Proprioceptive Information from the Pinna Provides
... Surg ical preparation. C ats were premedicated with xylazine (2 mg, i.m.) and atropine (0.1 mg, i.m.) and anesthetized with ketamine (initial dose of 40 mg / kg, i.m.; supplemental doses of 15 mg / kg, i.v.). Body temperature (measured rectally) was maintained at 38.5°C. The head was fixed in a nose ...
... Surg ical preparation. C ats were premedicated with xylazine (2 mg, i.m.) and atropine (0.1 mg, i.m.) and anesthetized with ketamine (initial dose of 40 mg / kg, i.m.; supplemental doses of 15 mg / kg, i.v.). Body temperature (measured rectally) was maintained at 38.5°C. The head was fixed in a nose ...
Basic principles of attention and decision
... • Do not mistake with the ‘where’ (old) pathway: SC and pulvinar • Parietal cortex represents potential targets to reach with respect to body, and is involved in motor control (see Ramachandran, Balint’s syndrom) • Lateral Intraparietal cortex (LIP): highest-order area in the visual hierarchy of t ...
... • Do not mistake with the ‘where’ (old) pathway: SC and pulvinar • Parietal cortex represents potential targets to reach with respect to body, and is involved in motor control (see Ramachandran, Balint’s syndrom) • Lateral Intraparietal cortex (LIP): highest-order area in the visual hierarchy of t ...
Neural Encoding I: Firing Rates and Spike Statistics
... Neurons are remarkable among the cells of the body in their ability to propagate signals rapidly over large distances. They do this by generating characteristic electrical pulses called action potentials, or more simply spikes, that can travel down nerve fibers. Neurons represent and transmit inform ...
... Neurons are remarkable among the cells of the body in their ability to propagate signals rapidly over large distances. They do this by generating characteristic electrical pulses called action potentials, or more simply spikes, that can travel down nerve fibers. Neurons represent and transmit inform ...
The Neuronal Correlate of Consciousness
... highly susceptible to excitatory input and capable of emitting action potentials. In the subsequent trough of the cycle the membrane potential is hyperpolarized and membrane conductance is high because of strong GABAergic inhibition generated by the rhythmically active inhibitory interneurons. Durin ...
... highly susceptible to excitatory input and capable of emitting action potentials. In the subsequent trough of the cycle the membrane potential is hyperpolarized and membrane conductance is high because of strong GABAergic inhibition generated by the rhythmically active inhibitory interneurons. Durin ...
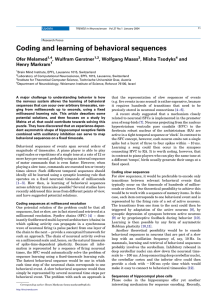
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... infection. Review of her medical records showed that she had experienced progressive lower back problems for the preceding 6 years. She had gained 15 pounds during that period but was not morbidly obese. MRI scan of the vertebral column (image above) showed an exaggerated anterior-posterior curvatur ...
... infection. Review of her medical records showed that she had experienced progressive lower back problems for the preceding 6 years. She had gained 15 pounds during that period but was not morbidly obese. MRI scan of the vertebral column (image above) showed an exaggerated anterior-posterior curvatur ...
[10] P. Paul, J de Belleroche, The role of D-amino acids in
... solely by glutamate, NMDA receptors are co-incidence detectors, that require the binding of ...
... solely by glutamate, NMDA receptors are co-incidence detectors, that require the binding of ...
Anatomy - Nervous System Test Chpt 9
... 1. What is the function of the nervous system? a. sensory input b. integration c. motor output d. all of the above 2. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. nerve b. neuron c. brain d. spinal cord 3. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in ...
... 1. What is the function of the nervous system? a. sensory input b. integration c. motor output d. all of the above 2. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. nerve b. neuron c. brain d. spinal cord 3. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in ...
Word doc - Center for Neural Science
... To examine the basis of frequency receptive fields in auditory cortex (ACx), we have recorded intracellular (whole-cell) and extracellular (local field potential, LFP) responses to tones in anesthetized rats. Frequency receptive fields derived from excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and LFPs ...
... To examine the basis of frequency receptive fields in auditory cortex (ACx), we have recorded intracellular (whole-cell) and extracellular (local field potential, LFP) responses to tones in anesthetized rats. Frequency receptive fields derived from excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and LFPs ...
Hormones - physiology
... So: the genetic processes that produce the α chains are the same. 2. β chains : unlike α chains , β chains are specific for each hormone. So: when you measure the activity of any hormone >> you measured the activity of β chains. E.g: FSH hormones, LH, HCG …. For example: HCG is the hormone that is i ...
... So: the genetic processes that produce the α chains are the same. 2. β chains : unlike α chains , β chains are specific for each hormone. So: when you measure the activity of any hormone >> you measured the activity of β chains. E.g: FSH hormones, LH, HCG …. For example: HCG is the hormone that is i ...
Neuroscience: the Science of the Brain
... well as the disciplines of anatomy, physiology and pharmacology. Their shared interest has led to a new discipline called neuroscience - the science of the brain. The brain described in our booklet can do a lot but not everything. It has nerve cells - its building blocks - and these are connected to ...
... well as the disciplines of anatomy, physiology and pharmacology. Their shared interest has led to a new discipline called neuroscience - the science of the brain. The brain described in our booklet can do a lot but not everything. It has nerve cells - its building blocks - and these are connected to ...
of the smooth muscles
... structures such as the iris of the eye, in which fine, graded contractions occur. It is not under voluntary control. ...
... structures such as the iris of the eye, in which fine, graded contractions occur. It is not under voluntary control. ...
