Health - Nervous System Review
... 11. Carries messages to the cell body of a neuron 12. Carries messages away from the cell body of a neuron 13. Basic unit of structure and function in the nervous system 14. Change in the environment that causes a response ...
... 11. Carries messages to the cell body of a neuron 12. Carries messages away from the cell body of a neuron 13. Basic unit of structure and function in the nervous system 14. Change in the environment that causes a response ...
Ch. 21.1 Nervous Lecture
... C. Motor neurons receive impulses from the interneurons and cause the tissues of the body to respond. 1. Ex: Muscles contract, glands release hormones, etc ...
... C. Motor neurons receive impulses from the interneurons and cause the tissues of the body to respond. 1. Ex: Muscles contract, glands release hormones, etc ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Nucleus – stores genes of the cell (DNA) Organelles – synthesize the proteins of the cell Cytosol – fluid inside cell Plasmic membrane – wall of the cell separating it from the fluid outside the cell. ...
... Nucleus – stores genes of the cell (DNA) Organelles – synthesize the proteins of the cell Cytosol – fluid inside cell Plasmic membrane – wall of the cell separating it from the fluid outside the cell. ...
The Biology of Mind
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
... How a Neuron Fires It is an electrochemical process Electrical inside the neuron Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter) The firing is call Action Potential ...
Unit V - Sensation and Perception
... ● Helmholtz's Place Theory- Believed different sound waves trigger activity at different places along basilar membrane. Believed brain determines sounds pitch by recognizing specific places that generate neural signals ➔ Explains how we hear high pitch but not low ➔ Proven to be false ● Frequency Th ...
... ● Helmholtz's Place Theory- Believed different sound waves trigger activity at different places along basilar membrane. Believed brain determines sounds pitch by recognizing specific places that generate neural signals ➔ Explains how we hear high pitch but not low ➔ Proven to be false ● Frequency Th ...
Slide ()
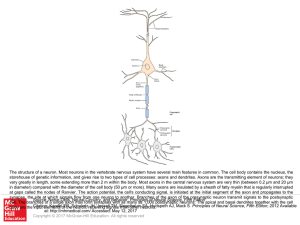
... The structure of a neuron. Most neurons in the vertebrate nervous system have several main features in common. The cell body contains the nucleus, the storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; ...
... The structure of a neuron. Most neurons in the vertebrate nervous system have several main features in common. The cell body contains the nucleus, the storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; ...
Quiz - Web Adventures
... a) Observe how frog hearts work b) Re-create Nobel Prize experiments c) Test how insulin binds to blood cells d) Understand how opioids work in the brain 6) Feelings of pleasure are triggered in the brain’s Reward Pathway by: a) Insulin b) Endogenous opioids c) NSAIDs d) Estrogen 7) Neurons transmit ...
... a) Observe how frog hearts work b) Re-create Nobel Prize experiments c) Test how insulin binds to blood cells d) Understand how opioids work in the brain 6) Feelings of pleasure are triggered in the brain’s Reward Pathway by: a) Insulin b) Endogenous opioids c) NSAIDs d) Estrogen 7) Neurons transmit ...
04 Sensation and perception
... Cone cells, which provide color vision and enable us to distinguish details, adapt quickly to light and are most useful in adequate lighting. Rod cells, which can pick up very small amounts of light but are not color-sensitive, are best suited for situations in which lighting is minimal. Because the ...
... Cone cells, which provide color vision and enable us to distinguish details, adapt quickly to light and are most useful in adequate lighting. Rod cells, which can pick up very small amounts of light but are not color-sensitive, are best suited for situations in which lighting is minimal. Because the ...
Research Methods
... Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function ...
... Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function ...
Sensory organs and perception
... Some experienced auditory or visual hallucinations. Although they were paid a generous sum for each day they participated in the experiment, most subjects refused to continue past the second or third day. After they left the isolation chamber, the perceptions of many were temporarily distorted, and ...
... Some experienced auditory or visual hallucinations. Although they were paid a generous sum for each day they participated in the experiment, most subjects refused to continue past the second or third day. After they left the isolation chamber, the perceptions of many were temporarily distorted, and ...
Neuron: Structure Neuron: Function
... a) Filters sensory information b) Regulate overall arousal in the brain ...
... a) Filters sensory information b) Regulate overall arousal in the brain ...
Chapter 14
... Outer layers of neurons that contribute to optic nerve called ganglion cells. Neurons receive synaptic input from bipolar cells, which receive input from rods and cones. Horizontal cells synapse with photoreceptors. Amacrine cells synapse with several ganglion cells. ...
... Outer layers of neurons that contribute to optic nerve called ganglion cells. Neurons receive synaptic input from bipolar cells, which receive input from rods and cones. Horizontal cells synapse with photoreceptors. Amacrine cells synapse with several ganglion cells. ...
Nervous System
... • Reflex cause an automatic response does not invovle the brain • Ganglion = a cluster of nerve cell bodies found outside of the CNS • Interneurons – neurons that integrate sensory input with motor output • Interneuron branches can carry signals to different parts of spinal cord or brain – Convergen ...
... • Reflex cause an automatic response does not invovle the brain • Ganglion = a cluster of nerve cell bodies found outside of the CNS • Interneurons – neurons that integrate sensory input with motor output • Interneuron branches can carry signals to different parts of spinal cord or brain – Convergen ...
(Early Period) - Connectionism
... numbers of units (the analogs of neurons) together with weights that measure the strength of connections between the units. A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impul ...
... numbers of units (the analogs of neurons) together with weights that measure the strength of connections between the units. A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impul ...
Special Senses
... fluid-filled tubes that are surrounded by bone. Again, these two structures are connected to one another. ...
... fluid-filled tubes that are surrounded by bone. Again, these two structures are connected to one another. ...
Powerpoint slides are here
... and feedforward control motoneurons in spinal cord (and analogous ...
... and feedforward control motoneurons in spinal cord (and analogous ...
NEURONS
... EX- light, gravity, food, etc. *The ability to RESPOND to a stimulus is common to _______ living things !!! ...
... EX- light, gravity, food, etc. *The ability to RESPOND to a stimulus is common to _______ living things !!! ...
Diapositive 1 - Andrei Gorea, Ph
... Figure 2. Eliminating 'false matches' in the stereo correspondence problem. A random dot stereogram at the top shows left and right eyes' images for crossed or uncrossed fusion (pair on the left or right respectively). Marr and Poggio's [10] proposal for establishing correct correspondences between ...
... Figure 2. Eliminating 'false matches' in the stereo correspondence problem. A random dot stereogram at the top shows left and right eyes' images for crossed or uncrossed fusion (pair on the left or right respectively). Marr and Poggio's [10] proposal for establishing correct correspondences between ...
Synapses
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...