) supply the peripheral parts of intrafusal ms fibers. ...
... represent 30% of AHCs. The axons (about 4 u) supply the peripheral parts of intrafusal ms fibers. ...
ABSTRACT BOOK CHAMPALIMAUD NEUROSCIENCE
... but maintain information exchange via cellular extensions that evolve into axonal connections. During evolution, more neuron types are intercalated into the circuit and take over different relay functions. Moreover, circuits can split and diverge at any level, specializing on different sensory modal ...
... but maintain information exchange via cellular extensions that evolve into axonal connections. During evolution, more neuron types are intercalated into the circuit and take over different relay functions. Moreover, circuits can split and diverge at any level, specializing on different sensory modal ...
to a of the units.
... The first lesson of this unit introduces different parts of the nervous system by constructing a model of the nervous system with a full body tracing. Students will learn how the brain sends and receives messages via the nervous system. Any part of the body that can move or feel is connected to the ...
... The first lesson of this unit introduces different parts of the nervous system by constructing a model of the nervous system with a full body tracing. Students will learn how the brain sends and receives messages via the nervous system. Any part of the body that can move or feel is connected to the ...
Suzuki and Eichenbaum, 2000
... all projections (except those between the different subregions of the hippocampal formation) are strongly reciprocal. For example, the perirhinal and parahippocampal cortices not only have strong and reciprocal connections with the entorhinal cortex, but also have weaker interconnections with the CA ...
... all projections (except those between the different subregions of the hippocampal formation) are strongly reciprocal. For example, the perirhinal and parahippocampal cortices not only have strong and reciprocal connections with the entorhinal cortex, but also have weaker interconnections with the CA ...
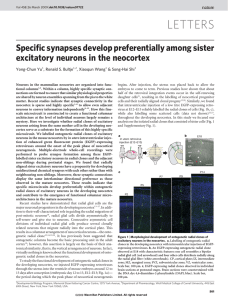
Specific synapses develop preferentially among sister excitatory
... actively form synapses, we set out to determine whether sister neurons in individual radial clones form synapses with each other. Simultaneous whole-cell recordings were performed on two EGFPexpressing sister neurons in individual radial clones, the cell bodies of which were often more than 100 mm a ...
... actively form synapses, we set out to determine whether sister neurons in individual radial clones form synapses with each other. Simultaneous whole-cell recordings were performed on two EGFPexpressing sister neurons in individual radial clones, the cell bodies of which were often more than 100 mm a ...
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder What Happens in the Brain?
... signal along the highway (keep the traffic flow going), and two: it has to transmit information to another nerve cell not on its axon (across the gap). Impulses along an axon are electrical, mediated by sodium and potassium ions. An impulse is an all or nothing proposition. It goes, or it does not g ...
... signal along the highway (keep the traffic flow going), and two: it has to transmit information to another nerve cell not on its axon (across the gap). Impulses along an axon are electrical, mediated by sodium and potassium ions. An impulse is an all or nothing proposition. It goes, or it does not g ...
Power point - Somatic and Special Senses
... Sound waves enter the external auditory canal, strike the eardrum, pass through the ossicles, strike the oval window, set up pressure waves in the perilymph, strike the vestibular membrane and scala tympani, increase pressure in the endolymph, vibrate the basilar membrane, and stimulate hair cells i ...
... Sound waves enter the external auditory canal, strike the eardrum, pass through the ossicles, strike the oval window, set up pressure waves in the perilymph, strike the vestibular membrane and scala tympani, increase pressure in the endolymph, vibrate the basilar membrane, and stimulate hair cells i ...
The mind`s mirror
... 529–535), he and his colleagues found some evidence that they can. The researchers used fMRI to examine 23 participants as they watched videos of a hand picking up a teacup. In one video, the teacup sat on a table amid a pot of tea and plate of cookies--a signal that a tea party was under way and th ...
... 529–535), he and his colleagues found some evidence that they can. The researchers used fMRI to examine 23 participants as they watched videos of a hand picking up a teacup. In one video, the teacup sat on a table amid a pot of tea and plate of cookies--a signal that a tea party was under way and th ...
the superior Olivary complex
... information about sound intensity as part of a feedback gain control system comprising the cochlea, cochlear neurons, CN, MOC neurons, and cochlear OHCs (Ghoshal & Kim, 1997; Ye et al., 2000). The function of the LOC neurons is not well understood because their small size and unmyelinated axons make ...
... information about sound intensity as part of a feedback gain control system comprising the cochlea, cochlear neurons, CN, MOC neurons, and cochlear OHCs (Ghoshal & Kim, 1997; Ye et al., 2000). The function of the LOC neurons is not well understood because their small size and unmyelinated axons make ...
SENSE AND THE SINGLE NEURON: Probing the Physiology of
... Approaches to Sensory Physiology Sensory physiology currently uses several approaches for investigating how the nervous system processes sensory information. The conceptually simplest of these is to measure tuning curves as selected parameters of the sensory stimulus are varied. A neuron is consider ...
... Approaches to Sensory Physiology Sensory physiology currently uses several approaches for investigating how the nervous system processes sensory information. The conceptually simplest of these is to measure tuning curves as selected parameters of the sensory stimulus are varied. A neuron is consider ...
Urinary Physiology Urine Formation Urine Formation Glomerular
... • Goal = Maintain a nearly constant GFR when MAP is in the range of 80–180 mm Hg – Renal autoregulation • Mechanisms that cause vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles in response to increased BP • Reduces glomerular flow to keep GFR the same ...
... • Goal = Maintain a nearly constant GFR when MAP is in the range of 80–180 mm Hg – Renal autoregulation • Mechanisms that cause vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles in response to increased BP • Reduces glomerular flow to keep GFR the same ...
common core achieve
... your body and protects your internal organs. The skeleton also serves as a reservoir for the storage of minerals, produces blood cells, and allows the body to move. A typical human skeleton is made up of 206 bones. The skull contains bones that surround and protect the brain. Bones of the spine supp ...