STINGLESS BEES: THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF FORAGING Abstract
... forager species of bees, the whitish reflective abdominal hairs may facilitate orientation as they leave the nest. An important tool used to control the course and speed of flight is vision. Speed is controlled by altering the angular velocity of the environment’s image on the retina, and the speed ...
... forager species of bees, the whitish reflective abdominal hairs may facilitate orientation as they leave the nest. An important tool used to control the course and speed of flight is vision. Speed is controlled by altering the angular velocity of the environment’s image on the retina, and the speed ...
Body Systems Study Guide
... -The muscles in our body help us do many important things like: breathe, blink, walk, and grab things. -There are 600 muscles in the body! -It takes 34 muscles to frown but only 13 muscles to smile! -The body is able to move because of muscles. -We have voluntary muscles, which we choose to move, an ...
... -The muscles in our body help us do many important things like: breathe, blink, walk, and grab things. -There are 600 muscles in the body! -It takes 34 muscles to frown but only 13 muscles to smile! -The body is able to move because of muscles. -We have voluntary muscles, which we choose to move, an ...
What We Can and What We Can`t Do with fMRI
... both the precise definition of the conditions that would justify assigning a functional role to an “active” area, and interpretation of the fMRI maps. Changes in E-I balance—whether they lead to net excitation, inhibition, or simple sensitivityadjustment—inevitably and strongly affect regional metab ...
... both the precise definition of the conditions that would justify assigning a functional role to an “active” area, and interpretation of the fMRI maps. Changes in E-I balance—whether they lead to net excitation, inhibition, or simple sensitivityadjustment—inevitably and strongly affect regional metab ...
File - Joris Vangeneugden
... genetic and pharmacological interventions to up- or down-regulate serotonin release within the circuitry. In order to know where to impinge in the circuitry we will also perform structural connectivity mapping. Once we have determined the key players within the circuit and have provided evidence for ...
... genetic and pharmacological interventions to up- or down-regulate serotonin release within the circuitry. In order to know where to impinge in the circuitry we will also perform structural connectivity mapping. Once we have determined the key players within the circuit and have provided evidence for ...
Target-Derived Neurotrophic Factors Regulate the
... effect. TrkB-IgG caused only a small reduction in viability at 1 and 2 d. Anti-BDNF (1:12 dilution, turkey polyclonal) added with CCM at 3 d also abolished the effect of CCM at 5 d ( filled circles), whereas addition of turkey serum with CCM at 3 d had no effect (symbols offset; n ⫽ 4 each). c, Samp ...
... effect. TrkB-IgG caused only a small reduction in viability at 1 and 2 d. Anti-BDNF (1:12 dilution, turkey polyclonal) added with CCM at 3 d also abolished the effect of CCM at 5 d ( filled circles), whereas addition of turkey serum with CCM at 3 d had no effect (symbols offset; n ⫽ 4 each). c, Samp ...
14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • The choroid plexus is a combination of specialized ependymal cells and capillaries that produce cerebrospinal fluid. The ependymal cells secrete CSF into the ventricles, remove waste products from the CSF, and adjust the composition of CSF over time. Circulation of CSF • The choroid plexus produce ...
... • The choroid plexus is a combination of specialized ependymal cells and capillaries that produce cerebrospinal fluid. The ependymal cells secrete CSF into the ventricles, remove waste products from the CSF, and adjust the composition of CSF over time. Circulation of CSF • The choroid plexus produce ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... the peritubular capillaries. (Table 26.3) H2O, glucose, amino acids, uric acid, urea, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, HCO3-, HPO42-. Note: large proteins such as albumin are not included in this list. Explain. What happens with glomerular nephritis? What is the Tmax for proteins? 7. How much water is reabsorbed ...
... the peritubular capillaries. (Table 26.3) H2O, glucose, amino acids, uric acid, urea, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, HCO3-, HPO42-. Note: large proteins such as albumin are not included in this list. Explain. What happens with glomerular nephritis? What is the Tmax for proteins? 7. How much water is reabsorbed ...
A Feedback Model of Visual Attention
... to multiplicatively modulate the synaptic strengths of inter-regional connections so that attended information can be selectively routed to higher cortical regions. Equivalent results can be achieved by using top-down signals to modulate the activity of neurons rather than weights of synapses (Salin ...
... to multiplicatively modulate the synaptic strengths of inter-regional connections so that attended information can be selectively routed to higher cortical regions. Equivalent results can be achieved by using top-down signals to modulate the activity of neurons rather than weights of synapses (Salin ...
Cues that hippocampal place cells encode
... were minimized by randomizing their locations, by making them irrelevant to task performance (O’Keefe and Speakman, 1987; O’Keefe and Burgess, 1996), and sometimes by randomizing the location of ongoing behavior relevant to those cues (Muller and Kubie, 1987; Muller et al., 1987). Typically in these ...
... were minimized by randomizing their locations, by making them irrelevant to task performance (O’Keefe and Speakman, 1987; O’Keefe and Burgess, 1996), and sometimes by randomizing the location of ongoing behavior relevant to those cues (Muller and Kubie, 1987; Muller et al., 1987). Typically in these ...
Artificial Neural Networks : An Introduction
... • Basic fundamental neuron modelMcCulloch-Pitts neuron and Hebb network ...
... • Basic fundamental neuron modelMcCulloch-Pitts neuron and Hebb network ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.



![[10] P. Paul, J de Belleroche, The role of D-amino acids in](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022394228_1-c70b74890df8cd7f8a841431fb6562f6-300x300.png)