... your body and protects your internal organs. The skeleton also serves as a reservoir for the storage of minerals, produces blood cells, and allows the body to move. A typical human skeleton is made up of 206 bones. The skull contains bones that surround and protect the brain. Bones of the spine supp ...
Integration of Visual and Auditory Information by Superior Temporal
... be based upon a matching of sensory input to the motor representation of the same action within premotor cortex (Bekkering & Wohlschlaeger, 2002; Prinz, 2002; Viviani, 2002; Iacoboni et al., 1999). Alternatively, a more feed-forward process could occur whereby a polysensory representation of the act ...
... be based upon a matching of sensory input to the motor representation of the same action within premotor cortex (Bekkering & Wohlschlaeger, 2002; Prinz, 2002; Viviani, 2002; Iacoboni et al., 1999). Alternatively, a more feed-forward process could occur whereby a polysensory representation of the act ...
Muscle - Midlands State University
... The action potential activates voltage gated calcium ion channels on the axon, and calcium rushes in. The calcium causes acetylcholine vesicles in the axon to fuse with the membrane, releasing the acetylcholine into the cleft between the axon and the motor end plate of the muscle fiber. The acetylch ...
... The action potential activates voltage gated calcium ion channels on the axon, and calcium rushes in. The calcium causes acetylcholine vesicles in the axon to fuse with the membrane, releasing the acetylcholine into the cleft between the axon and the motor end plate of the muscle fiber. The acetylch ...
Neural Plasticity in Auditory Cortex
... ‘neural plasticity’ refers to systematic long-term (minutes to months) changes in the responses of neurons to the same physical stimulus (e.g., a tone), due to experience. Neural plasticity in the auditory cortex is interesting not only in itself but also as a case study in the intersection of two s ...
... ‘neural plasticity’ refers to systematic long-term (minutes to months) changes in the responses of neurons to the same physical stimulus (e.g., a tone), due to experience. Neural plasticity in the auditory cortex is interesting not only in itself but also as a case study in the intersection of two s ...
A Model for Delay Activity Without Recurrent Excitation
... baseline could emerge in such a population, if there is no compensating extra potentiation of its inhibitory inputs. This possibility is crucial for the model described here. A large number of parameters is necessary to describe local pools E, I, which are firing at stable and low firing rates, but th ...
... baseline could emerge in such a population, if there is no compensating extra potentiation of its inhibitory inputs. This possibility is crucial for the model described here. A large number of parameters is necessary to describe local pools E, I, which are firing at stable and low firing rates, but th ...
Interactions between Segmental Homologs and between
... has six first-order branches approximately perpendicular to the main projection (see Fig. 1A). The major projection extends along the middle annulus of the five that make up a segment, and the first-order branches extend about three to four annuli anteriorly and posteriorly, into the adjacent segmen ...
... has six first-order branches approximately perpendicular to the main projection (see Fig. 1A). The major projection extends along the middle annulus of the five that make up a segment, and the first-order branches extend about three to four annuli anteriorly and posteriorly, into the adjacent segmen ...
Real-time tomography from magnetoencephalography (MEG
... 2003]. It is however unclear what is measured by a sensor of interest (SOI) analysis [Liu et al., 2002] which depends critically on the differences between conditions at the level of individual sensors. Ambiguities of this type abound in the literature, where the raw signal of one or more sensors is ...
... 2003]. It is however unclear what is measured by a sensor of interest (SOI) analysis [Liu et al., 2002] which depends critically on the differences between conditions at the level of individual sensors. Ambiguities of this type abound in the literature, where the raw signal of one or more sensors is ...
Joint maps for orientation, eye, and direction preference in a self
... [11] S. Wimbauer, O. G. Wenisch, J. L. van Hemmen, and K. D. Miller, Development of spatiotemporal receptive fields of simple cells: II. Simulation and analysis, Biol. Cybernetics (1997), 77:463–477. [12] J. Wolfe and L. A. Palmer, Temporal diversity in the lateral geniculate nucleus of cat, Visual ...
... [11] S. Wimbauer, O. G. Wenisch, J. L. van Hemmen, and K. D. Miller, Development of spatiotemporal receptive fields of simple cells: II. Simulation and analysis, Biol. Cybernetics (1997), 77:463–477. [12] J. Wolfe and L. A. Palmer, Temporal diversity in the lateral geniculate nucleus of cat, Visual ...
cortico-cortical feedback controls spatial summation in
... combination we have developed provides purely anterograde labeling. D) Borders of cortical layers were determined based on current source density analysis of evoked LFP signals to 100 ms luminance increment (0.5-100 cd m -2) at every 400 ms (400 trials). SG (supragranular), IG (infragranular). E) Mi ...
... combination we have developed provides purely anterograde labeling. D) Borders of cortical layers were determined based on current source density analysis of evoked LFP signals to 100 ms luminance increment (0.5-100 cd m -2) at every 400 ms (400 trials). SG (supragranular), IG (infragranular). E) Mi ...
motor neurons
... The types of the Stretch Flex 2) Muscle tonus (static stretch reflex): Caused by a weaker and continues stretch of the muscle, Transmitted from the IA and II sensory ending of the M. S. Multiple synaptic pathway, continues for a prolonged period. Non-synchronized contraction, M. C. for at ...
... The types of the Stretch Flex 2) Muscle tonus (static stretch reflex): Caused by a weaker and continues stretch of the muscle, Transmitted from the IA and II sensory ending of the M. S. Multiple synaptic pathway, continues for a prolonged period. Non-synchronized contraction, M. C. for at ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.